CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a cutting-edge, non-traditional machining process that removes material using electrical discharges or sparks. Unlike conventional cutting methods, CNC EDM does not require physical contact, making it ideal for machining hard metals and complex geometries with high precision.
This technique is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and mold-making industries for intricate and high-tolerance components. Despite its advantages, EDM has limitations, including slower processing speeds and higher operational costs. This article explores the fundamentals of CNC EDM, its working principles, advantages, applications, cost factors, and comparisons with other machining techniques.
Basics of CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
What is CNC EDM
CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a non-traditional manufacturing process that removes material from a workpiece using controlled electrical discharges, or sparks. Unlike conventional cutting methods, EDM does not require direct contact between the tool and the material, making it ideal for machining hard metals and complex shapes. A computer numerically controlled (CNC) system precisely controls the process, ensuring high accuracy and repeatability. This technique is widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and mold-making for intricate and high-precision components.
How CNC EDM Works
The CNC EDM machine follows a pre-programmed design to shape the workpiece. The electrode moves along the programmed path, generating controlled electrical sparks. The dielectric fluid cools the workpiece, stabilizes the discharge process, and removes eroded material. This method ensures high precision, making it perfect for delicate and complex components.
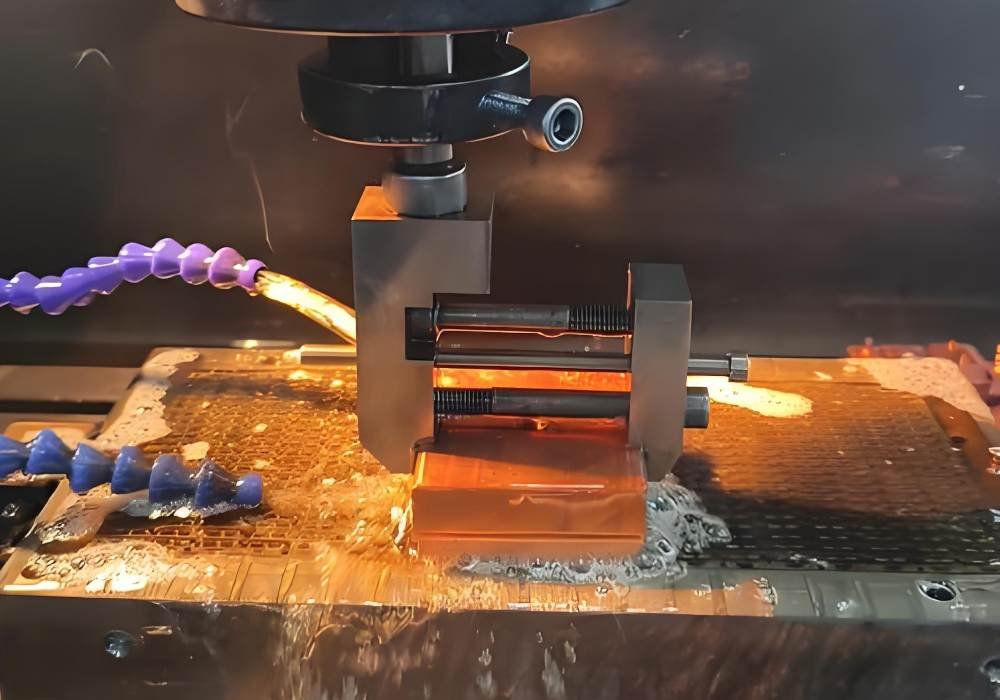

Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC EDM
CNC EDM offers unique benefits that make it invaluable for machining complex and tough materials. However, like any process, it has limitations that should be considered.
Advantages
- High Precision & Complex Shape Cutting: CNC EDM can create extremely detailed and intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional machining methods.
- No Mechanical Stress: Since there is no direct contact between the tool and the workpiece, there is no mechanical force applied, reducing the risk of deformation or material warping.
- Works on Hard Materials: CNC EDM can efficiently machine tough materials like tungsten, titanium, and hardened steel, which are challenging for conventional cutting tools.
- Burr-Free Finish: Unlike traditional cutting processes, CNC EDM does not produce burrs, reducing the need for secondary finishing operations and improving surface quality.
- Ability to Machine Delicate and Thin Parts: Since there is no physical contact, fragile and thin parts can be machined without the risk of breakage.
