Injection molding is one of the fastest and most efficient manufacturing processes, but its exact time depends on several factors. From material selection to mold complexity, cycle times can range from a few seconds to several minutes.
So, in this article, we’ll break down how long does injection molding take, the key factors that impact injection molding time, and what you can expect. Let’s get into the details!
Understanding the Injection Molding Production Time
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process. It enables the mass production of plastic parts with high precision and efficiency. A crucial aspect of this process is the cycle time, which directly influences production rates, costs, and overall efficiency.
On average, injection molding takes between 30 seconds to 2 minutes per cycle, depending on the material, mold complexity, and machine settings. However, the exact duration varies based on several factors which we’ll discuss ahead.
But first, let’s discuss the different stages of the injection molding process.
The Cycles of Injection Molding Process
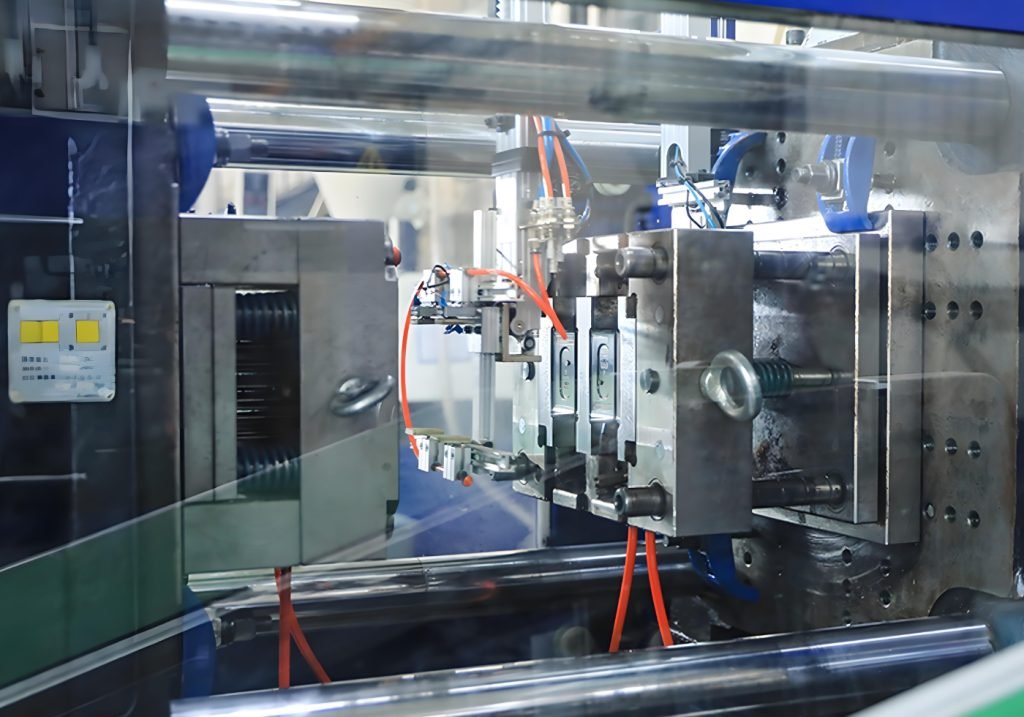
Injection molding is a step-by-step manufacturing process where plastic is melted, injected into a mold, cooled, and then ejected as a final product. Here’s how the whole process works:
1. Mold Opening and Closing Time
The injection molding cycle starts with mold opening and ends with its closing. On average, this takes about 2 to 5 seconds per cycle. In this phase:
- A hydraulic or electric press controls the mold’s movement, which ensures precision and repeatability.
- The time taken for the mold to open and close depends on the machine’s speed, mold size, and complexity.
- Well-maintained molds with proper lubrication reduce friction and minimize time delays.
2. Clamping Time
Once the mold closes, the clamping unit applies pressure to keep it tightly shut during injection. This is known as the clamping time and is crucial for preventing material leakage. The clamping force must be strong enough to resist the internal pressure of injected parts, especially the larger ones.
However, excessive clamping force can wear down the mold, while insufficient force may lead to defects like flash (excess plastic on the edges of the part).
For this reason, advanced machines use servo-driven clamps to optimize force application and reduce cycle time. On average, this process only takes 1 to 3 seconds.
3. Injection Time
The injection phase is when molten plastic is forced into the mold cavity. This is one of the most critical steps as it determines the part’s shape, accuracy, and structural integrity.
You might think the faster the injection time, the better it is. However, excessive speed can cause defects like short shots (incomplete parts) or warping.
