Let’s first take a look at EPDM rubber, a well-known material in various sectors. Its excellent performance characteristics have made it highly sought-after. EPDM rubber has truly earned its place as a top-tier material in industries such as automotive and construction. It stands out because it can withstand extreme heat, has remarkable resistance to UV rays, and can last for decades without showing signs of cracking.
When it comes to the manufacturing process, engineers often face the challenge of mass-producing parts like intricate seals or vibration dampers. This is when a common question arises: Can EPDM rubber be used in injection molding?
The short answer is yes. In the past, compression molding was the popular choice. However, modern injection molding technology now enables manufacturers to shape EPDM into complex designs more quickly and cost-effectively.
What Is EPDM Rubber Injection Molding?
This process starts by heating EPDM pellets until they melt into a thick, flowable liquid. The molten rubber is then forced under high pressure into a steel mold, where it vulcanizes (cures) into its final shape. Think of it like baking a cake—the mold is the pan, and the vulcanization step is the oven setting that turns batter into a solid treat.
• Recipe Tweaks: Skip the standard EPDM pellets. Blending in 20-30 phr (parts per hundred rubber) of carbon black isn’t just for color—it’s the “glue” that stops the mix from tearing mid-flow. Pro tip: Some shops swear by adding a dash of paraffin oil to keep the compound “slippery” in the barrel.
• Temperature Tightrope: 170°C is the sweet spot. Go lower, and the rubber stiffens like cold syrup, leaving voids. Go higher, and it scorches, stinking up the workshop with that burnt-toast smell operators hate.
• Mold Hacks: Polish those cavities to mirror shine. Even a 0.1mm roughness can make EPDM grip the mold like Velcro. Bonus move: Add 2° draft angles—it’s the difference between parts popping out clean or snapping your ejector pins.
EPDM rubber injection molding isn’t magic—it’s more like baking bread. Control the variables, and you’ll churn out parts that last longer than the machinery making them. Just don’t expect perfection on the first try.
Can EPDM Rubber Be Injection Molded?
Yes! How can you injection mold EPDM? Here’s how EPDM Rubber works in real production and EPDM injection molding process.
Step 1: Dry the Rubber Pellets
Workers put EPDM pellets into drying ovens. This takes 1-2 hours at 80°C.
Step 2: Mix in Special Ingredients
Next, they add sulfur powder (like adding yeast to bread dough) and color pigments. A car engine hose might need black pigment, while a bathroom seal could use white.
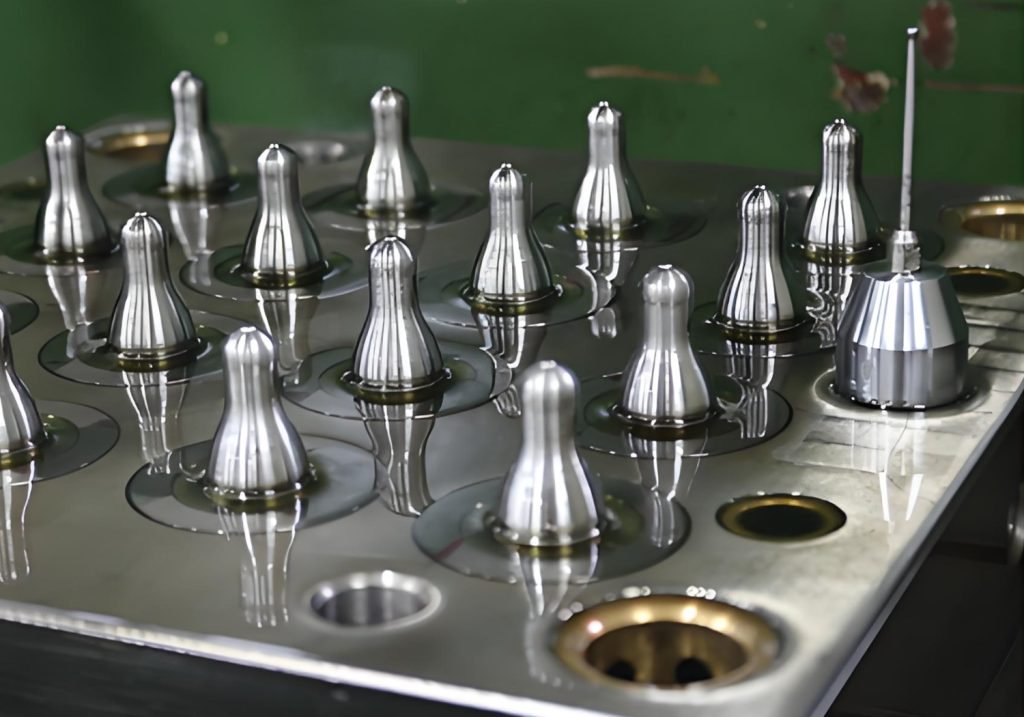
Step 3: Build the Steel Mold
Engineers cut molds from steel blocks using CNC machines. For a car window seal, the mold has precise curves. Tiny air vents (0.1mm wide) let trapped air escape – just like poking holes in plastic wrap before microwaving!
