Selecting the appropriate molding technique affects your production speed, cost, and product quality. Choosing the incorrect approach can result in wasted money and time. Two well-known choices are injection molding and compression molding, which operate differently and serve distinct needs. You might be wondering which is more appropriate for your project.
The answer depends on your design, material, and budget. This guide will cover the primary distinctions between injection molding and compression molding, including their advantages, drawbacks, and associated expenses. You will know which approach best suits your needs by the end of the conclusion. Let’s dive in and compare these two molding processes step by step.
What Is Injection Molding?
One technique called injection molding forces molten material under pressure into a mold cavity. The mold shapes the substance as it cools and hardens.
Step-by-Step Process
- Heat plastic pellets until molten
- Inject the melted material into a steel or aluminum mold
- Cool and solidify inside the cavity
- Open the mold and eject the part
Injection molding can produce thousands or millions of identical parts due to its quick cycle times.
Applications and Industries
Where accuracy and consistency are crucial, injection molding is widely utilized. You can observe it in:
- Medical device components
- Automotive interior and exterior parts
- Electronic housings and connectors
- Consumer products like toys and appliances
Injection molding is a great option if your project calls for precise tolerances and seamless finishes.
What Is Compression Molding?
A process that involves heat and pressure to shape material within a mold is known as compression molding. Before compression starts, a pre-measured material is placed into the mold cavity.
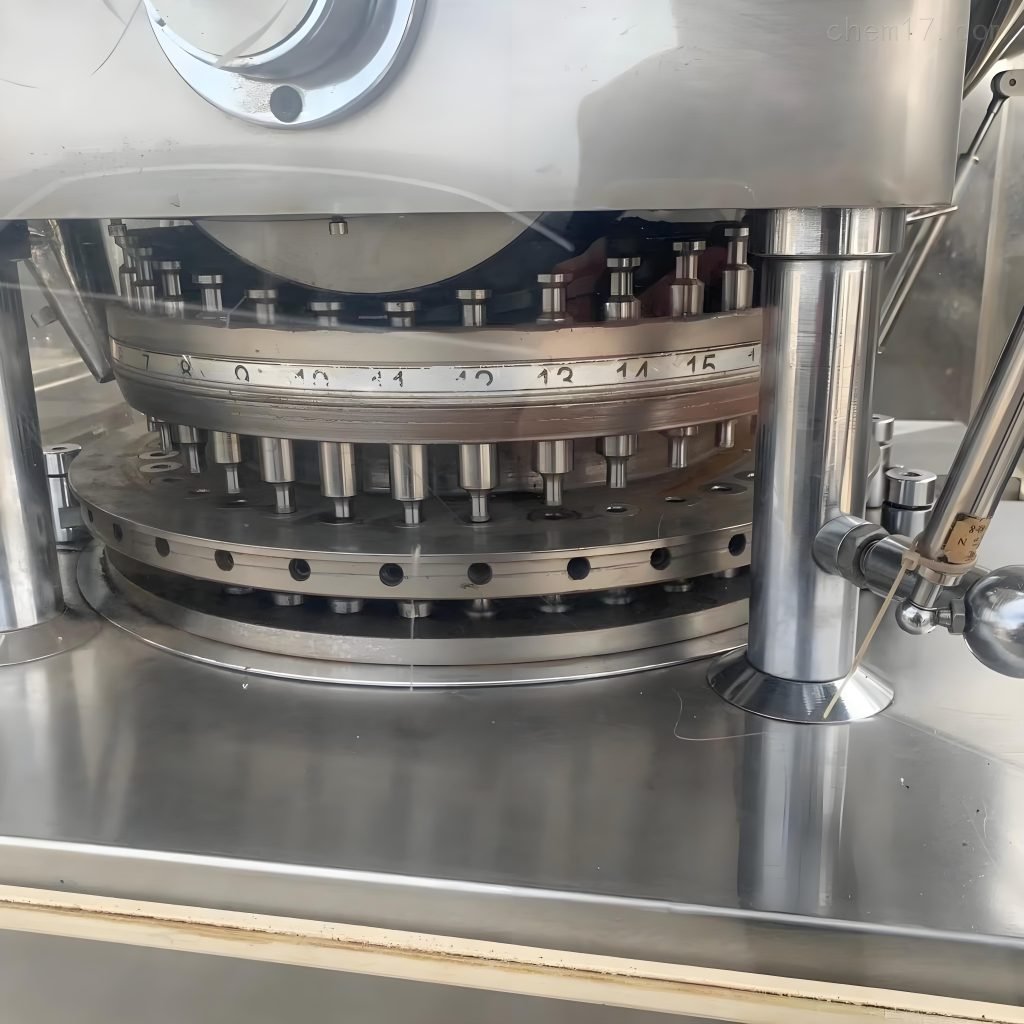

Step-by-Step Process
- Place a preheated charge or raw material into the mold cavity
- Close the mold and apply pressure
- Heat and pressure cure the material
- Open the mold and remove the part
Because curing takes time, cycle times are longer than with injection molding. Nonetheless, the procedure produces incredibly robust, long-lasting parts.
