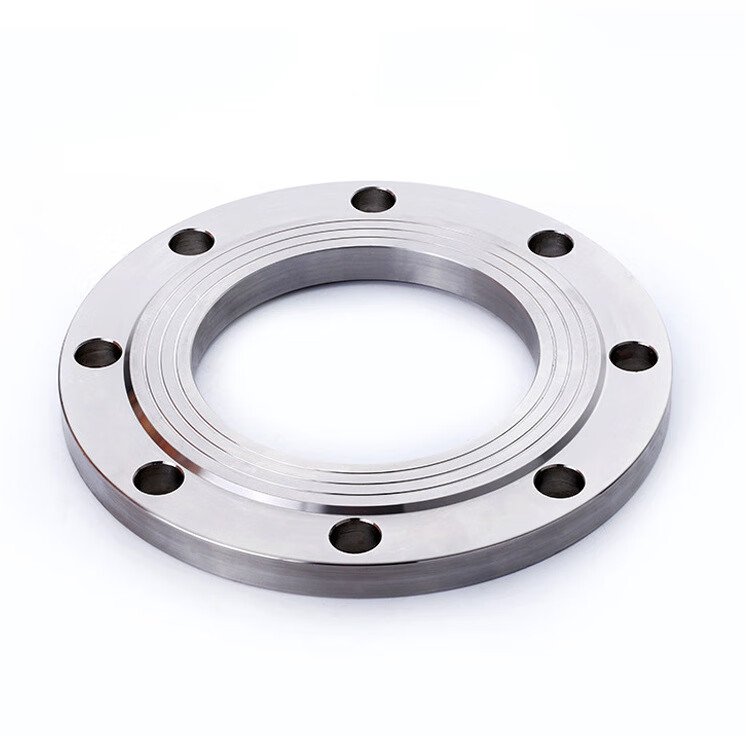
Flanges are a vital part of any piping system. Flanges enable sections of pipes to be joined, removed, or accessed for maintenance. It makes maintenance convenient. Plus, they provide a reliable, sealed connection between valves, pumps, and other piping parts. Take note that all flanges are not identical. Each type of flange is designed differently based on the counter-pressure, temperature, and the type of fluid.
Let us outline the different types of flanges used in commercial and industrial piping systems. We have also compiled their functional uses.
1. Weld Neck Flange

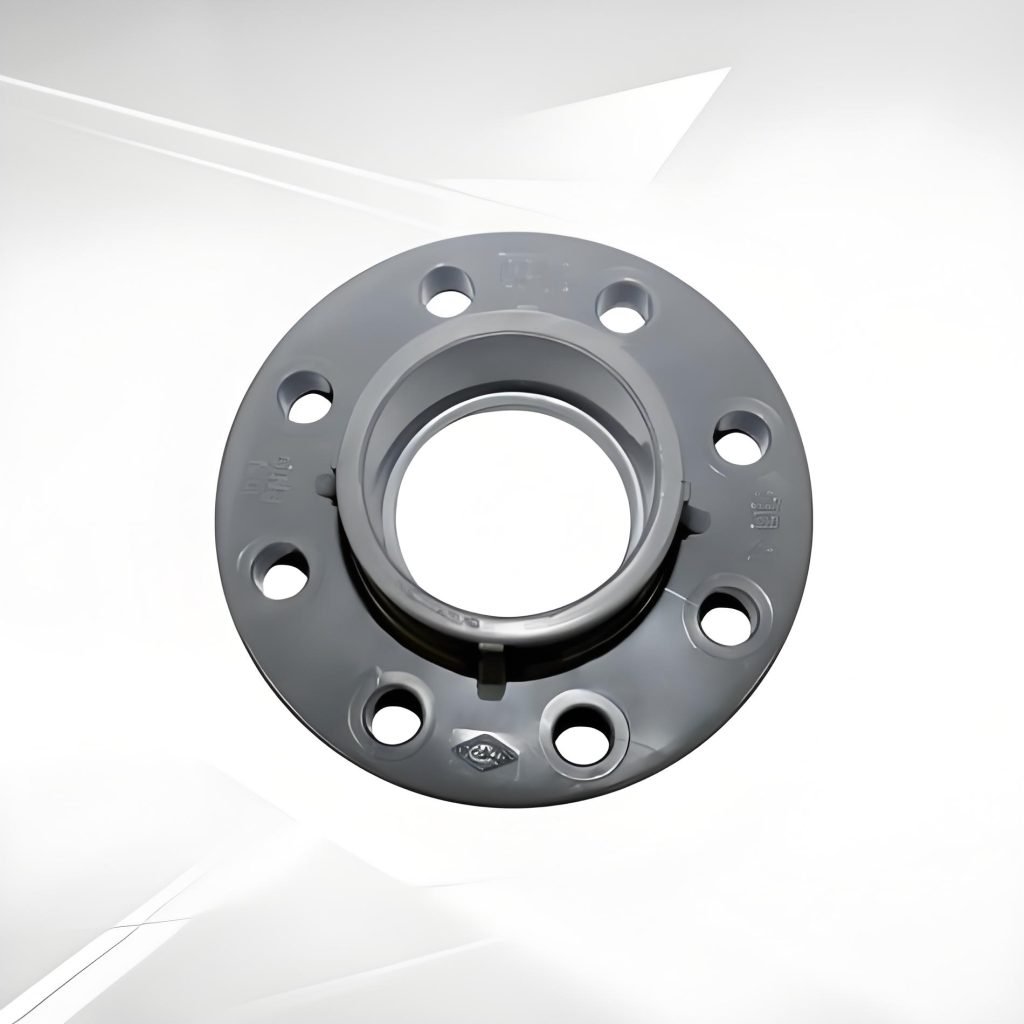
Weld Neck Flange can be easily identified by the long tapered hub. It is welded directly to the pipe. This design is strong enough to resist high pressure and high temperature. The smooth transition from flange to pipe cuts back turbulence and stress concentration at the weld point.
