Injection molded optics provide the capability to produce glass-like precision without the significant time associated with grinding or polishing. Optical injection molding changes a 3D file to high-volume, micron accurate plastic lenses, light guides, and diffusers in days. It is an incredibly efficient way to manufacture complex optical components.
In the next few sections, we will walk you through this advanced manufacturing technology. You will learn the key manufacturing process and the highly specialized materials used; you will also gain an understanding of the different high-precision components possible through this method.
What Is Optical Injection Molding?
Let’s first clarify what this specialized process is and explore the fundamental value it brings to your precision projects.
Defining Optical Injection Molding
Optical Injection Molding (OIM) is an advanced and specialized manufacturing method for producing high-precision plastic components. It focuses on forming optical-grade thermoplastic materials into complex shapes that possess specific properties for controlling light.
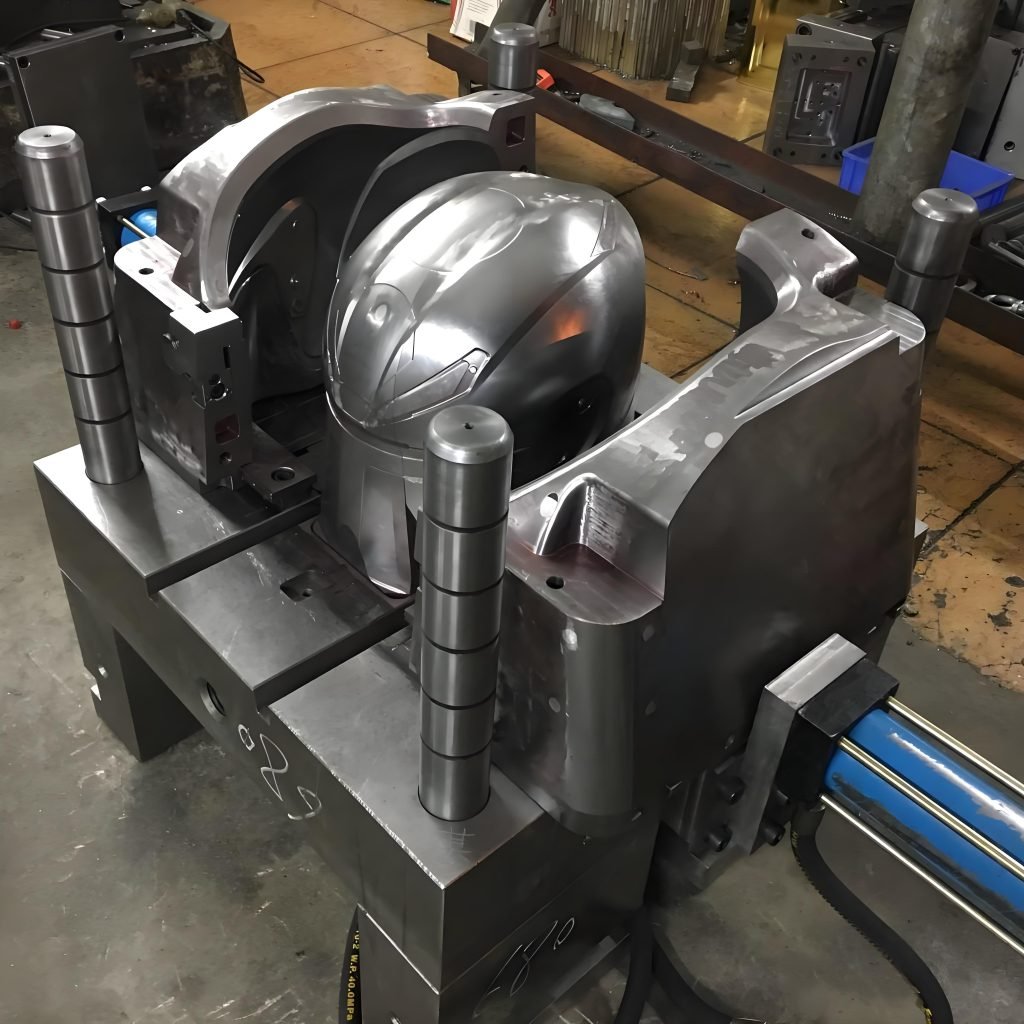

The technique requires heating the polymer until it becomes completely molten, and then injecting it under high pressure into an extremely accurate mold cavity. This entire process is well-designed, so the final molded plastic optic is formed with great surface quality and exact dimensional accuracy.