Applications And Industries
Heavy-duty industries extensively utilize compression molding. Typical applications consist of:
- Automotive parts like bumpers, gaskets, and brake components
- Aerospace structural parts requiring strength under stress
- Electrical housings and insulation products
- Industrial machinery components
When durability and strength are more important than fine details, this approach is recommended.
Compression Molding vs Injection Molding: Key Differences
With both processes explained, it’s time to compare them side by side for clarity.
| Aspect | Injection Molding | Compression Molding |
| Process | Inject molten material into the mold cavity | Press material in a heated mold under pressure |
| Speed | Fast, ideal for mass production | Slower cycle times |
| Tooling Cost | High due to complex mold design | Lower cost molds |
| Cost per Part | Low for large volumes | Higher for very large runs |
| Design Complexity | Excellent for intricate shapes | Limited, best for simple parts |
| Material Type | Thermoplastics and some thermosets | Thermosets and composites |
| Best For | High-volume, precise parts | Large, strong components |
This table gives you a quick snapshot. Each method has strengths, so the choice depends on your priorities.
Which Is Better for Complex Shapes?
Once you know the general differences, the next question is about handling intricate designs and details.
Injection Molding For Precision

For complex components, injection molding is the better option. It easily manages fine details, thin walls, and complex geometries. Tight tolerances ensure consistent precision; the smooth surface finish often eliminates the necessity for additional polishing.
Compression Molding Limitations
Compression molding is less suited for detailed features. Although it offers strength, it lacks the accuracy of injection molding. For thicker, more robust components that emphasize durability over sophisticated design, this process is best suited.
Compression vs Injection Molding Cost Comparison
Beyond shape and design, cost plays a major role in selecting the right molding method.
Tooling Cost Differences
Often created from hardened steel or aluminum, injection molding demands costly molds. Large manufacturing runs fit it since the high tooling cost makes it perfect. Lower initial expenditure can result from the use of compression molding’s simpler, less expensive tooling.
Material Waste, Energy, and Efficiency
Injection molding can generate waste from runners and sprues, but recycling is a viable option. At scale, it is energy-intensive but extremely effective. Although compression molding generates less waste, its longer cycle time per unit limits efficiency in large-scale projects.
When Each Method Is Cost-Effective
When you require millions or billions of pieces, injection molding starts to save money. For smaller batches or large, robust parts that do not require exacting accuracy, compression molding is preferable. Understanding the cost of compression molding versus injection molding is key because it reveals how volume and tooling investment influence the best choice.
Design and Material Considerations
After costs, materials, and design factors become the next deciding elements in the selection process.
Material Compatibility
Thermoplastics, which can be melted and reshaped, are the primary material used in injection molding. Thermosets and composites, which cure permanently when heated and compressed, are the main focus of compression molding. The process is frequently determined by the materials you choose before other considerations are made.
Strength vs Detail
- Injection molding excels at precision and detail.
- Compression molding offers superior strength and heat resistance.
Consider whether your component needs to display fine details or withstand stress. It helps in identifying the superior choice.
Which Process Is Best for Your Project?
Finally, let’s bring everything together and see how to decide for your specific situation.
Decision-Making Factors
Evaluate your project with four key factors:
- Production volume
- Material selection
- Design complexity
- Total cost
Injection molding is frequently preferred for high-volume projects. Compression molding is typically superior for parts made from thermoset composites or for low-volume runs. Maintaining equilibrium between these variables guarantees that the procedure aligns with your financial and technical objectives.
When to Choose Each Method
Choose injection molding when:
- Your design has complex shapes
- You require tight tolerances and smooth finishes
- You plan mass production
Choose compression molding when:
- You need thick, durable, or heat-resistant parts
- Your batch size is smaller
- Material is a thermoset or reinforced composite
Consulting Experts
Consider part size, material, and budget constantly. Selecting the correct option costs time and money. Seek specialist assistance if you have any doubt. Fengchi helps you make informed choices and provides high-quality results through mold manufacturing and CNC machining services.
Conclusion:
Volume, budget, and component design determine whether injection molding or compression molding is the preferred process. Injection molding is ideal for achieving high accuracy and large-scale production. Select compression molding if you want strength and lower tooling costs.
Still unsure? Let Fecision show you. We enable you to achieve the ideal balance of quality, cost, and speed by combining expertise in CNC machining and mold manufacturing. Contact us immediately to start with the ideal molding solution tailored to your requirements.