Weld neck flanges are suitable in harsh situations. You can find weld neck flanges in the oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation industries, where durability and reliability are essential.
Applicable In
- High-pressure applications
- High-temperature systems
- Piping that undergoes periodic thermal expansion or stress
2. Slip-On Flange

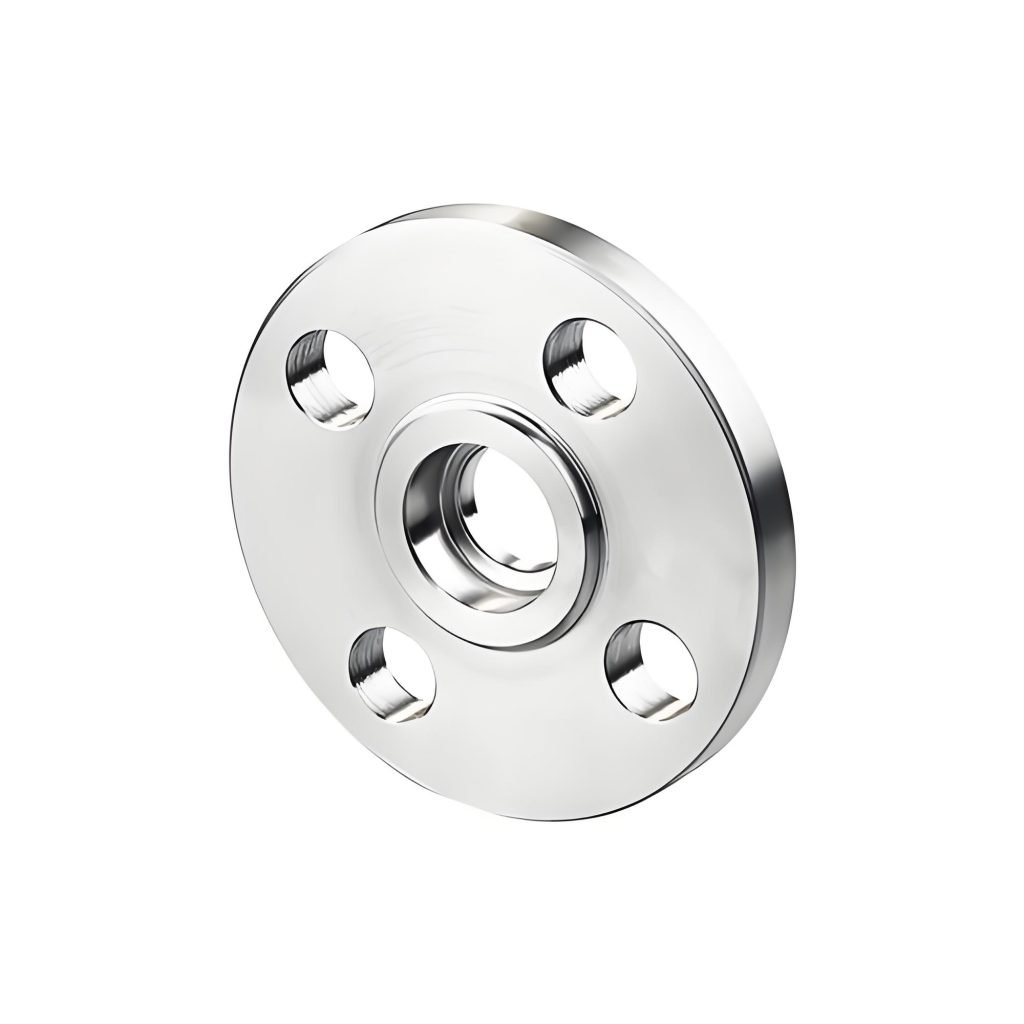
With the Slip-On Flange, the flange is a bit bigger than the pipe. It can be slipped over the pipe. The flange is welded on the inside and outside. In simple words, welding is done after the flange is slipped over the pipe. Alignment is not a big issue during installation as the flange can be slipped over the pipe.
