Did you know that companies implementing Six Sigma methodology have seen a significant reduction in defects? This data-driven approach to quality control has revolutionized the manufacturing industry since its introduction at Motorola in the 1980s.
By focusing on reducing process variation, Six Sigma enables organizations to achieve near-perfect quality levels. As a purchasing or engineering professional, you understand the importance of working with suppliers who can deliver high-quality products consistently. This is where Six Sigma comes in – a powerful tool for driving continuous improvement and data-driven decision making in manufacturing.
Understanding Six Sigma Methodology
As you explore the world of manufacturing quality control, understanding the Six Sigma methodology becomes crucial. This data-driven approach is designed to improve business processes by identifying and eliminating defects.
The Origins and Evolution of Six Sigma
The term Six Sigma originates from statistical quality control, referring to six standard deviations between the process mean and the nearest specification limit. Motorola pioneered Six Sigma in 1986 as a response to increasing competition from Japanese manufacturers, with engineer Bill Smith developing the framework to systematically reduce defects.
Key Principles of Six Sigma
The key principles of Six Sigma include a relentless focus on customer requirements, data-driven decision making, process improvement, and proactive management to prevent defects rather than detecting them after production. This approach emphasizes measurable financial returns, making it particularly attractive to manufacturing organizations seeking to improve quality while reducing costs.
The Statistical Foundation of Six Sigma
At its core, Six Sigma is built on the statistical concept that when a process operates at six standard deviations from the mean, the defect rate drops to just 3.4 defects per million opportunities. This statistical foundation underpins the methodology’s effectiveness in improving manufacturing processes.
Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma has revolutionized the manufacturing sector by providing a data-driven approach to quality improvement. As a result, manufacturing organizations are able to significantly reduce defects and variability in their processes.
How Six Sigma Transforms Manufacturing Processes
Six Sigma transforms manufacturing processes by identifying and removing defect-causing elements. This methodology reduces the variability of business and manufacturing processes, leading to improved output quality. Manufacturing environments are ideal for Six Sigma implementation because production processes typically involve repetitive operations that can be measured, analyzed, and optimized with statistical precision.
By mapping the entire production process, identifying critical-to-quality characteristics, and establishing baseline performance metrics, companies can implement improvements that enhance overall quality.
The 3.4 Defects Per Million Opportunities Standard
The goal of Six Sigma implementation is to achieve 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO), representing a near-perfect quality standard. This standard fundamentally changes how manufacturing organizations approach process capability and product consistency. Achieving this level of quality requires a rigorous methodology that focuses on continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making.
Six Sigma Roles in Manufacturing Organizations
Six Sigma creates a structured hierarchy of roles within manufacturing organizations, from Executive Leadership and Champions to Master Black Belts, Black Belts, and Green Belts. Each role has specific responsibilities in the quality improvement process, ensuring that projects are managed effectively and that improvements are sustained over time. Companies like Motorola, General Electric, and Boeing have successfully implemented Six Sigma, achieving significant savings through reduced waste, rework, and warranty costs.