Step 4: Melt and Inject
The machine heats rubber to 100°C – hot enough to melt it but not burn. The pressure pushes the sticky liquid into mold gaps. Simple parts need 20 MPa pressure (like a car tire pump), but detailed parts like radiator hoses require 150 MPa (10x stronger!).
Step 5: Cook the Rubber
The mold heats to 180°C for 5 minutes. Sulfur makes rubber molecules link together, like eggs solidifying when fried. Thicker parts (e.g., truck suspension bushings) need longer cooking.
Step 6: Cool and Remove
Workers spray water to cool the mold to 50°C. Then hydraulic arms push out the part. Ever seen silicone ice cubes pop out? It works similarly!
Step 7: Trim and Check
Using sharp blades, they cut off extra rubber edges (called “flash”). Inspectors test parts – a good door seal should stretch 300% without tearing.
Why This Works?
EPDM’s heat resistance makes it perfect for engine parts. The process combines material science (sulfur curing) and engineering (high-pressure injection). Compared to plastic molding, EPDM needs lower temperatures but longer curing time.

Types of EPDM Injection Molding Techniques
EPDM rubber uses 4 main injection methods depending on product needs. Here’s how factories choose between them:
1. Compression Molding
Process: Pre-heated EPDM is placed in an open mold, and then pressed until cured.
Best for: Thick parts like truck engine mounts.
2. Injection Molding
Process: Melted EPDM is injected into closed molds under high pressure.
Best for: Complex parts with details (e.g., radiator hose connectors.
Key fact: Uses 20-150 MPa pressure, higher than compression molding.
3. Transfer Molding
Process: Rubber is heated in a chamber, and then forced into the mold through a narrow gate.
Best for: Precision parts like medical device gaskets.
Why?: Reduces air bubbles compared to standard injection.
4. Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Co-Molding
Process: Injection molding EPDM and silicone are molded together in one cycle.
Best for: Hybrid parts needing heat resistance (e.g., car headlight seals.
| Technique | Common Products |
| Compression | Thick seals, shock pads |
| Injection | Hoses, detailed gaskets |
| Transfer | Medical parts, O-rings |
| LSR Co-Molding | Heat-resistant hybrids |
Why These Methods Work
Compression: Cheap for simple designs but slower.
Injection: Faster and better for thin walls (e.g., 1.5mm waterproof sheets.
Transfer: Less waste material – critical for expensive medical grades.
LSR Co-Molding: Combines EPDM’s UV resistance with silicone’s flexibility.
Why EPDM Injection Molding?
EPDM injection molding dominates industries like automotive and construction for 5 key reasons:
1. Heat Resistance That Saves Money
EPDM handles 150-200°C mold temperatures–perfect for engine gaskets exposed to exhaust heat. Unlike silicone (costs 3x more), EPDM parts last 5+ years in hot environments.
2. Waterproof Like a Duck’s Feather
The rubber’s closed-cell structure blocks water absorption. Car door seals made this way pass 100,000+ door slam tests without leaks. Boat hatch gaskets have survived saltwater storms for decades.
3. Chemical Fighter
Gasoline spills? Battery acid? No problem. EPDM resists 90% of automotive fluids. Mechanics prefer it over nitrile rubber (swells in oil) for fuel line connectors.
4. Fast Production, Less Waste
One mold makes 500+ parts/day. Compare this to compression molding (200/day). Scrap rates below 2% thanks to precise pressure control (20-150 MPa).
5. Easy to Customize
Add 30-70% carbon black for UV-resistant roof seals. Mix in clay fillers for soft HVAC dampers. Even color options – white for medical devices, red for fire-resistant cables.
What Rubber Parts Can Be EPDM Injection Molded?
EPDM rubber’s heat resistance and durability make it ideal for these 5 common injection-molded products you see every day:
1. Automotive Seals & Hoses
Door/window seals – Soft EPDM prevents rain leaks (used in 90% of cars.
Radiator hoses – withstand engine heat up to 150°C.
Example: A Toyota Corolla’s door seal uses EPDM 60 durometer grade.
2. Building Waterproofing
Window/door seals – Lasts 10+ years in sun and rain.
Roofing membranes – Survive -40°C to 120°C temperature swings.