Disadvantages
- Slower Processing Time: Compared to CNC milling or drilling, EDM is a slower process, making it less suitable for high-speed, high-volume production.
- Higher Operational Costs: The costs of consumable electrodes, high power consumption, and dielectric fluid maintenance make EDM more expensive than some traditional machining methods.
- Limited to Conductive Materials: CNC EDM can only be used on electrically conductive materials, restricting its application to metals and excluding non-metallic materials like plastic and wood.
CNC EDM Process and Techniques
CNC EDM involves various techniques and processes that enable precise material removal, making it a preferred method for machining intricate and hard-to-cut materials.
Types of EDM
CNC EDM come in different types, each designed for specific applications and machining needs.
Wire EDM: Wire EDM uses a thin, electrically charged wire to cut through the workpiece with extreme precision. This method is best suited for producing intricate and delicate designs with high accuracy. It is commonly used for manufacturing complex components such as medical implants, aerospace parts, and intricate gears.
Sinker EDM: Sinker EDM, also known as Ram EDM, utilizes a custom-shaped electrode that is pressed into the workpiece to create detailed cavities, slots, and three-dimensional shapes. This method is widely used in mold and die-making industries, where high accuracy and fine details are required.
Hole Drilling EDM: Hole Drilling EDM is specifically designed to create deep, narrow holes in hard-to-machine materials. It is commonly used in the aerospace industry for producing cooling holes in turbine blades, as well as in medical and automotive industries for precision drilling applications.
Key EDM Operations
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) offers two primary methods die-sinking and wire EDM each suited for specific applications requiring precision and complexity.
Die-Sinking EDM for Mold Making: Die-sinking EDM, also known as ram EDM or sinker EDM, is widely used for creating detailed molds and dies. In this process, a specially shaped electrode is used to erode the material from the workpiece, forming intricate cavities and complex shapes. This technique is especially useful in the manufacturing of injection molds, stamping dies, and aerospace components where precision and surface finish are critical. Since there is no direct contact between the electrode and the workpiece, die-sinking EDM can achieve high accuracy without causing mechanical stress or distortion.
Wire EDM for High-Precision Cuts: Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) is a technique that uses a thin, electrically charged wire as the cutting tool. The wire moves along a programmed path, cutting through the workpiece with extreme precision. This process is ideal for manufacturing delicate components, gears, medical implants, and aerospace parts that require tight tolerances. Wire EDM allows for the creation of intricate shapes and fine details that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using conventional machining methods. Additionally, it provides a burr-free finish, eliminating the need for secondary processing.
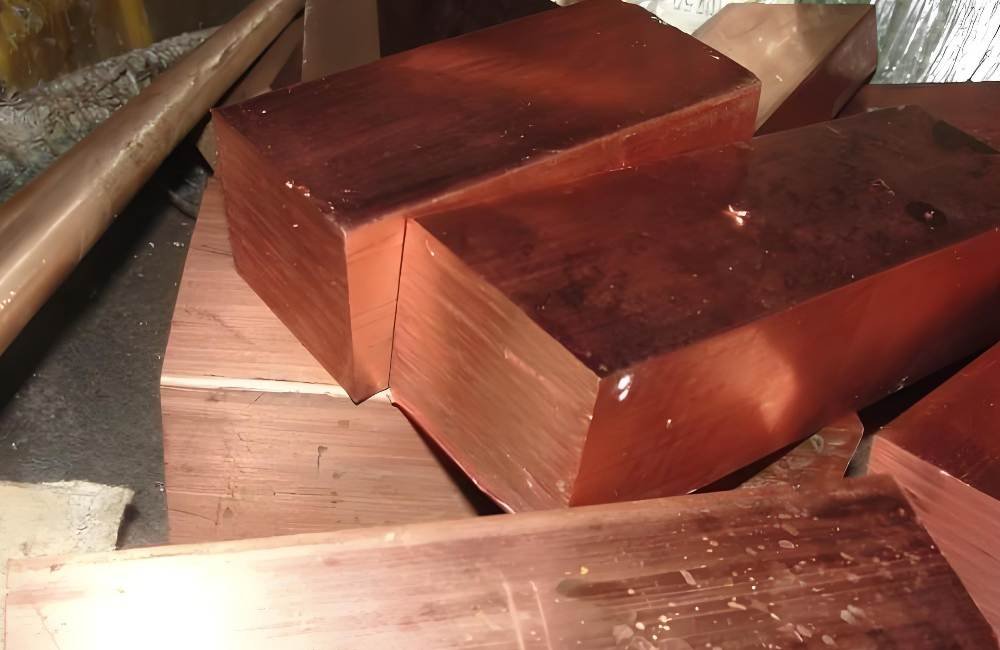

Materials Used in CNC EDM
CNC EDM is effective for machining hard and conductive materials that are challenging to process with conventional cutting tools.