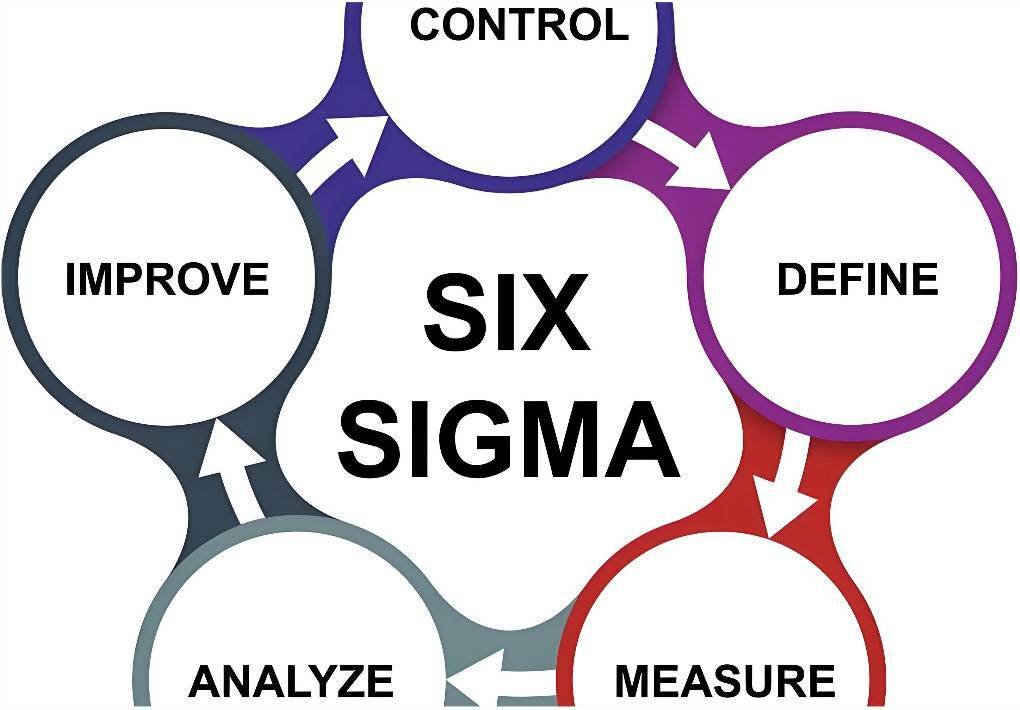
The DMAIC Framework: Core Steps of Six Sigma
At the heart of Six Sigma lies the DMAIC framework, a systematic method for enhancing manufacturing processes. This structured approach provides a data-driven template for process improvement, ensuring that changes are based on factual data rather than assumptions.
Define: Identifying Problems and Setting Goals
In the Define phase, manufacturing teams identify specific problems, establish project scope, determine customer requirements, and set clear, measurable goals for improvement initiatives. This stage is crucial for focusing efforts on areas that will have the most significant impact on quality and customer satisfaction.
Measure: Collecting Data on Current Processes
The Measure phase involves collecting baseline data on current manufacturing processes, establishing valid measurement systems, and quantifying the existing level of performance and process capability. Accurate data collection is essential for understanding the current state and identifying areas for improvement.
Analyze: Finding Root Causes of Defects
During the Analyze phase, teams use statistical tools to identify root causes of defects and process variation, separating the vital few factors from the trivial many that impact quality outcomes. This step is critical for understanding why defects occur and how to address them effectively.
Improve: Implementing Solutions
The Improve phase focuses on developing, testing, and implementing solutions that address root causes, with the goal of achieving significant process improvement. This stage involves creativity and innovation in finding and testing potential solutions.
Control: Maintaining Process Improvements
The Control phase establishes monitoring systems to maintain gains and prevent regression to previous performance levels. By implementing controls, organizations ensure that improvements are sustained over time, leading to long-term quality enhancement.
Benefits of Implementing Six Sigma in Manufacturing
By adopting Six Sigma, manufacturers can experience substantial improvements in product quality and operational efficiency. This methodology has been widely adopted across various industries due to its effectiveness in reducing defects and enhancing overall process performance.
Reduced Defects and Improved Product Quality
The primary benefit of Six Sigma in manufacturing is the dramatic reduction in defect rates. Organizations often see 50-70% fewer quality issues after implementation. This improvement is achieved through rigorous data analysis and process optimization, leading to higher quality products and reduced waste.
Increased Operational Efficiency and Throughput
Improved process stability and predictability lead to increased throughput and capacity utilization. This allows manufacturers to produce more with existing resources, enhancing overall operational efficiency. By streamlining processes, manufacturers can meet customer demands more effectively.
Cost Reduction and Financial Impact
The financial benefits of Six Sigma typically include reduced scrap and rework costs, lower warranty claims, decreased inventory requirements, and improved asset utilization. These savings contribute to higher profit margins. Companies like Johnson & Johnson, Texas Instruments, and Telefónica have reported significant savings after implementing Six Sigma.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction increases as product quality and consistency improve. This leads to stronger customer relationships, repeat business, and an enhanced market reputation. By delivering high-quality products consistently, manufacturers can build trust with their customers and gain a competitive edge.
Challenges and Limitations of Six Sigma
While Six Sigma has proven to be a valuable tool in enhancing manufacturing processes, its implementation is not without challenges. As you consider adopting Six Sigma methodologies, it’s essential to be aware of the potential obstacles that may arise.
