Vacuum forming is a common method for manufacturing plastic parts and is widely embraced across various industries, where raw plastic is formed into designed shapes using a mold, and it is affordable. The upcoming sections of this article will discuss the basics of vacuum forming, explore the intricate process, identify the common materials used in vacuum forming, and reveal its applications.
What Is Vacuum Forming?
Vacuum forming, sometimes called vacuum molding, refers to a method where a plastic sheet is clamped, heated, and then pulled onto a mold by vacuum pressure. This process allows the softened plastic to take on the exact shape and surface of the mold cavity. After cooling, the molded component is released and trimmed as needed.
The molds used are typically simpler than those in processes like injection molding, lacking complex internal cavities. This makes vacuum forming ideal for small to medium production runs (less than 3000 pieces) of large, relatively simple parts such as containers and packaging.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastic Vacuum Forming
Like all technologies, vacuum forming has its advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to manufacture. | Longer cycle times and relies on manual labor for loading, unloading, and tool changes. |
| A cost-effective alternative for low to medium-volume batch production. | Can’t handle some intricate products, like internal cavities, channels, and curved surfaces. |
| A relatively lower investment compared to other processes like injection molding. | The precise technique in vacuum is relatively low, within the range of ±0.25 to 1.5 millimeters. |
| Can alter the design based on the actual situation during the iterative process. | Can lead to warping and surface imperfections. |
| Can handle various sizes, up to a maximum of 2000mm x 1000mm. |
Vacuum Forming vs. Thermoforming vs. Pressure Forming
Vacuum forming, thermoforming, and pressure forming are all techniques used to shape plastic parts. For their similarity, there are subtle and important differences in these terms and processes that may not be well known outside of the plastic manufacturing industry.
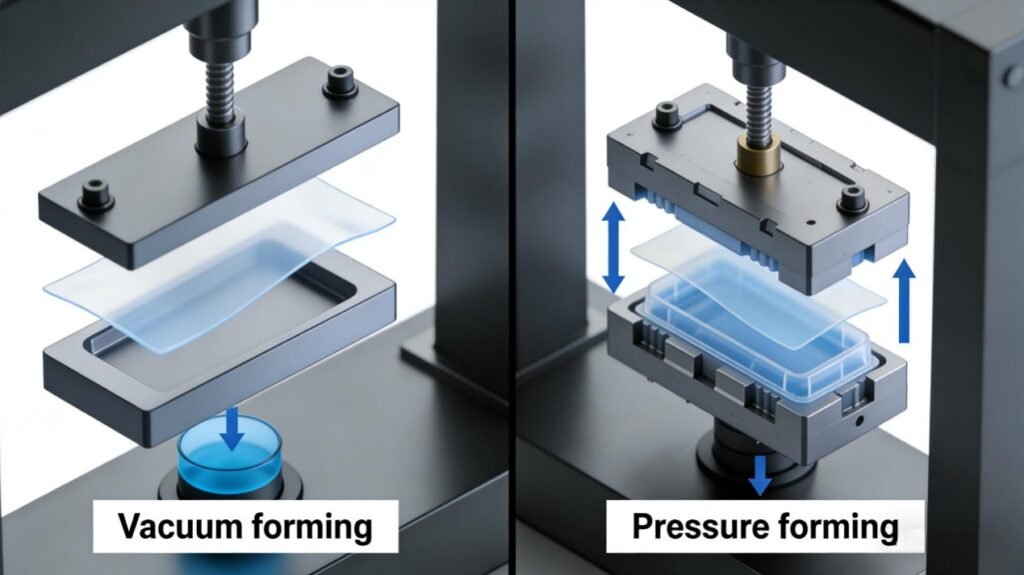
Vacuum Forming vs Pressure Forming
Vacuum forming and pressure forming take the opposite approach to getting the plastic into the mold. In vacuum forming, a sheet of thermoplastic material is first heated to a precise temperature, and it becomes pliable. When the sheet is ready, vacuum pressure draws the hot plastic into or over the mold. Pressure forming is different from vacuum forming in that it uses air pressure. The same step of heating a sheet of plastic kicks off the process. Material pressure forming uses compressed air to force the warm sheets of plastic into the waiting mold.