Hard Metals
- CNC EDM is highly effective for machining hard metals that are difficult to cut using conventional methods.
- Common materials include tungsten, titanium, hardened steel, and carbide.
- These metals are widely used in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries due to their durability and strength.
Conductive Materials
- CNC EDM requires the material to be electrically conductive for the machining process to work.
- Metals such as aluminum, copper, brass, and graphite are commonly used for EDM operations.
- Non-metallic substances like ceramics and plastics cannot be processed with EDM as they do not conduct electricity.
Manufacturing Costs of CNC EDM
The cost of CNC EDM varies based on multiple factors, including electrode wear, power consumption, and setup complexity, making it more expensive than traditional machining in many cases.
Cost Factors
- Electrode Wear: Electrodes gradually degrade during the EDM process, leading to recurring costs for electrode replacement. The type of material and machining duration influence electrode wear rates.
- Power Consumption: CNC EDM machines require a continuous electrical discharge, consuming more power than traditional machining methods. This adds to operational costs, particularly for long machining cycles.
- Setup Costs: The initial setup of an EDM machine, including programming, electrode preparation, and workpiece alignment, requires skilled labor and time, increasing production costs.
Cost Comparison with CNC Milling and CNC Drilling
CNC EDM is typically more expensive than CNC milling and drilling due to slower processing speeds, higher power consumption, and the need for specialized electrodes. However, it provides unmatched precision for complex shapes and hard materials, making it cost-effective for applications requiring high detail and minimal tool wear. CNC milling and drilling, on the other hand, are more suitable for high-speed production and machining softer materials at a lower cost.
Applications of CNC EDM
CNC EDM plays a crucial role in industries where traditional machining struggles to achieve the required precision and complexity.
Aerospace and Defense Components: CNC EDM plays a crucial role in the aerospace and defense industries, where precision and durability are essential. It is used to manufacture critical components such as turbine blades, engine parts, and fuel system components.
The ability to machine tough alloys, including titanium and Inconel, makes EDM indispensable for producing high-performance aerospace parts. Additionally, EDM is used to fabricate complex, lightweight structures that meet strict military and aviation standards.
Injection Molding and Die Making: CNC EDM is widely used in the tooling and mold-making industry to create high-precision molds and dies for plastic injection molding and metal stamping. The process ensures superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy, allowing manufacturers to produce intricate mold cavities and detailed engravings. EDM is particularly beneficial for hard-to-machine materials like hardened steel, ensuring extended mold life and minimal wear.
The ability to create complex geometries and fine details makes EDM essential for industries requiring high-quality molded products, such as automotive, medical, and consumer electronics manufacturing.
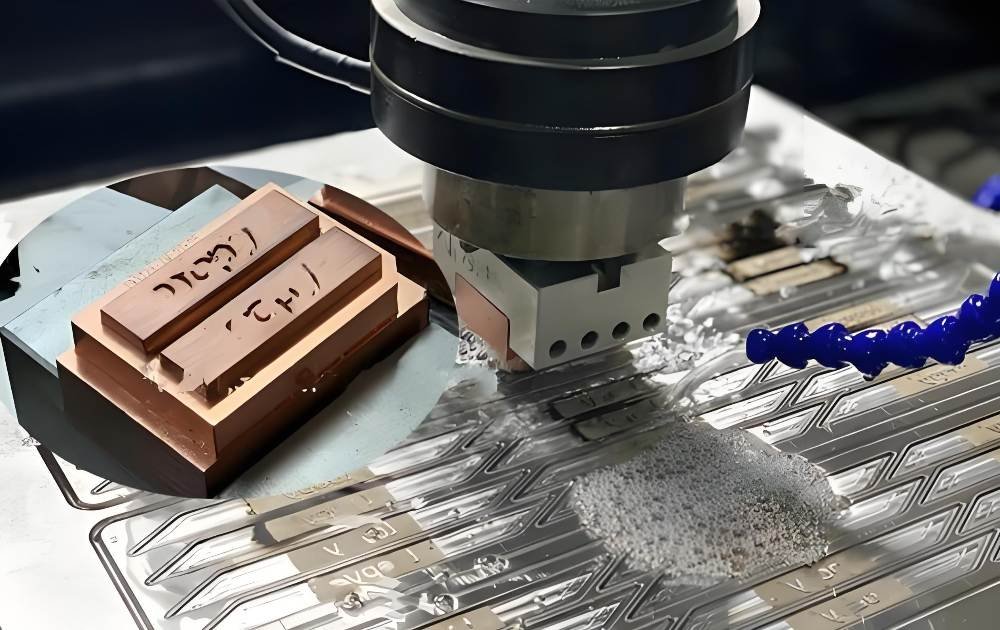
CNC EDM vs. Other Machining Methods
CNC EDM differs significantly from other machining methods in terms of process, cost, and efficiency.
