Have you ever wondered if injection molding falls under the category of additive manufacturing (AM)? Absolutely not! Even though both of these are used to create parts, they are fundamentally different processes.
With over 80% of plastic parts in consumer products made through injection molding, it remains the preferred choice for mass production. But does that mean additive manufacturing is less valuable? Let’s find out.
Can Injection Molding Be Considered Additive Manufacturing?
The short answer? No, injection molding is not additive manufacturing. It’s actually a formative process, which means it shapes material inside a mold rather than building it layer by layer like 3D printing.
You might think, “Both make objects, so what’s the big difference?” The key is how they do it.
Injection molding takes melted material (like plastic) and injects it into a mold, shaping it instantly. Meanwhile, additive manufacturing builds parts layer by layer from digital files.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to quickly and efficiently create large numbers of identical parts. It works by injecting melted material (mostly plastic) into a mold, which cools and hardens into the final shape.
This process is widely used in the automotive, medical, consumer goods, and packaging industries because it’s fast, cost-effective, and highly precise.
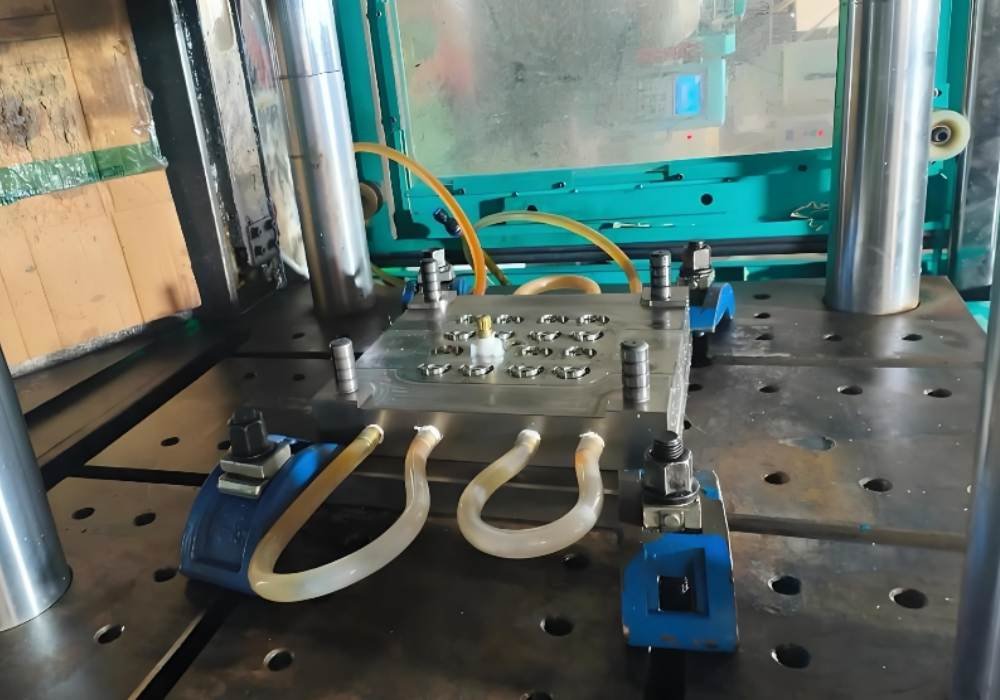
Process of Injection Molding
This process follows a few simple steps, including:
- Mold Creation: A custom metal mold is designed and made to shape the final product.
- Material Melting: Plastic or other materials are heated until they become liquid.
- Injection: The melted material is injected into the mold under high pressure while ensuring that it fills every detail.
- Cooling & Hardening: The material cools inside the mold and then takes the shape of the final product.
- Ejection & Finishing: Once hardened, the part is removed from the mold, trimmed, and polished if needed.