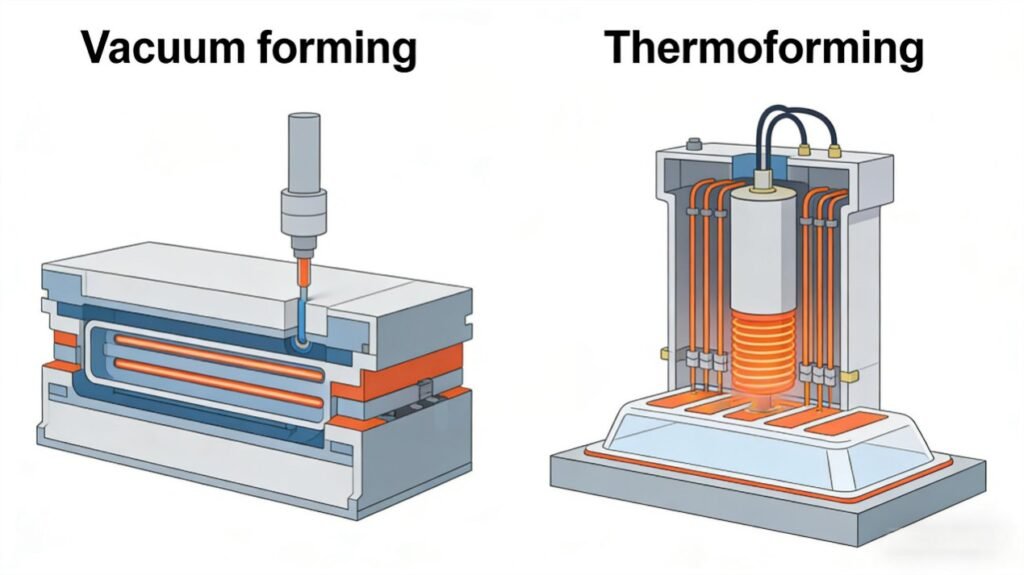
Vacuum Forming vs Thermoforming
While often used interchangeably, there’s a key distinction: vacuum forming is a specific type of thermoforming that relies solely on vacuum pressure. More broadly, thermoforming encompasses both vacuum and pressure forming.
Vacuum forming uses a single mold, while thermoforming uses male and female molds. CNC-machined aluminum is also needed for use in thermoforming. Once shaped, the plastic is cooled and trimmed to achieve the final product.
Thermoforming is, currently, best suited to produce complex pieces. It’s particularly useful for manufacturing high-performance or heavy-duty parts in some areas like medical trays, car panels, and high-finish consumer parts.
How Vacuum Forming Works
Vacuum forming is the process used to shape and form plastic products from a sheet of plastic and is usually used in making large plastic components, but can also be used to make precise plastic components. This guide will guide the readers through every step of the vacuum-forming process, from marking the tools to finishing the plastic.
- Tool making
- Setting up the vacuum forming machine
- Heating
- Vacuuming
- Cooling, trimming, and finishing the plastic
Now, give a full look at how vacuum forming works.
Tool Making
Start by making the tool using vacuum forming materials like model board or aluminum, depending on the complexity and quantity of the plastic component being formed. The mold has better have the tapered sides of a minimum of 2 degrees. When finishing the plastic parts, the parts can be released from the mold easily within this design.
Setting up the Vacuum Forming Machine
Once the mold is created and placed over the former, firmly clamp the plastic sheet to be formed to the forming machine. A plastic sheet can stay in a fixed position during heating and forming. The clamp is enough to firm the plastic sheet during the forming process because the sheet is above the former but not on it.
Heating
Using heaters, the plastic sheet is heated to be pliable. During forming, keeping the precise temperature is really important because pneumatic pressure is applied above and below the plastic sheet. Pyrometers can be used to monitor the plastic sheet temperature in a vacuum machine. Sheet-level monitoring and pre-stretching are very good auxiliary tools that help to ensure a consistent finish.
Vacuuming
Mold is positioned on the table, and the pneumatic moves upwards to the plastic. Once the plastic is at the appropriate temperature and is sufficiently pliable, the sheet is pulled toward the surface of the mold, where the vacuum sucks the air out between the mold and the plastic sheet.
Cooling, Trimming, and Finishing the Plastic
Fans and cool air can cool and harden the newly formed plastic that is attached to the mold, and therefore, it can be released. Especially spraying chilled water on the newly formed plastic is effective to save cooling times, maintain the shape and detail of the molded form, and avoid deformation. Separate the formed component from the mold and go to the next process of trimming, like using scissors to trim off, sand, or smooth the edge of the plastic, and then clean up the final product.
Common Materials Used for Vacuum Forming
There are many plastic materials available for vacuum forming; selecting the right material suited for the project is crucial. Here are the kinds of material commonly used in vacuum forming.