3. Appliance Components
Washing machine door gaskets – Flexible enough for 10,000+ door closings.
Refrigerator insulation seals – Blocks cold air leakage effectively.
4. Sports & Playground Surfaces
Running track layers – EPDM granules absorb foot impacts (like school tracks.
Gym equipment grips – Non-slip even with sweaty hands.
5. Industrial Parts
Chemical tank seals – Resists acids like H₂SO₄.
Electrical wire coatings – Stops short circuits in underground cables.
Why Choose EPDM?
Unlike silicone (costs 3x more) or natural rubber (rots in water), EPDM:
✔ Handles -50°C to 160°C
✔ Absorbs vibrations (car suspension bushings
✔ Non-toxic (safe for playgrounds
Pro tip: For food-grade parts (e.g., juicer seals), use peroxide-cured EPDM to avoid sulfur odors.
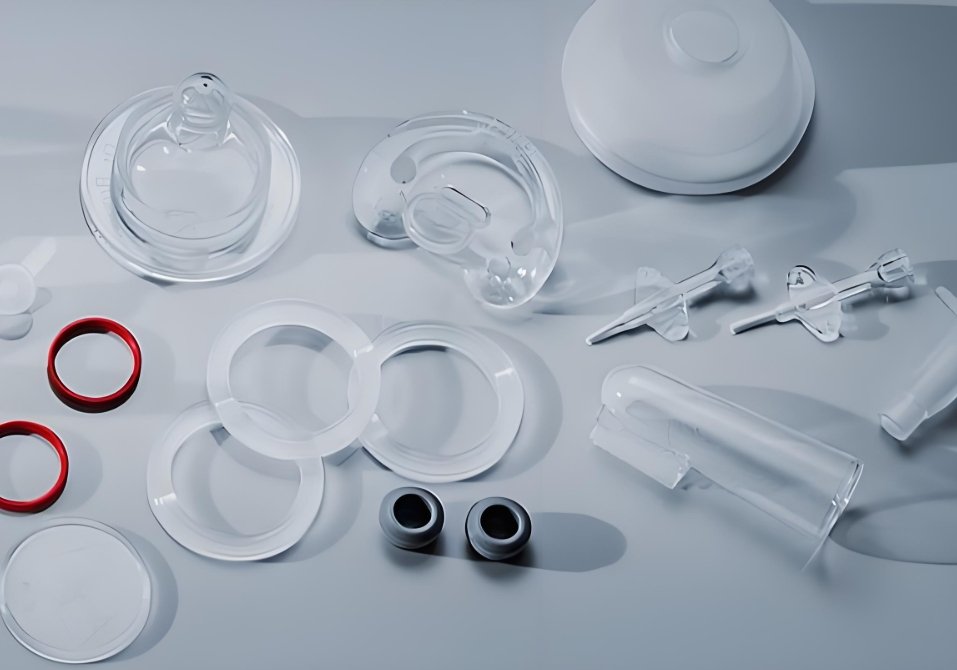

Work with a Trusted Custom Rubber Parts Supplier for Your Molding Needs
When creating high-performance rubber parts like EPDM seals or automotive hoses, choosing the right partner matters. Imagine baking a cake without a reliable oven—temperature fluctuations or poor molds ruin the result. Similarly, injection molding EPDM rubber demands precision at every step. This is where Fecision, a trusted manufacturer, steps in to turn complex designs into durable, real-world solutions.
Why Fecision Stands Out
- Tailored Material Expertise
Fecision adjusts EPDM formulas like a chef perfecting a recipe. They blend carbon black to prevent tearing during injection and add paraffin oil for smooth flow—just as the article describes. Need UV-resistant roofing seals or soft HVAC dampers? Their team customizes compounds without guesswork.
- Precision Mold Engineering
Using CNC machines, Fecision crafts molds with mirror-like finishes and air vents to eliminate trapped air. For car window seals, their molds include draft angles, ensuring parts are released cleanly—no snapped ejector pins or delays.
- Temperature Control Mastery
Sticking to the “sweet spot”, Fecision avoids scorched rubber or incomplete fills. Their process mirrors the article’s guidelines, ensuring parts are cured properly, whether thin sheets or thick bushings.
- Rigorous Quality Checks
Like testing a door seal’s 300% stretch limit, Fecision trims flash and validate every part. Their scrap rate stays very low, thanks to pressure controls and real-time adjustments.
Your Project, Their Promise
From automotive engine mounts to medical-grade gaskets, Fecision’s injection molding solutions combine material science with engineering rigor. They don’t just mold rubber—they build partnerships, ensuring your parts outlast the competition. Now click and get more information.