Key Advantages of OIM
You will find many compelling reasons to choose OIM for your projects. This process provides remarkable consistency and repeatability so that you can ensure that every single part meets your extremely high quality requirements. Plastic optics are also significantly lighter than traditional glass optics – an important consideration for any weight-sensitive application.
The flexibility of OIM offers another great benefit. For instance, you can utilize multi-shot molding for the purpose of creating a gasket and a lens all within a single, integrated part. This high degree of integration simplifies your assembly process and reduces your overall material and processing costs.
Understanding the Limitations
However, you should be fully aware of a few inherent limitations before starting. The initial investment required for the tooling is typically high. This significant up-front cost is necessary to ensure the extreme precision and quality demanded by optical components.
Managing birefringence, a double-refraction effect, is another technical challenge that requires you to precisely control and avoid it altogether during the entire molding cycle. Additionally, there are only specific grades of thermoplastics and optical silicone molding materials you are able to choose from, making your overall range of materials less extensive.
The Manufacturing Process of Optical Injection Molding
The journey from raw plastic to a finished optic involves highly controlled, multi-stage steps. Let’s dive into the core techniques that guarantee the precision of your final molded components.
1. Master Tooling and Mold Insert Creation
The process begins with creating an incredibly precise mold component. A diamond-turned nickel insert is necessary to perfectly copy the inverse wavefront of your designed optic. An extremely smooth surface finish is critical; this guarantees your final molded plastic optics are perfectly flawless and free from surface imperfections.
2. Material Preparation and High-Speed Injection
Before molding, the polymer material undergoes strict preparation. Plastic pellets must be fully dried to remove the moisture content to prevent internal streaking issues. The material is then melted and injected into the mold cavity at high speed and pressure. This rapid filling is essential to immediately freeze micro-features before material relaxation can cause any blurring.
3. Precision Cooling and Quality Control
Once the cavity is filled, the material is held under pressure and precisely cooled. Controlling the temperature is vital to prevent internal stress and maintain the component’s exact dimensions. After ejection, every part undergoes automated, 100% quality control using advanced vision systems to map any surface error and sort parts accordingly.
4. Integrated and Post-Mold Enhancements
A significant benefit of modern OIM is the ability to integrate post-processing features. An Anti-Reflective (AR) or IR blocking film can be applied directly on the hot optic inside the mold, eliminating a secondary process. The coatings can also be applied at a later time in specialized processes to protect the plastic and improve the optical performance.
Common Materials Used in Optical Injection Molding
The materials selection of the correct polymer is paramount because it defines the optical and mechanical performance of your optical part. Next, we will review the most common optical materials and their optimum use.
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic, abbreviated PMMA, is a popular material as it provides a great balance of price and performance. It has 92% transmission and a refractive index (RI) of 1.49, and is easy to polish. As such, it is ideally suited for cost-effective injection molding optical lenses in cameras and larger light-guide panels.
Polycarbonate (PC)
If your application requires high durability, you will want to use Polycarbonate (PC). It is highly impact-resistant and performs within a wide temperature range, having a 1.59 RI. Because of its toughness, PC is regularly used for automotive headlamp lens covers and durable VR Fresnels.
Polystyrene (PS)
Often, Polystyrene (PS) material is the choice when material cost is your top priority. While it offers a slightly lower 88% transmission and a 1.59 RI, it is very economical. PS is best suited for less demanding uses like disposable diffuser sheets and simple toy or promotional projectors.
Cyclic Olefin Copolymer (COC)
COC is an advanced material highly valued for its stability and extremely low moisture absorption. It provides 90% transmission and a 1.53 RI. This makes COC the ideal fit for sensitive microfluidic and medical molded plastic optics requiring superior material integrity.
Cyclic Olefin Polymers (COPs)
You will want to consider COPs if your project requires glass-like clarity at a lower weight. COPs allow very high transmission with extremely low haze. It is increasingly used to replace traditional glass components in various sensitive instruments, such as high-end endoscopes and precision sensing caps.
Types of Optical Molding
Optical injection molding isn’t one process. It covers several specialized methods. These techniques let you push design limits for specific components like lenses or light guides.
Precision Lens Molding
When you require the highest performance, you will use precision lens molding. This advanced method achieves incredibly tight form errors for complex aspheric smartphone injection molding optical lenses. This precision is usually accomplished by using a sophisticated process called variotherm cycling to precisely control the mold temperature.