Common Applications of Injection Molding
It is used in many industries because of its speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, this process produces large volumes of parts with consistent quality. Below are some of the most common uses:
1. Automotive
Injection molding is used to make dashboard panels, bumpers, and interior parts in the automotive industry. These parts need to be strong, lightweight, and heat-resistant. Automotive plastics like ABS and polycarbonate are durable and help reduce vehicle weight, which eventually improves fuel efficiency. They’re a perfect choice for car manufacturers as they can produce parts in bulk.
2. Medical
The medical industry relies on injection molding for precise and sterile equipment. Items like syringes, IV components, and surgical instruments are produced using medical-grade plastics. Many FDA-approved materials, such as polypropylene and PEEK (Polyetheretherketone), are commonly used for it.
3. Plastic Parts
Many consumer products, packaging, and electronic parts are made using injection molding. As of 2024, the injected molded plastics market was valued at $335.4 billion globally. Due to low product cost, injection molding is a preferred choice for high-volume plastic manufacturing.
Advantages of Injection Molding
Here are some key benefits of the injection molding process:
1. High Volume Production
This process is perfect for mass production. Once the mold is created, millions of identical parts can be made with minimal defects. The cost per part decreases as production increases, making it a cost-effective solution for large orders. Injection molding is also fast, with some molds producing a single component in as little as 10–30 seconds.
2. No Limits on Part Size
There’s no limit to the part size you can produce with the injection molding method. However, small parts require precision, while large parts must be strong and lightweight. This is why most manufacturers use multi-cavity molds, as it allows them to produce several parts at the same time.
What is Additive Manufacturing? (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, is a process that creates objects layer by layer from a digital file. In this process, the parts are built from scratch.
Unlike injection molding, which requires pre-made molds, additive manufacturing allows on-demand production. This makes it faster and more flexible for custom designs and rapid testing.
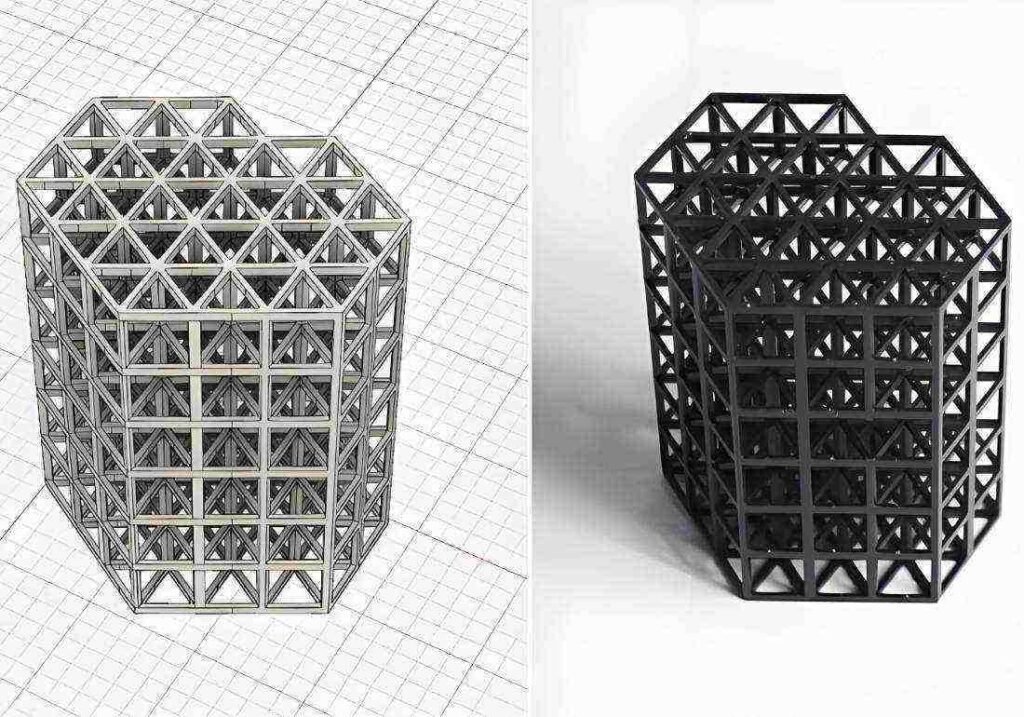
Process of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing follows a step-by-step digital process to create precise, high-quality parts. It includes:
1. Designing the 3D Model
Every 3D-printed part starts as a digital CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model. This design determines the final shape, dimensions, and structure of the object.