Implementation Barriers in Manufacturing Settings
Implementing Six Sigma in manufacturing environments can be challenging due to resistance to change, resource constraints, and difficulty in maintaining momentum over time. You may face cultural barriers as Six Sigma requires a fundamental shift in how employees approach their work, moving from reactive problem-solving to proactive process management.
Statistical Complexity and Training Requirements
The statistical complexity of Six Sigma tools demands significant training investment, which can be a barrier for smaller manufacturing operations with limited resources for employee development. You need to consider the cost and time required for training when planning to implement Six Sigma.
Balancing Quality Improvement with Innovation
Some critics argue that Six Sigma’s focus on reducing variation can potentially stifle innovation and creativity, as the methodology emphasizes standardization and consistency over experimentation. You must strike a balance between quality improvement and innovation to reap the full benefits of Six Sigma.

Six Sigma vs. Lean Manufacturing: Complementary Approaches
When it comes to enhancing manufacturing processes, two popular methodologies often come into play: Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing. Both aim to improve business operations, but they have different focuses and approaches.
Core Differences Between Six Sigma and Lean
Six Sigma primarily focuses on reducing variation and defects through statistical analysis, while Lean Manufacturing concentrates on eliminating waste and improving flow in production processes. This fundamental difference in approach means that Six Sigma is often used to tackle complex quality issues, whereas Lean is applied to streamline processes and eliminate non-value-adding activities.
How Lean Six Sigma Combines Both Methodologies
The Lean Six Sigma methodology emerged as a powerful hybrid approach, combining the speed and efficiency of Lean with the quality and precision of Six Sigma. By integrating both methodologies, organizations can create a comprehensive improvement strategy that addresses both waste reduction and quality enhancement. Typically, organizations begin with Lean techniques to streamline processes before applying Six Sigma tools to address more complex quality issues.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Manufacturing Operation
The decision between implementing Lean, Six Sigma, or Lean Six Sigma depends on your specific manufacturing challenges. If your primary issues are waste and flow, Lean might be the starting point. For quality and defect problems, Six Sigma could be more appropriate. By understanding the strengths of each methodology, you can choose the best approach to improve your manufacturing processes and overall business performance.
Real-World Applications of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of Six Sigma in manufacturing, with companies achieving remarkable results. Several leading organizations have successfully implemented Six Sigma methodologies to improve their processes and product quality.
Motorola’s Pioneering Implementation
Motorola pioneered the use of Six Sigma in the 1980s, setting a “six sigma” goal for its manufacturing business. This initiative led to a 94% reduction in defects and significant savings in manufacturing costs over the following decades. By 2005, Motorola attributed over $17 billion in savings to Six Sigma.
General Electric’s Six Sigma Success
General Electric, under Jack Welch’s leadership, became one of the most prominent Six Sigma success stories. GE made Six Sigma central to its business strategy in 1995, resulting in more than $10 billion in savings during Welch’s tenure. By 1998, GE announced $350 million in cost savings thanks to Six Sigma.
Boeing’s Quality Improvement Journey
Boeing implemented Six Sigma to address complex quality challenges in aircraft production. The initiative significantly reduced assembly defects and improved delivery reliability, demonstrating the effectiveness of Six Sigma in complex manufacturing environments.
Lessons from Successful Implementations
Common factors among successful Six Sigma implementations include strong leadership commitment, adequate resource allocation, effective training programs, and integration with existing business processes. Companies like Toyota, Honeywell, and Caterpillar have also achieved substantial quality improvements and cost reductions by adapting Six Sigma principles to their specific manufacturing environments.
Conclusion: The Future of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma has transformed from a quality-focused methodology to a comprehensive business improvement approach in manufacturing. As you look to the future, it’s clear that Six Sigma will continue to play a vital role in driving quality, reducing defects, and improving processes.
The integration of Six Sigma with digital technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning will enhance data collection and analysis capabilities. Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing initiatives will also present new opportunities for Six Sigma implementation, enabling more sophisticated process monitoring and control.
As customer expectations for quality, customization, and sustainability rise, Six Sigma methodologies will need to adapt while maintaining core principles of variation reduction. Organizations that successfully implement Six Sigma as part of their continuous improvement culture will be better positioned to navigate future manufacturing challenges.
By embracing Lean Six Sigma and other complementary approaches, you can drive business improvement, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. The future of Six Sigma in manufacturing is bright, with ongoing evolution and adoption expected to drive significant business value.