Birefringence-Controlled Molding
To manage light polarization in sensitive systems, birefringence-controlled molding is employed. It uses techniques like sequential valve gating and specific resins, such as COP, to ensure light retardation is kept extremely low. This control is vital for advanced applications like 3D sensing LiDAR windows.
Diffuser Molding
If your goal is to uniformly spread light across a large area, you will need diffuser molding. This process utilizes mold cavities containing micro-beads that efficiently scatter light uniformly over a wide angle. It is a standard practice in LED panel molded plastic optics to eliminate bright spots and ensure smooth illumination.
Multishot (Two-Shot) Molding
Multishot (or two-shot) Molding is a unique method for combining two different materials in a single, rapid injection molding cycle. For example, you can overmold a rigid black molded ABS mount with a clear PMMA lens. This advanced technique, by creating a single integrated part, can significantly reduce your final assembly cost.
Micro-Optics Molding
When dealing with extremely small features, you must turn to micro-optics molding. This method produces incredibly tiny elements, such as Fresnel rings for fiber-optic transceivers. Success requires the use of ultra-precise diamond inserts and strict production within a Class 100 clean-room environment.
Light Guide Molding
Light guide molding is specifically designed for creating thin, edge-lit components for illumination. It produces parts like thin light guides used in complex automotive dashboards. To ensure perfectly uniform light output, a precise dot-pattern is often laser-ablated onto the core side before the optical injection molding process begins.
Key Components Produced via Optical Injection Molding
The capabilities of OIM translate into an enormous range of final products. Let’s look at some of the key components you can achieve with this high-precision molding process.
Lenses
OIM is ideal for producing high-performance lenses, including aspheric, Fresnel, and pancake designs for today’s AR glasses. One of the key features of these high-quality injection molded optics is their ability to have extremely low distortion, which is essential for maintaining a comfortable viewing experience with a high quality image in any imaging system.
Reflectors
You can utilize OIM to produce lightweight and highly efficient reflectors. For example, coated PC reflectors can significantly boost head-lamp efficiency while weighing much less than traditional metal versions. This substantial weight reduction is a major advantage in automotive design and energy savings across all lighting applications.
Optical Filters
Optical filters can be directly and cost-effectively molded using materials like IR-cut PMMA to a very thin profile. These components are essential for CMOS camera modules and simplify your product design by replacing older, more complex, and expensive glued glass stacks with a single plastic part.
Light Guides
OIM creates long and complex light guides for everything from small buttons to large console panels molded in COP. The process guarantees extraordinary light uniformity along the entire length of the component, and is vital for consistent illumination in automotive and display backlights.
Light Diffusers
For advanced display technology, OIM manufactures highly efficient light diffusers. These include frosted COC films that create uniform light distribution and minimize glare. The films are designed to balance high haze with high transmission, resulting in an evenly bright picture in micro-LED TVs and similar displays.
Display Panels & Windows
Durable display panels and windows are commonly made using OIM, such as anti-scratch PC windows for HUD combiners. These parts can be coated in-mold to achieve very low reflection rates, significantly improving the visibility and image quality for the end user in demanding environments.
Optical Sensors & Detector Housings
OIM is excellent for creating robust and integrated housings, such as two-shot PP + COP enclosures for TOF sensors. The advanced multi-shot process creates an integrated unit that offers self-sealing and potentially eliminates the need for secondary O-rings, resulting in improved protection against moisture and dust for industrial and drone applications.
Conclusion
Optical injection molding transforms transparent pellets into high-precision molded plastic optics with scalable, cost-effective formations. This rapid processing technology seamlessly engages complex mechanical and optical integrated functionality from smartphone lenses to rugged LiDAR windows. Your success depends on choosing the right materials and specialized technical processes to maximize your geometric and functional design freedom.
Fecision offers optical injection molding services with high tolerance precision, applying advanced technology along with strong quality control to meet the toughest specifications. We handle everything from rapid prototyping and material selection to high-volume production of your most complex molded plastic optics. Our comprehensive capabilities will give you both optical and mechanical perfection.
Key Advantages Fecision Offers
- Certified Quality – ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certified processes
- Advanced Capabilities – Micro molding, two-shot molding, and optical silicone molding expertise
- Rapid Scaling – Fast prototyping to high-volume production with consistent results
- Precision Measurement – CMM and vision systems ensuring optical-grade tolerances
- Material Expertise – Comprehensive selection of optical-grade polymers (PC, PMMA, COC, COP)
Contact Fecision today to launch your next high-precision optical project!




