An insert molding plastic injection molding process includes placing a metal, ceramic, or electronic component inside the mold before injecting molten plastic around it. In this process, the insert is permanently bonded to the plastic, and a single, unitary part is formed.
Key Components of Insert Molding
Insert Molding typically involves:
✔ Screws, pins, bushings, terminals, or threaded fasteners
✔ Circuit boards, sensors, or connectors
✔ Plastic Resin – Thermoplastics like ABS, Nylon, PEEK, or Polycarbonate
✔ Injection Molding Machine – Imposes high pressure to flow melt plastic around the insert
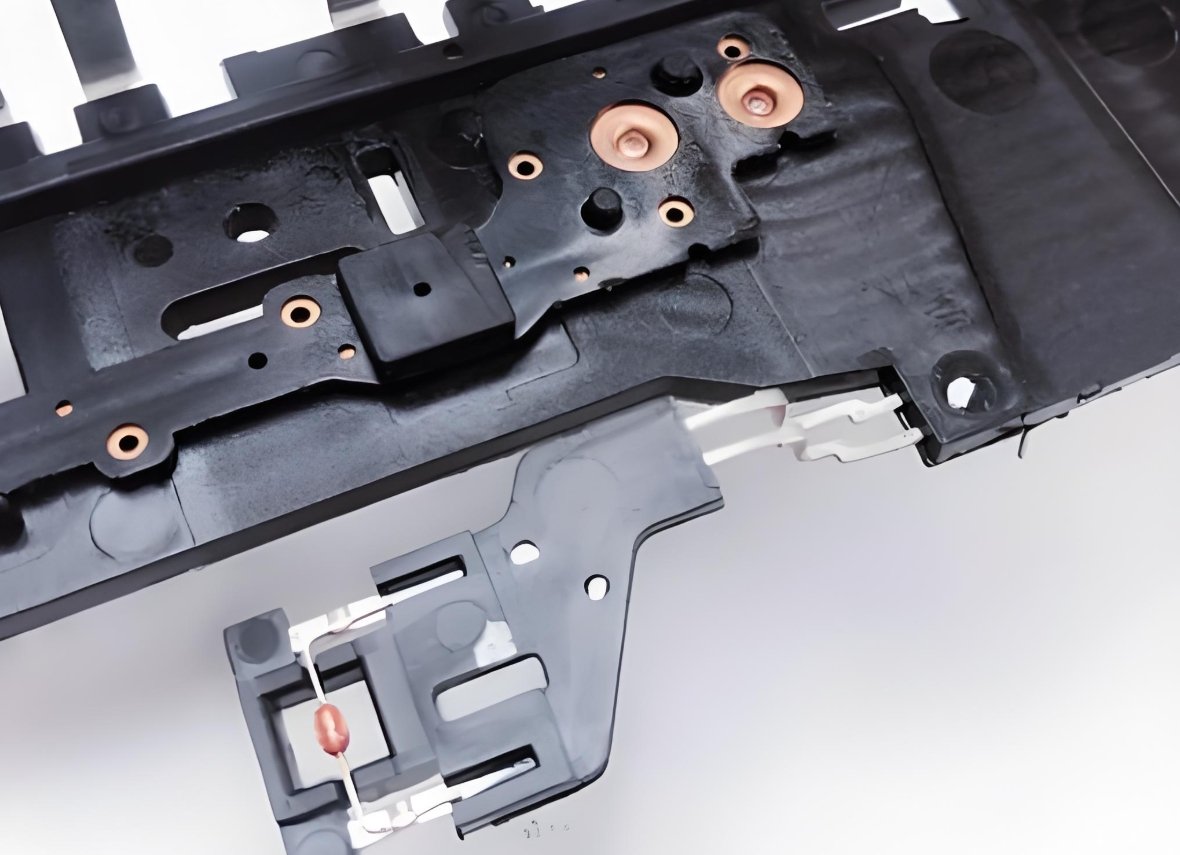
How to Insert Molding Works: Step-by-Step Process
- Pre-Manufacturing Insert – The pre-manufacturing insert consists of the pre-manufactured insert placed in the mold manually or processed with automation.
