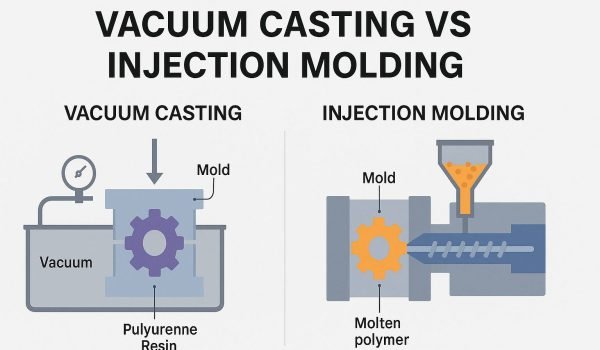
Are you ready to bring your product to life but not sure which plastic manufacturing method fits best? Choosing between vacuum casting and injection molding is one of the biggest decisions manufacturers face when planning production. Each process affects cost, lead time and scalability in different ways. Vacuum casting uses low cost silicone molds to produce small batches of 10-100 units with quick turnaround. It’s ideal for prototypes and bridge manufacturing.
Injection molding uses steel or aluminum molds to mass produce thousands of identical parts daily. This article breaks down everything you need to know about vacuum casting vs injection molding to help you decide which process is best for your manufacturing needs.
What Is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting, also known as urethane casting or polyurethane casting, is a manufacturing process that uses silicone molds and vacuum pressure to produce high quality plastic parts. It’s used for small batch production, prototype testing and bridge manufacturing between prototyping and full scale production.
The process starts with a master model, usually 3D printed or CNC machined, that defines the shape of the final part. The master is then encased in liquid silicone, cured and split open to form a flexible mold. Once the mold is ready, polyurethane resin is poured in and vacuum pressure removes the air bubbles, resulting in a flawless surface finish and dimensional accuracy. The result is a durable and visually appealing part ready for testing or limited use.
A single silicone mold yields 20-50 parts before degradation. Because the molds are cheap and quick to produce, vacuum casting is perfect for small runs of 10-100 units with a turnaround time of around one week.
Industries using vacuum casting include:
- Automotive: dashboards, trim panels, emblems
- Consumer electronics: enclosures, interfaces, phone cases
- Medical devices: prosthetics, hearing aids, custom housings
- Consumer goods: sunglasses, appliance components, small accessories

What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a high volume manufacturing process that mass produces identical plastic parts by injecting molten thermoplastic material into metal molds under high pressure. This is the backbone of plastic injection molding services, producing millions of parts daily.
In a typical injection molding cycle, plastic pellets are melted in a heated barrel, homogenized by a rotating screw and then injected into a steel or aluminum mold. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens and ejector pins push out the finished part, ready for use or minimal post processing.
This process supports a wide range of thermoplastics (ABS, polypropylene, polycarbonate, nylon, etc.) and even some metals or elastomers. Because of its precision and speed, plastic injection molding is ideal for high volume production of complex, durable and repeatable components.
Industries that rely on injection molding:
- Automotive: bumpers, interior panels, connectors
- Medical: syringes, housings, instruments
- Aerospace: lightweight brackets, components
- Consumer goods: toys, packaging, tools
Process Overview: How Vacuum Casting and Injection Molding Work
Both processes follow different steps that determine their capabilities and applications. Understanding these workflows will help you see why each is best for different production needs.
Vacuum Casting Process:
- Master pattern creation – Usually 3D printed or CNC machined.
- Mold preparation – Silicone poured around the master and cured at 40°C.
- Casting under vacuum – Polyurethane resin is poured in, and a vacuum is applied to remove bubbles.
- Curing and demolding – Mold heated (around 70°C), part cured, removed and trimmed.
Injection Molding Process:
- Mold clamping – Two halves of the mold are locked together.
- Plastic injection – Molten polymer injected under high pressure.
- Cooling phase – Material solidifies inside the mold.
- Ejection – Finished part pushed out, and the cycle repeats.
