Whether in the aerospace or automotive industry, complex plastic components like gears and brackets are essential for different applications. But have you ever wondered how these intricate parts are manufactured with such precision? The injection molding process is the answer!
Nowadays, injection molding machines are almost everywhere, enabling businesses to mass produce different plastic components efficiently. That’s the reason their market size is quickly growing and is expected to hit a massive USD 12.4 billion by 2027.
If you want to learn more about the injection molding process, its materials, benefits, limitations, and applications, continue reading.
Basics of Injection Molding Design
The injection molding design plays a critical part in the overall functionality and quality of the desired product. So here are the basic design tips that you must follow to ensure the manufactured components have high strength and withstand chemical and mechanical stress:
Right Materials
Know that different materials offer varying characteristics like strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. You should pick the ones that perfectly match the requirements of the application.
For this, it’s important to consider the melt flow rate, shrinkage, and warpage of the material, along with mold compatibility.
Semi-crystalline resins are a good example due to their excellent chemical and electrical resistance and lower thermal friction.
Wall Thickness
Another basic injection molding design tip is to maintain uniform wall thickness for consistent cooling and minimize the risk of warping. For example, most products or applications require a wall thickness of 1.5 mm to 2.5 mm, but you should also refer to the recommended wall thickness of the material you are working with.
Undercuts
It’s a good idea to avoid undercuts if you want to minimize your design costs and make sure your materials are taken out from the mold without any damage. However, if undercuts are necessary, like in snap-fit designs, you can use side actions or lifters.
Ribs and Gussets
You can add ribs and gussets instead of increasing the wall thickness of plastic parts to give them additional strength and maintain their structural integrity. They lower the risk of cosmetic defects like sinks, voids, and warping. It’s suggested that keeping rib thickness around 50% to 60% of that of a wall can reduce warping greatly.
Gating
Gatings refer to small openings in the mold that let hot plastic enter the mold cavity. It controls the flow of plastic that moves to the mold, ensuring that the final product offers good performance and high quality. Typically, a direct sprue gate is used to introduce molten plastic into the mold during the injection molding process.
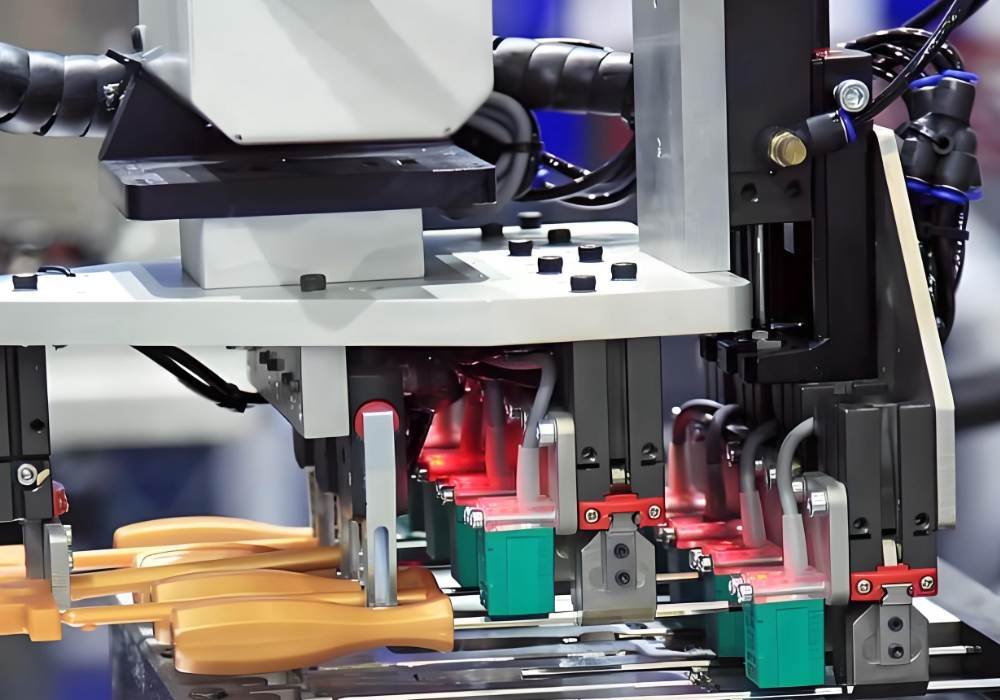

How Injection Molding Works?
The working of injection molding is pretty straightforward; the material, whether it’s plastic, elastomer, or metal, is injected into a heated barrel and mixed using a screw.
Once the heating bands heat the material and convert it into molten form, it’s moved to the mold, typically made of metals like aluminum or steel and divided into two halves.
There, the material cools down and hardens, taking the shape of the mold. After completely hardening, the manufactured part is ejected by opening both sides of the mold.
Different Types of Injection Molding Processes
To properly understand the workings of injection molding, learning about different types of processes is important. If so, here are some of them:
- Two-Shot or Multi-Shot Injection Molding: As the name implies, two-shot or multi-shot injection molding is a process in which you combine and convert two materials, like plastic resins, into a single component or part. It’s a cost-effective technique to produce multi-color and multi-functional industrial components.