- Mould closing securing the insert is in place.
- Plastic Injection – Melted plastic is injected into the mold and flows around the insert bonding.
- Cooling and Solidification – Upon cooling and solidification, this leads to a single substantial piece part.
- Ejection & Inspection – The part is ejected and inspected for quality control.
- This process eliminates secondary assembly or adhesives to link plastic and insert up robustly.
Advantages of Insert Molding
The advantages provided by insert molding surpass those of traditional manufacturing techniques include:
1. Increased Product Strength & Durability
The tight plastic bond works around the insert to increase structural quality.
Insert molding techniques to decrease the mechanical components’ normal wear and tear.
An object gains better resistance against impacts and vibrations and operational durability in extreme conditions through insert moulding.
2. Cost Savings & Production Efficiency
The elimination of secondary assembly procedures leads to lower labour expenses.
The manufacturing process becomes faster when combined with a rise in operational performance.
The mould process optimization enables a reduction of excess material waste.
3. Enhanced Design Flexibility
✔ Enables the integration of multiple materials into a single part.
The production method enables the creation of complex designs which traditional manufacturing technologies cannot handle easily.
The system enables users to customize designs according to distinct application requirements.
4. Reduced Weight & Material Usage
✔ Uses lighter thermoplastics instead of bulky metal components.
The overall product lightness becomes possible through this method, which benefits automotive and aerospace applications.
5. Improved Electrical Performance
The process works perfectly for protecting electronic parts which need insulated operations.
The process secures delicate parts through secure encapsulation that stops any damage.
6. Enhanced Aesthetic & Functional Properties
✔ Produces seamless designs with no visible joints.
Products achieve superior design quality through insert moulding that raises consumer market appeal.
The combination of advantages drives industries to adopt insert Molding as a standard manufacturing technique.
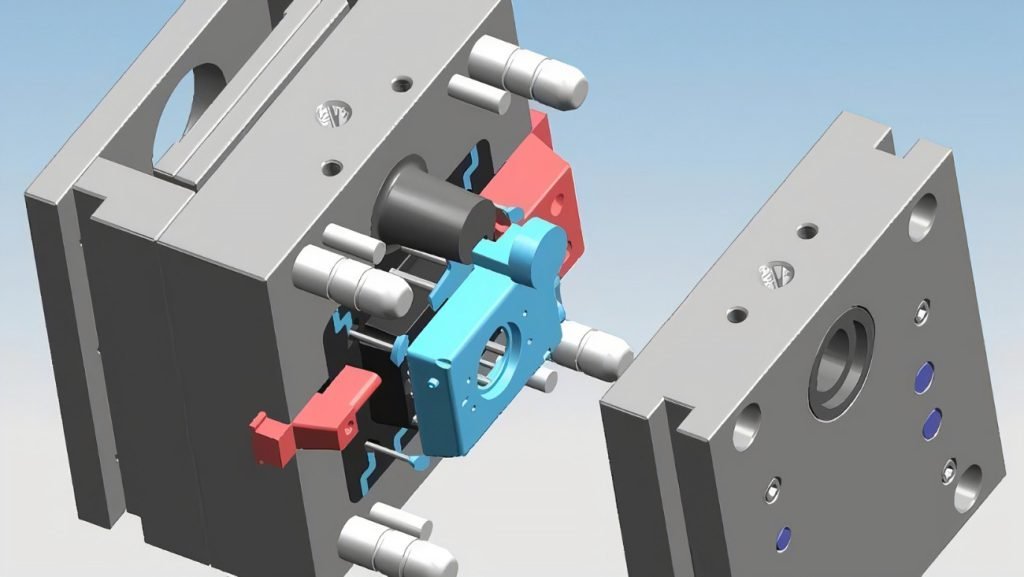
Common Materials Used in Insert Molding
1. Plastic Resins
Plastic choice depends on three categories: mechanical attributes and chemical and thermal demands.