A slower, controlled injection is recommended as it leads to better filling and part quality. Generally, this step takes about 0.5 to 2 seconds.
4. Pressure Holding Time
Once the mold is filled, the machine enters the pressure-holding phase, also called the packing phase. This stage ensures that the part maintains its shape and avoids shrinkage or voids (internal air pockets).
The molten plastic inside the mold shrinks naturally as it cools, so additional pressure is applied to push more material into the mold and maintain proper dimensions.
This phase takes about 2 to 5 seconds to complete.
5. Cooling Time
Cooling time is one of the most important and the longest phases in the injection molding process, taking up to 120 seconds. This phase allows the molten plastic to solidify into its final form before being removed from the mold.
Cooling begins as soon as the plastic touches the mold walls and continues until it reaches a stable, solid state.
It accounts for 50% to 80% of the entire cycle, so reducing this phase without compromising the part quality is the key to improving overall efficiency.
6. Ejection Time
When the part is fully cooled and solidified, it must be ejected from the mold. The ejection time determines how quickly this step is completed without damaging the part.
Ejection itself is done using pins, air blasts, or mechanical plates that push the part out of the mold. If the ejection time is slow, it prevents warming or part deformation, especially with delicate materials. This step only takes about 1 to 2 seconds to complete.
A well-designed mold ensures that parts release smoothly and prevents sticking or misalignment. Ejection aids like mold release coatings help reduce friction and improve cycle efficiency. It is an important step for safely removing the part, and preparing the mold for the next cycle.

Factors Affecting Injection Molding Lead Time
Factors that could affect the overall injection molding time include:
1. Mold Design Parameters
Some mold design parameters that you should keep in mind:
- Cooling System: Cooling is the longest phase in the injection molding cycle. By having a well-designed cooling system, you can speed up production by ensuring even heat dissipation.
- Runner and Gate: It controls how molten plastic flows into the mold. Smaller, optimized gates can reduce material waste and speed up part filling. Moreover, the hot runner system reduces lead time and eliminates solidified plastic waste.
- Number of Cavities: Molds with multiple cavities can produce several parts simultaneously, reducing total cycle time per unit. However, more cavities require higher clamping force and precise mold balancing.
2. Part or Product Design Requirements
Parts or product design requirements can also affect injection molding time:
- Processed Part Size: Larger parts require more material and longer cooling times, which increases lead time. In contrast, thinner and lighter designs help shorten cycle times without compromising strength.
- Product Structure: Complex shapes, undercuts, and thick walls extend the molding process. However, simplified designs reduce material flow challenges and cooling inefficiencies, and lead to faster production.
3. Injection Molding Machine Performance
The machine’s speed, clamping force, and precision affect lead time. Advanced machines with optimized injection pressure, automated controls, and real-time monitoring can significantly reduce delays. So, if you want smooth operation and consistent quality, make sure to use the right machine size for the part.
4. Materials
Here’s a general calculation for cooling times based on material type and thickness.
| Material | Thickness (mm) | Cooling Time (Seconds) |
| ABS | 2 | 10–20 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 2 | 8–15 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 2 | 12–25 |
| Nylon (PA) | 2 | 15–30 |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | 2 | 8–18 |

How to Optimize Injection Molding Cycle Time
If you want to optimize the molding cycle time, here’s what you need to do.
- Injection Phase: Carefully adjust injection speed, apply slightly higher pressure for complex mold, and design gates to ensure even material flow.
- Cooling Phase: Use efficient cooling channels as they help dissipate heat faster, select fast-cooling polymers to minimize wait time, and maintain an optimal mold temperature to prevent warping.
- Ejection Phase: Proper ejection methods like pins and air blasts speed up removal, mold release agents reduce friction, and polished or coated surfaces prevent sticking.
- Mold Closing Time: High-speed clamping units accelerate the process, automated mold alignment prevents delays, and regular lubrication keeps moving parts running smoothly.
- Improving Equipment Accuracy: Get assistance from high-precision machines to enhance efficiency, monitor the process in real-time to detect inconsistencies and schedule routine calibration to ensure consistent performance.
- Choose Good Quality Molds: Try out hardened steel molds as they last longer, schedule regular maintenance to prevent defects, and design parts with minimal sharp corners and thick walls to reduce cooling time.
Reduce Your Injection Molding Cycle Time and Optimize Production
So, how long does injection molding take? About 2 minutes depending on what you’re manufacturing. However, you can optimize the injection molding cycle time further which could eventually lower the production costs and produce better-quality parts.
Small improvements in injection speed, cooling efficiency, ejection methods, and mold design can make a big difference.
So, start refining your process today and see the impact on your production.