The main difference is that vacuum casting uses soft silicone molds under vacuum pressure. While injection molding uses metal molds and high pressure injection for fast and automated production.
Key Differences Between Vacuum Casting and Injection Molding
While both create detailed plastic components, the production principles, tooling and scalability are very different.
| Characteristic | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
| Tooling Material | Silicone | Steel or Aluminum |
| Mold Creation Time | 5–7 days | 2–4 weeks |
| Cycle Time per Part | 30–60 minutes | 10–60 seconds |
| Typical Batch Size | 10–100 parts | 1,000+ parts |
| Tolerance | ±0.3 mm | ±0.025 mm |
| Mold Lifespan | 20–30 parts | Thousands to millions |
| Material Type | Polyurethane resins | Thermoplastics (ABS, PC, PP, etc.) |
| Per-Part Cost | Higher for low volume | Lower for large volume |
| Tooling Cost | Low | High ($1,500–$50,000+) |
| Production Speed | Slow (manual) | Fast (automated) |
| Best For | Prototyping, small runs | Mass production |

Cost Comparison: Tooling, Materials, and Per-Part Pricing
When making cost-effective decisions, you need to know the costs involved in vacuum casting and injection molding. The cost structure is very different between these two processes and affects production budgets at all scales.
1) Tooling Costs: Silicone vs Steel/Aluminum Molds
The upfront tooling cost is the biggest difference between the two. Injection molding requires a significant upfront investment in metal molds, often over $50,000 for steel tooling. Vacuum casting uses silicone molds which are much cheaper and can be made in a few days. For those looking for a middle ground, aluminum tooling for injection molding starts at $1,500.
2) Per-Part Cost: Low Volume vs High Volume
Although vacuum casting has lower tooling cost, the per-part cost is higher due to manual labor involved in casting, demolding and finishing each part. Injection molding reverses this equation, after recovering the initial investment, additional parts are relatively cheap. This is visible in production capacity, vacuum casting yields 1-10 parts per day vs hundreds or thousands with injection molding.
3) Material Cost: Polyurethane Resins vs Thermoplastics
Material selection also affects the overall cost. Vacuum casting uses polyurethane resins which cost around $1,865 per metric ton in the US as of September 2024. Injection molding can use various thermoplastics including polypropylene at $0.55-0.89 per kilogram which is much cheaper than polyurethane’s $5.50-6.10 per kilogram.
4) Economies of Scale: When Each Method Becomes Cost-Effective
So vacuum casting is economical for small batches up to around 100 parts. Since silicone molds deteriorate after 20-30 uses, frequent replacements increase long term cost. Injection molding becomes more cost effective at higher volumes as the big tooling investment spreads across thousands or millions of parts. So the crossover point where injection molding becomes more economical than vacuum casting depends on your project’s expected lifetime production quantity.
Production Speed and Volume Capabilities
Production speed varies greatly between vacuum casting and injection molding, affecting production timeline and capacity. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right process for your production needs.
1) Lead Time for Mold Creation: 5 Days vs 2 Weeks
Mold creation timeframes impact project schedules dramatically. Vacuum casting has much faster tooling development, with silicone molds ready in 5-7 days. Rapid tooling for injection molding takes a minimum of 2 weeks. This is where vacuum casting really shines for time critical projects that need quick turnaround.
2) Cycle Time per Part: Manual vs Automated
Once the tools are ready, the two processes are worlds apart. Vacuum casting is manual and takes about 30-60 minutes per part. Injection molding is automated and takes 10-60 seconds, sometimes up to 120 seconds for complex shapes.
3) Daily Output: 10 Parts vs Thousands
Production volume is where the biggest difference is. Vacuum casting yields 1-10 parts per day, limited overall production. Injection molding can produce hundreds or thousands of parts per day depending on mold cavities and machine capacity.
4) Prototyping vs Mass Production
In the end, each process is suited for different production volumes. Vacuum casting is great for prototyping or small runs of 10-100 units, for faster iteration cycles for testing design versions. Injection molding is more efficient for runs over 1,000 parts, where cost per part decreases as volume increases.