ABS manufacturing dominates the market because of its strength, impact resistance, and broad industrial adoption.
✔ Nylon (PA) – High strength, heat resistance, and low friction properties.
✔ Polycarbonate (PC) – Excellent electrical insulation and impact resistance.
✔ Polyether Ether Ketone-The high-performance medical-grade aerospace product PEEK functions as a Polyether Ether Ketone material.
✔ PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) – Good wear resistance and electrical properties.
2. Insert Materials
Insert Molding makes use of various standard components, among which are:
Brass and Aluminum and Stainless Steel are the best options for threaded fasteners and structural components.
✔ Copper – Used in electrical applications for conductivity.
✔ Ceramic – Provides high-temperature resistance in specialized industries.
A proper material selection choice leads to parts with the best performance characteristics and extended service life in insert-moulding applications.
Insert Molding vs. Overmolding: Key Differences
Many people confuse insert Molding and over molding, but they serve different purposes:
| Feature | Insert Molding | Overmolding |
| Definition | Embeds a metal or non-plastic insert into molded plastic | Applies a second layer of plastic over an existing component |
| Applications | Fasteners, medical devices, automotive parts | Soft-touch grips, handles, protective coatings |
| Material Bonding | Permanent bond between plastic and insert | Can be bonded mechanically or chemically |
| Manufacturing Steps | Single-step process with metal placement | Two-step process requiring separate injection cycles |
Insert Molding is ideal for durable, functional components, while overmolding enhances aesthetics and ergonomics.
Applications of Insert Molding Across Industries
1. Automotive Industry
✔ Threaded fasteners and bushings for dashboards and interiors.
Many sensor use cases include protective structures which contain embedded electronic components.
Engine components that need resistance to high temperatures.
2. Medical Industry
✔ Surgical instruments with ergonomic grips.
✔ Implantable medical devices with bio-compatible materials.
✔ Catheter hubs and drug delivery systems.
3. Electronics & Telecommunications
Electrical connectors and sockets make use of contacts, which are integrated into their structure.
The smartphone manufacturing process demands components that have insulation properties and need to maintain their durability, such as PCB assemblies with integrated metal parts.