- Gas-Assisted Injection Molding: In this process type, inert gases like nitrogen are added into the mold cavity that pushes the plastic against mold walls until it solidifies. It results in a better surface finish and gives a fine texture to the end product.
- Insert Molding: It’s a process in which the preexisting part or insert (any plastic or metal component) is combined with a second layer of plastic or some other material to create a strong bond and eliminate the need for adhesives.
Injection Molding Materials
These are the variety of injection molding process materials used to create different components:
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene: ABS is a durable thermoplastic material with incredible impact resistance and a melting point of 190 °C to 220°C. It’s also quite lightweight and is used for manufacturing pipes and other automotive parts via the injection molding process.
- Nylon: Nylon is another injection molding material that’s naturally water and abrasion-resistant. It can be used to manufacture different components like car tires and insulators.
- Polyoxymethylene: It’s also known as acetal polyacetal. It’s perfect for manufacturing precision parts requiring high stiffness. Polyoxymethylene is used in automotive parts, zippers, and fan wheels.
In addition, some other materials like metals (e.g., zinc due to its excellent casting properties) and ceramics are also employed in the injection molding process.
Options for Surface Finishing
There are multiple surface finishing options in the injection molding process, like Grade A (glossy finish), Grade B (semi-glossy finish), Grade C (matte finish), and Grade D (textured finish). Let’s have a look at all of them:
| Finish | SPI Standard | Definition | Materials |
| Glossy Finish | A | Highly polished surface that’s achieved using diamond buffing | Acrylic, PC |
| Semi Glossy Finish | B | Smooth finish with a slight reflection that’s achieved using sanding | ABS, HDPE, Nylon, PP, Polystyrene |
| Matte Finish | C | Low reflection finish having a dull and non-glossy appearance | ABS, HDPE, Nylon, PP, Polystyrene |
| Textured Finish | D | A rough surface has texture and patterns, which are achieved using abrasive blasting. | ABS, HDPE, Nylon, PP, Polystyrene, TPU |
3D Printing vs. Injection Molding
Both 3D printing and injection molding are used to create physical components that can be used in different industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace. However, they have key differences:
- 3D printing relies on additive manufacturing, where materials are layered one over the other to build a part. On the other hand, the injection molding process involves melting material and then injecting it into a mold to get the desired product.
- Compared to injection molding, 3D printing is suitable when you need a quick turnaround time, like 1 to 2 weeks. On the other hand, injection molding has a longer turnaround time, typically ranging from 5 to 7 weeks.
- 3D printing is viable for low-volume production and manufacturing of simpler parts. Contrarily, injection molding can design complex parts at high volumes.

Benefits & Limitations of Injection Molding
Now, let’s explore the many benefits and limitations of the injection molding process:
Benefits
- High and Efficient Production: Once the molds are developed and set up, the cycle time is about 10 seconds. Depending on the type of mold you are using, you can easily produce 10,000 to 100,000 units.
- Versatility: Injection molding isn’t just limited to one type of material; instead, you can use a variety of plastics like ABS, Nylon, and other metals or even ceramics to create a variety of parts.
- Low Waste: Manufacturing waste is quickly polluting the environment, but in injection molding, you don’t have to worry about this! This process results in very little waste; even if there’s any, you can recycle it to create more components.
Limitations
- Design Restrictions: It’s quite difficult to achieve certain shapes or designs like thin walls or sharp corners, and it can take a lot of time.
- High Initial Cost: Getting the whole injection molding facility ready can be cost-intensive. Especially the molding tool, which is the primary piece of the injection molding machine, demands a lot of manpower, time, and materials, which add up to the overall cost.
Factors Influencing The Cost of Injection Molding
There are certain factors that may impact the cost of the injection molding process, so you should be aware of them to save money. Here are some of these:
Size
Firstly, the size of the component or part greatly affects the overall injection molding cost. For instance, larger parts require more expensive molds, thus increasing the molding price. In contrast, smaller components require fewer materials and smaller molds, so they are budget-friendly.
Mold Material
The mold material you are using is also a deciding factor in the cost of injection molding. For example, if you opt for low-quality aluminum molds, they are less expensive but not as durable. But if you seek long-lasting molds made of expensive materials like hardened steel, the initial cost will increase.
Complexity
Know that the more intricate the design of a component, the more difficult it is to produce and the higher the cost. You may have to add lifters or undercuts as well as maintain a particular wall thickness, which can be quite costly.
Standards & Certifications
Here’s a list of standards and certifications that are used in the injection molding processes and industry:
- ISO 13845 for Medical Industries
- Automotive Injection Molder Certification (IATF 16949:2016)
- International Traffic in Arms Regulations, Registration, and Compliance (ITAR)
- American School of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Certifications
Common Items Manufactured through Injection Molding
If you are wondering what items can be manufactured via the injection molding processes, here’s the answer:
- Bottle caps and other everyday items like toys, Jewels, etc.
- Medical devices such as catheters, syringes, and needles
- Automotive components like bearings, gears, dashboard switches, and knobs
- Electronic components, including buttons, switches, insulators
Conclusion
The injection molding process is incredible for manufacturing durable plastic and metal components that are used in different applications. If you want injection molding services for your manufacturing business, contact Fecision and make your production smooth and cost-effective!