These flanges, while not as strong as weld neck flanges, are used in low-pressure systems because they are inexpensive. Slip-On flanges are used in HVAC systems and fire protection systems because they are inexpensive and easy to maintain.
Applicable In
- Low-pressure fluid systems
- Pipelines that are meant to be temporary or used seasonally
- Residential and light commercial water pipeline systems
3. Socket Weld Flange

With the Socket Weld Flange, a pipe can be put into a recess, and a fillet weld done around the pipe’s edge. The bottom side of the flange is smoothly round. It has immense mechanical strength since the internal flow path is round.
Due to the design of these flanges, they are used widely in small-diameter, high-pressure lines and in places where welding space is a premium. You will find these in steam lines, hydraulic systems, and high-pressure chemical distribution systems, where strength and compact design are critical.
Applications
- Small-bore high-pressure piping
- Steam and hydraulic systems
- Contained industrial piping systems
4. Blind Flange
A Blind Flange has no bore or opening, and so may be used to blank off the end of a pipe or valve. It provides access to the system for pressure testing, system inspection, or expansion work, and so can be considered a blind.
It is a construction designed to withstand a static load. Therefore, it must be strong and able to withstand high internal pressure. Blind flanges are used widely in petrochemical plants, refineries, and industrial testing laboratories.
Applications
- Termination of the big piping system
- Pressure testing and system isolation
- Access for future expansion
5. Threaded Flange
A Threaded Flange is provided with internal threads to enable it to be screwed onto pipes with external threads. This makes welding unnecessary, which is critical in explosive or flammable environments. These flanges are preferred in utility and piping systems for natural gas and compressed air and are used for small-diameter and low-pressure systems.
Applications
- Avoidable welding zones for flammable or hazardous materials
- Connections that are not critical or under low pressure
6. Lap Joint Flange
The Lap Joint Flange is associated with a stub end that is welded to the pipe. The flange is not welded; instead, it slides over the pipe and is supported by the stub end. This configuration permits rotational freedom of the flange, facilitating bolt hole alignment.
It also allows the flange material to differ and be cheaper than the pipe, as it would not be exposed to the fluid. It is ideal for dismantling corroded systems as it helps to prevent corrosion in food or pharmaceutical processing plants. This is one of the most flexible flange types available today.
Uses
- Systems that require frequent disassembly
- Systems that are hard to access in corrosive or sanitary environments
- Systems that are hard to access and require precise alignment
7. Orifice Flange
The Orifice Flange is used in measuring the flow of fluids as it holds an orifice plate and features pressure taps to measure pressure drop across the plate. This pressure drop is utilized to derive flow rates accurately. Such flanges are not simply connectors; they are vital components for process control and monitoring.
They are widely used in real-time data collection in the oil and gas sector, utilities, and chemical manufacturing. Among the various types of flanges, this one serves a metering function beyond mechanical connection.
Applications
- To measure the inflow and outflow of liquids and gases
- To measure the system’s pressure drop
- In the automation of industrial processes
8. Long Weld Neck Flange
The Long Weld Neck Flange is an extension of the standard weld neck flange. Rather than joining pipes, it is more common to find this flange type welded to pressure vessels or tanks.
The Long Weld Neck flange is designed to provide additional mechanical support and thermal stability in high-pressure or extreme-temperature environments. It is commonly used in boilers, high-rise piping systems, and in structural steel applications which require load-bearing stability.
Uses
- Connecting to tanks or pressure vessels
- High-pressure thermal systems
- Elevated structural piping
9. Ring-Type Joint (RTJ) Flange
The Ring Type Joint Flange is characterized by a machined groove on the face, which receives a metal ring gasket to provide a tight, leak-proof seal. It is used in applications where even a minuscule leak may result in catastrophic consequences.
The seal is also used in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, as the metal-to-metal seal works excellently in those conditions. RTJ flanges are commonly used in offshore drilling, subsea pipelines, and high-pressure steam systems where sealing integrity is critical. It’s one of the most secure options among all flange types.
Applications
- Underwater and offshore installations
- Containment of dangerous fluids
- High-temperature, high-pressure systems
Bottom Line!
Like any other machine parts, flanges must work in perfect unison for the system to deliver the performance and safety needed. For those working with high-pressure steam, corrosive chemicals, or even simple water lines, the right flange for every application exists.
For frequent disassembly, lap joint flanges are perfect, and for extreme durability, weld neck flanges are the go-to.