4. Aerospace & Defense
✔ Lightweight, high-strength aircraft components.
Radar and communication systems consist of enclosed electronic components.
✔ Vibration-resistant military-grade equipment.
5. Consumer Products & Home Appliances
✔ Power tools with ergonomic plastic handles.
✔ Kitchen appliances with metal-plastic hybrid parts.
✔ Wearable technology and smart gadgets.
InsertInsert Molding transformed manufacturing processes while creating superior products in these commercial sectors.
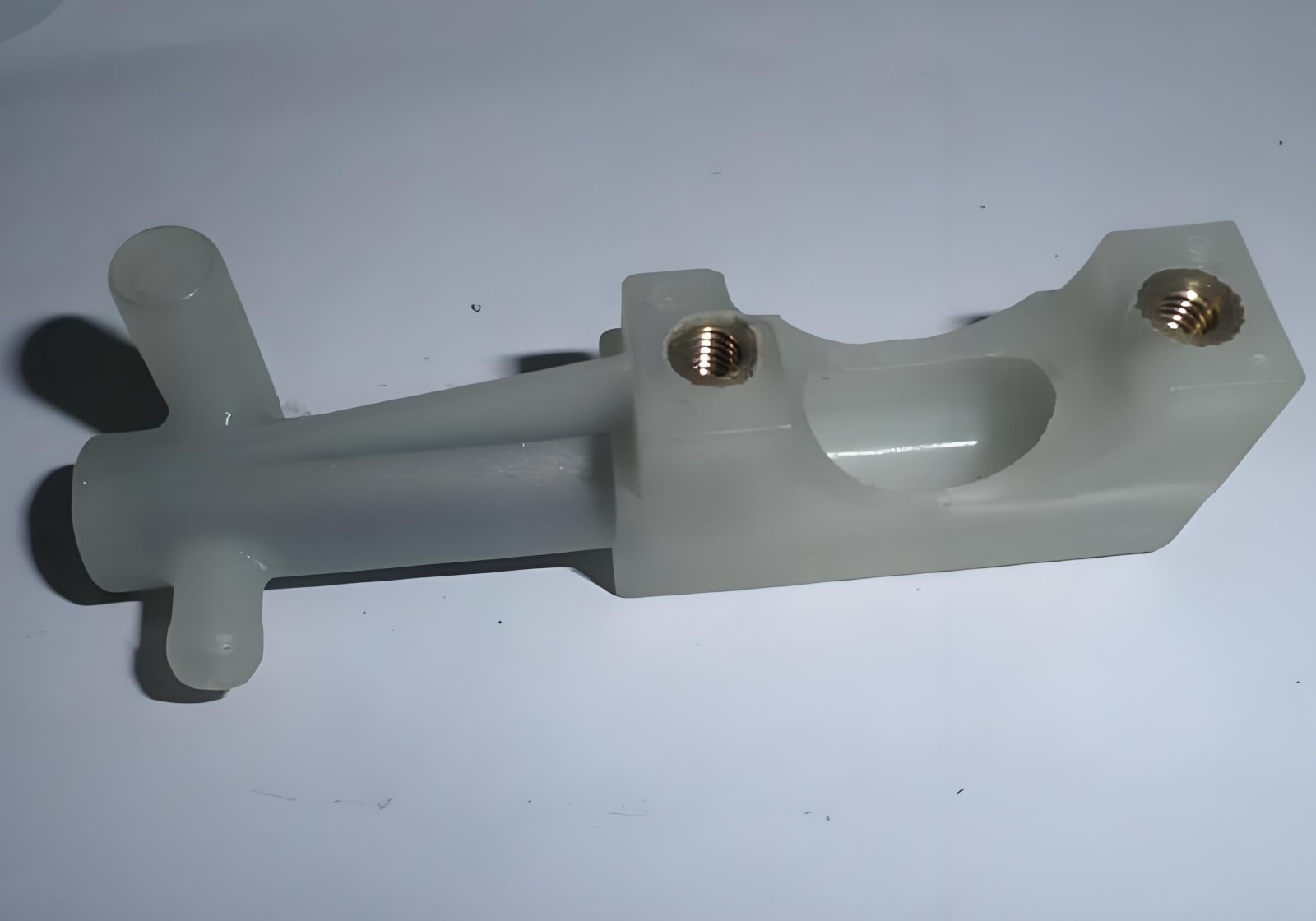

Quality Control in Insert Molding
Quality control requirements need to be rigorous to obtain stable product quality from insert moulding processes:
✔ Material Inspection – Ensures plastic and metal compatibility.
✔ Testing & Validation – Includes tensile strength, thermal resistance, and electrical conductivity tests.
✔ Surface Finishing – Cosmetically flawless surfaces and no cosmetic defects.
Our Fengchi operation follows rigorous quality control standards, producing high-performance components without defects in their final state.
Why Choose Fecision for Insert Molding?
- The precision insert moulding solutions developed at Fengchi excel in serving multiple industrial sectors across the board.
- The company implements its operations through advanced CNC machining systems and injection molding machines.
- The company provides customizable insert molding products that resolve your specific operational requirements.
- Bloodlight pairs with leading materials while running full-scale quality examinations for flawlessly operational outcomes.
- Cost-effective and efficient manufacturing for small and large production runs.
- Fengchi welcomes your immediate contact for accessing design-based insert molding solutions that enhance your product creation and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Multiple industry sectors achieve better product resistance and economical benefits through the insert molding manufacturing method, which also provides sophisticated design elements. Product victory in the automotive, medical devices, electronics, and aerospace industries depends on the appropriate selection of an insert moulding partner.
Fecision provides top-tier insert injection molding solutions that comply with every existing industry requirement. Contact us to discuss all aspects of your insert molding requirements.