Material and Design Flexibility
Material selection is a key differentiator between vacuum casting and injection molding, each with its own advantages for specific applications.
1) Material Options: Polyurethane vs ABS, PC, Nylon
Vacuum casting uses polyurethane resins that can simulate properties of various thermoplastics. Injection molding can use ABS, polycarbonate, nylon, polypropylene and many engineering grade thermoplastics. This broader material range allows injection molding to meet mechanical requirements such as strength, durability and chemical resistance.
2) Part Strength and Durability Differences
Parts from vacuum casting are about 70-80% as strong as injection molded parts. Injection molded parts have better mechanical properties, uniformity and dimensional stability. But polyurethane materials excel in applications that require flexibility, resilience and impact resistance.
3) Design Complexity: Undercuts and Fine Details
While vacuum casting can handle moderate complexity, injection molding excels at intricate details, complex geometries and tight tolerances. Undercuts and internal features can be easily achieved in injection molding through side actions or specialized tooling mechanisms.
4) Tolerances: ±0.3 mm vs ±0.025 mm
Vacuum casting typically has tolerances of ±0.3 mm. Injection molding has better tolerances of ±0.025 mm (±0.005 inches).
5) Environmental Impact: Resin vs Recyclable Plastics
Both have environmental trade-offs. Thermoplastics used in injection molding are fully recyclable and can be reprocessed without significant degradation of their properties. Polyurethane resins vary in environmental impact. Some formulations are designed to reduce emissions.
Vacuum Casting Advantages
- Low Tooling Cost: Silicone molds are cheap and quick to make.
- Fast Turnaround: Typical lead times are 5–10 days.
- Good Surface Finish: Produces parts directly from the mold with a smooth finish.
- Design Flexibility: Easier to modify designs between runs.
- Small Batches: Best for 5–100 units.
- Material Options: Polyurethane resins can simulate ABS, rubber or transparent plastics.
If you’re in the early stages of product development, vacuum casting services allow you to test designs and market response without big investment.
Injection Molding Advantages
- High Speed and Efficiency: Cycle times as low as 10 seconds.
- Consistency and Precision: Tolerances as tight as ±0.025 mm.
- Durable Tooling: Steel molds can last for millions of cycles.
- Low Per-Part Cost at Scale: The more you produce, the cheaper each unit becomes.
- Material Options: Compatible with thousands of engineered thermoplastics.
- Automation Friendly: Minimal labor cost due to automated production lines.
- Recyclable Materials: Thermoplastics can be reground and reused, promoting sustainability.
For large production volumes, injection molding services offer unbeatable quality and cost.
When to Choose Vacuum Casting
Choose vacuum casting when:
- You need 5–100 units of a product.
- Your design is still evolving and may change after testing.
- You’re on a tight budget or timeline.
- You need excellent surface finish and detail replication.
- You need a bridge solution before moving to full-scale injection molding.
Vacuum casting services are popular among startups, R&D teams and product designers who need real-world prototypes before committing to expensive tooling.
When to Choose Injection Molding
Choose injection molding when:
- You need thousands or millions of parts per year.
- Your design is finalized and stable for long term production.
- You want high strength, durability and material variety.
- You need automation and consistency at scale.
- You want the lowest per-part cost in the long run.
Companies in automotive, medical, aerospace and consumer goods industries rely on injection molding services for precision, repeatability and cost efficiency.
Conclusion
The choice between vacuum casting vs injection molding depends on your production needs. If you need low volume, cost effective prototypes with good surface quality, vacuum casting services are your best option. For high volume production requiring precision, speed and durability, plastic injection molding is unbeatable. Both processes complement each other in a complete product development cycle.
Many companies start with vacuum casting to test designs and transition to injection molding for mass production when demand scales. For expert advice and end-to-end manufacturing solutions, visit Fecision today. Fecision offers world-class vacuum casting and injection molding services, helping you turn your ideas into reliable and high quality products.