CNC EDM vs. CNC Milling
| Feature | CNC EDM | CNC Milling |
| Process | Sparks | Cutting Tool |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Precision | High | Medium |
| Cost | High | Medium |
| Material | Conductive Only | Various |
CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) and CNC milling are both used to shape materials, but they operate differently. CNC EDM uses electrical sparks to erode material, making it ideal for hard metals and intricate shapes. Since there is no direct contact between the tool and the workpiece, EDM prevents mechanical stress and deformation. In contrast, CNC milling relies on rotating cutting tools to remove material, making it faster for bulk material removal but less effective for extremely fine details or hardened metals.
CNC EDM vs. CNC Drilling
| Feature | CNC EDM | CNC Drilling |
| Process | Erosion | Cutting |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Precision | High | Moderate |
| Material | Conductive | Any |
| Application | Complex Shapes | Hole-Making |
| Cost | High | Low |
CNC drilling is primarily designed for creating holes in materials with precision and speed. It uses a rotating drill bit to penetrate the workpiece, making it highly efficient for repetitive hole-making operations. CNC EDM, on the other hand, can create deep and precise holes without generating mechanical stress, which is beneficial for delicate components. However, EDM is significantly slower than drilling and is only suitable for conductive materials, whereas CNC drilling can work on a wider range of materials, including non-conductive ones.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
When choosing a machining process, cost and efficiency are crucial factors. CNC EDM is known for its precision, but it also has higher operational expenses and slower processing times compared to CNC milling and drilling.
- Speed: CNC EDM is inherently slower than CNC milling and drilling. Since material removal occurs through electrical discharges, the process is gradual, making it unsuitable for high-speed production. In contrast, milling and drilling achieve faster material removal rates with conventional cutting tools.
- Cost: CNC EDM generally incurs higher costs due to the need for specialized electrodes, significant power consumption, and maintenance of dielectric fluid. Milling and drilling, however, require less electricity and tool replacements, making them more cost-effective for large-scale production.
- Precision: CNC EDM is superior in terms of precision and the ability to machine complex, fine details without mechanical stress. It is ideal for applications that demand high accuracy, such as aerospace components and intricate mold designs. On the other hand, CNC milling offers good precision but may struggle with extremely intricate details, while drilling prioritizes speed over accuracy.
- Material Limitations: CNC EDM is limited to electrically conductive materials, restricting its application to metals like steel, titanium, and copper. Milling and drilling, however, can work on a broader range of materials, including non-metals like plastic and composites.
This balance between cost, speed, and precision makes CNC EDM an excellent choice for specialized, high-precision tasks, while CNC milling and drilling remain preferred options for general-purpose machining and mass production.
Conclusion
CNC EDM is a highly specialized machining process that provides exceptional precision and the ability to work with hard materials. It is particularly useful for applications requiring intricate shapes, minimal tool wear, and stress-free machining. However, due to its slower processing speed and higher costs, it is best suited for specialized manufacturing rather than high-speed production. Choosing CNC EDM is ideal for industries such as aerospace, mold making, and medical device manufacturing, where precision and surface finish are critical factors.
At Fecision, we provide advanced CNC EDM services, with a strong focus on manufacturing precision molds, including injection molds and stamping dies. By combining EDM with our comprehensive machining and tooling expertise, we help customers achieve superior mold performance, longer tool life, and consistent production results.
If your project requires high-precision mold components or complex tooling solutions, contact Fecision today to learn how our CNC EDM services can support your manufacturing goals.




