Injection molding is a popular manufacturing method for creating plastic parts quickly and accurately. It is vital in producing everyday products, from household goods and automotive parts to medical equipment and electronic devices.
A key factor in this process is the flow of molten plastic into the mold cavities. Poor flow can lead to defects, waste material and longer cycle times, which increase production costs. Enter the Hot Runner system, a modern solution to optimize the injection mold process by reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
Hot Runner in injection mold applications has become very popular in high volume manufacturing where precision, speed and material efficiency are key. This article will explain how hot runners work, their components, benefits and when they might not fit in a manufacturing setup.
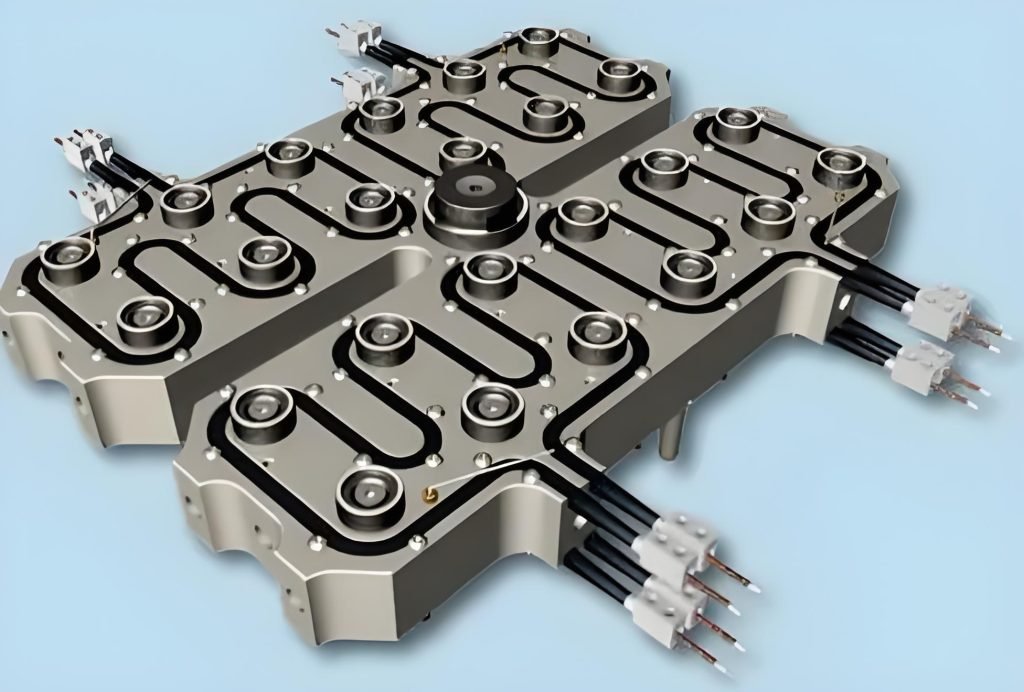
What is a Hot Runner System in Injection Molding?
A hot runner system in injection molding is a heated component system that injects molten plastic directly into mold cavities. It consists of a heated manifold and nozzles that keep the plastic in a liquid state as it flows from the injection machine to the mold. Unlike conventional cold runner systems, hot runner systems keep the material in a molten state within the runners, which eliminates plastic waste and shortens cycle times.
These systems are commonly known as runnerless molding systems. First introduced in 1963 by Mold-Masters Ltd, hot runner systems have become essential for efficient, fast and cost effective plastic manufacturing especially in high volume production environments. They improve part quality, minimize post processing and overall mold performance.
Types of Hot Runner Systems
Hot runner systems come in several types, each designed to meet specific molding requirements based on part size, material properties and gating preferences.
- Pinpoint-Style (Hot Tip) Systems: Ideal for molding smaller parts, pinpoint or hot tip systems create a small vestige – typically between 0.005″ to 0.020″, on the finished part. These systems offer direct gating, commonly used when minimal gate marks are acceptable.
- Sprue-Style Systems: Sprue-style hot runners form a small sprue on the part or runner. This type is useful when direct gating to the part isn’t feasible. It’s a reliable option for general applications that require a centralized material flow.
- Valve Gate Systems: It is designed for applications that require high precision and surface quality, valve gate systems leave no vestige on the molded part. They are ideal for processing challenging materials like glass filled nylon. Valve gate nozzles provide excellent control over material flow for consistent high quality results.
Hot runner vs cold runner systems
Understanding the difference between hot runners and cold runners is key to choosing the right molding strategy:
| Feature | Hot Runner System | Cold Runner System |
| Plastic Flow | Maintained in molten state | Solidifies in the runner |
| Material Waste | Minimal (no solid runners) | High (runners must be trimmed and recycled) |
| Cycle Time | Shorter due to faster flow | Longer due to solidification and ejection |
| Mold Complexity | Higher initial cost and design complexity | Simpler and cheaper to implement |
| Maintenance | More complex and costly | Easier and less expensive |
While hot runner systems offer better performance and material efficiency, they require more complex setup and maintenance. Cold runners are simpler and more economical but generate material waste and require more post processing.
How Does a Hot Runner Work?
Understanding how a Hot Runner works will explain why it’s such a game changer in plastic molding.
Step 1: Material Melting
Plastic pellets are fed into the barrel of the injection molding machine, where they are melted using screw driven friction and barrel heaters. Once melted the plastic is pushed into the Hot Runner system via the machine nozzle.