2. Preparing the Print File
The 3D model is converted into a printable format (STL or OBJ file). The software slices the model into thin horizontal layers, which creates a blueprint for the printer to follow.
3. Printing the Object
Once the 3D model is sliced into layers, the printing process begins. The printer deposits or solidifies material layer by layer until the final structure is formed. For this, several printing technologies are used, including:
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Uses heater thermoplastic filaments, which are deposited layer by layer. It is affordable, widely used, and great for functional prototypes.
- SLA (Stereolithography): Utilizes a UV laser to cure liquid resin, which creates highly detailed and smooth surface finishes. Best for dental, jewelry, and high-precision applications.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): In this, a laser is used to fuse powdered material (nylon, metal, or composites). It allows for strong, durable parts without support structures. Best for aerospace and industrial components.
4. Cooling and Post-Processing
After the object is printed, it needs to cool and solidify. Some parts require additional processing, such as:
- Polishing: To smooth out rough edges.
- Painting or Coating: Used to improve the surface quality of the parts.
- Heat Treatment: Strengthens the final product.
Common Applications of Additive Manufacturing
Some common applications of additive manufacturing process include:
1. Prototyping
Over 75% of manufacturers said 3D printing allowed them to make complex products, aka prototyping. Unlike traditional methods, which require expensive molds and long production times, 3D printing enables quick and low-cost prototype production.
2. Aerospace
The aerospace industry has embraced additive manufacturing because it can reduce weight and improve efficiency. NASA and Boeing use 3D-printed titanium and composite materials to create lightweight yet strong aircraft parts.
By using 3D-printed components, GE Aviation reduced jet engine weight by 25%. Additionally, SpaceX and Blue Origin use metal 3D printing to manufacture rocket nozzles and fuel injectors.
Advantages of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing offers significant advantages over traditional methods, including:
1. Minimal Time Setup
In contrast to CNC (Computer Numerical Control) or injection molding, 3D printing requires no molds, fixtures, or cutting tools. This empowers companies to lower their manufacturing cost by as much as 70%.
It also reduces setup time from weeks to hours, allowing for faster design iterations. So, if you’re from an industry that needs a quick turnaround time, additive manufacturing is the perfect solution.
2. Ideal for Complex Designs
Additive manufacturing allows geometries that traditional manufacturing cannot achieve. It creates a lightweight lattice structure for aerospace and medical implants, reducing weight while maintaining strength. Research shows that additive manufacturing also reduces material waste by up to 90%.
Injection Molding vs. Additive Manufacturing: Key Differences
The table below highlights the key differences between the two.
| Factor | Injection Molding | Additive Manufacturing |
| Manufacturing Method | Forms parts by injecting molten material into molds. | Builds parts layer by layer from a digital file. |
| Production Volume | Best for high-volume production (thousands to millions). | Ideal for low-volume or custom production. |
| Material Usage | Uses predetermined materials (mostly plastics & metals). | Works with various materials, including polymers, metals, etc. |
| Cost Considerations | High upfront mold cost, but low per-unit cost for large runs. | No mold is required, but higher per-unit cost for large production. |
Optimize Your Manufacturing: Utilize the Strength of Each Technique
Both injection molding and additive manufacturing serve the same purpose—creating parts. However, they are fundamentally different in how they do it.
If you need large-scale, durable, cost-efficient parts, use injection molding. However, if you’re looking for highly customized, or intricate designs, additive manufacturing should be the go-to choice.
Fecision offers molding services to help you create designs easily. Contact us today to discuss your manufacturing needs and get a quick quote.