Acrylic-Perspex (PMMA)
PMMA is temperature-sensitive and a medium to strong material. Some applications have the requirement for clarity; it is recommended to use PMMA. PMMA is widely used in lights, light diffusers, roof domes, and signs. But PMMA is easy to shatter, so it is suitable for manual work to avoid its limitations. Its shrinkage rate is 0.3%-0.8%. PMMA is also compatible with cellulose and enamel sprays.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), a blend of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene polymers, is strong, hard, and rigid. ABS plastics excel in resisting both weather and impact. ABS plastic is used in electrical enclosures, luggage, sanitary parts, and vehicle parts. ABS plastic also forms easily into a high definition.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is known for its extensional hygroscopic properties, strength, and forms well to a high definition. PC can be machined, ultrasonically welded, and has excellent electrical insulation, taped and drilled, and takes spray. PC are with strong chemical resistance except to alkalis, aromatics, and hydrocarbons. Commonly used in vacuum forming products like eyewear lenses, automotive components, protective gear, and construction materials.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is very strong but challenging to form. PP requires precision control of temperature to prevent sheet sag during plastic vacuum forming. PP is not hygroscopic and has a 1.5–2.2% shrinkage rate. PP has the color of translucent, black, white, or other colors, even though it cannot be sprayed. PP is flexible and not absorbent, which makes it suitable for chemical tanks, enclosures, luggage, and packaging for food or toys.
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS), a blend of polystyrene and 5-10% rubber, is not hygroscopic but medium to strong to form well and support high degree of definition. HIPS has a 0.3-0.5 shrinkage range, which can be machined well but needs a special primer to be sprayed. HIPS have poor resistance, so it is optimal for indoor applications. It is very easy to form and available in a wide range of colors, patterns, and textures to choose from. HIPS can be applied to most high-volume/low-value items, such as a lot of (non-sterile) packaging.
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol/Co-Polyester (PETG)
PETG is attractive, strong, and offers excellent formability, capable of high definition, making it highly suitable for hygienic packaging (e.g., for foods and medicines), plus displays (e.g., point-of-sale displays). It can be sawn, cut, and routered, characteristics that enhance its ease of use, which can be die-cut and punched to a limited extent. It can be applied in printing using paints and inks intended for polyester. PETG is sterilizable and resistant to alcohols and acidic oils, but not recommended for use with high-alkaline solutions.
Polyethylene (HDPE)
PE itself is challenging. PE FOAM is easier to manage but needs to be formed at low temperatures. PE foam is a good material ideal for various applications due to its strong and high shrinkage rate with 2.0-3.5%, and good chemical resistance. HDPE cannot be sprayed, but can be printed with certain inks. HDPE is used in caravan parts, enclosures, housings, as well as vehicle parts.

Main Applications of Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming can shape plastic into several kinds of functional and decorative products to show its flexibility and availability. Here are some common samples of the main areas where it is used.
Automotive and Transportation
Vacuum forming is used extensively in the automotive sector, where it is used to produce parts that are light enough for aeroplanes or robust enough for some firm buses, boats, and airplanes, or car parts like lampshades, bumpers, window blanks, and door panels. Vacuum forming is proud of its ability to create robust, lightweight parts that help to reduce costs for both the manufacturer and the purchaser without compromising on quality.
Industrial
Vacuum forming plastic is used extensively in the production of durable item like crates and contoured containers for machinery. These kinds of products require crafting sturdy and resistant parts that can endure harsh industrial environments. In addition, vacuum forming can also be used in small-volume products or prototypes.
Packaging
The food packaging industry likes to use vacuum forming to produce packaging boxes for snacks or other foods. Vacuum forming is increasingly being used due to its ability to mold food-grade plastic easily and help prevent contamination, preserve freshness, and reduce damage, which is a cost-effective way for manufacturers.
Conclusion
Vacuum forming in plastic part manufacturing appeared over 20 years ago and creates a wide range of vacuum formed plastic products with characteristics of cost-efficiency, quick processing, and versatility in producing detailed products. For businesses seeking to leverage these advantages, partnering with an experienced manufacturer is key.
Fecision delivers engineering support and quality assurance to optimize efficiency and adaptability for vacuum forming products. Fecision has the comprehensive quality control processes from molding to vacuum forming products that can meet the highest quality standards.
Fecision focuses on precise tolerance and fast turnaround to manufacturer compact design, industrial-grade components, which work perfectly with custom vacuum forming characteristics of its speed, versatility, and affordability.
Contact us today to discover how our advanced vacuum-forming solutions can meet your prototyping and manufacturing needs>>