Step 2: Entry Into the Manifold
The molten resin enters the heated manifold, typically through a centrally located locating ring that aligns the mold with the machine’s nozzle. This entry point is critical for proper sealing and balanced pressure distribution.
Step 3: Distribution Through the Manifold
The manifold evenly distributes the molten material to several nozzles. The manifold design ensures balanced flow paths. Each cavity gets the same volume of material at the same pressure and temperature.
Step 4: Gate Injection
Plastic reaches the nozzles, which then inject the material into the mold cavities through precision designed gates. Depending on the nozzle type (hot-tip or valve gate), the system may either allow continuous flow or use mechanical valves to control fill timing.
Step 5: Cavity Filling and Part Formation
The plastic fills the mold cavity, which is cooled by water channels to solidify the part. Importantly the runner system remains hot and ready for the next shot as soon as the part is ejected.
This parallel processing, cooling the part while preparing the next shot, reduces cycle time.
Hot Runner System Components
The quality and design of the hot runner system components directly impact manufacturing efficiency and part quality. Each component serves a specific purpose in maintaining temperature control throughout the injection process.
1) Heated Manifold
The heated manifold is the heart of every hot runner system, responsible for distributing molten plastic to multiple nozzles. This distribution must be done at a consistent temperature to avoid defects. Manifolds use either embedded or external heat sources.
Embedded heat sources such as brazed-in, paste-in or push heaters offer better thermal control and energy efficiency. Brazed-in heaters provide excellent balance and can last over 10 years. Paste-in heaters offer mid-level performance and easy maintenance, while push heaters are designed for quick replacement and reduced downtime.
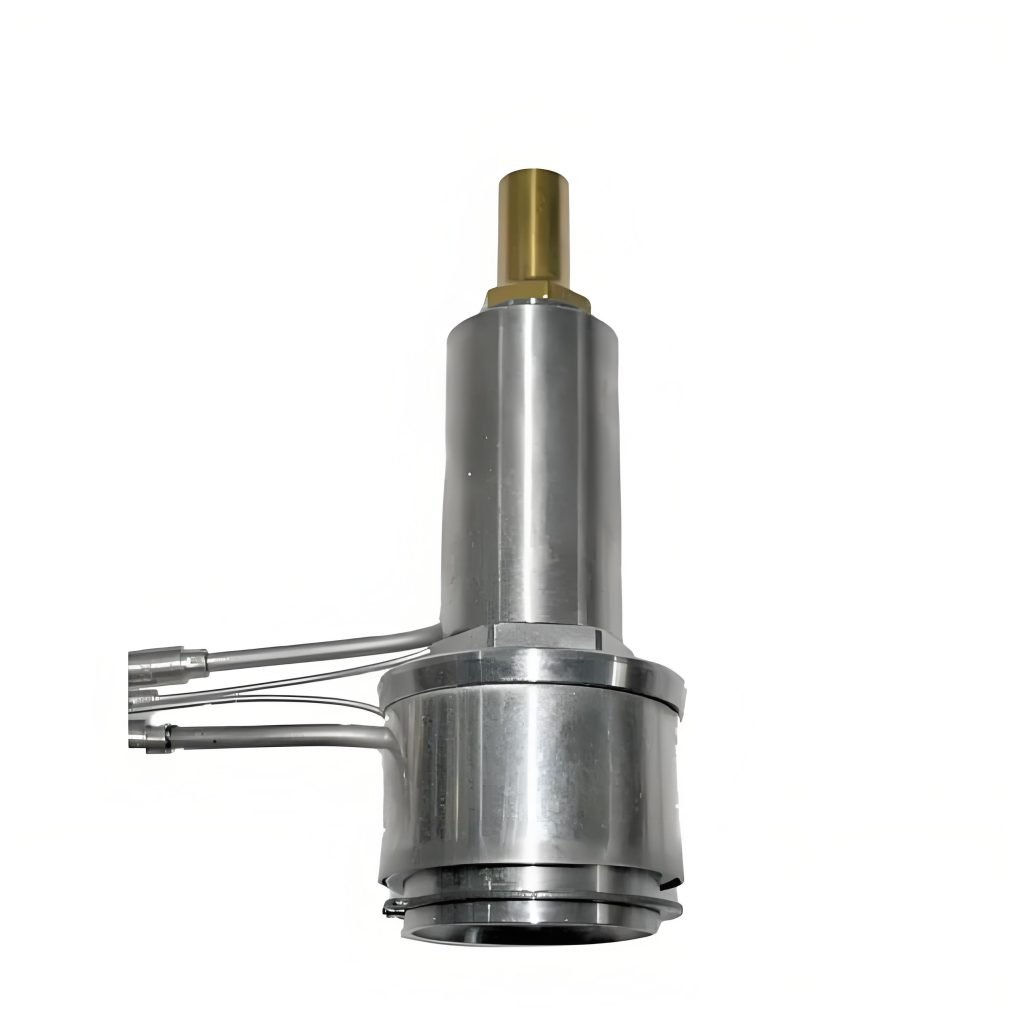
2) Nozzles
Nozzles deliver the molten plastic from the manifold to each specific mold cavity. Their design must ensure consistent flow and prevent material degradation. Direct Gate Nozzles made from solid H-13 steel are very durable and suited for consumer electronics and caps.
Valve Gate Nozzles enhance surface quality by providing tight control over material flow which is especially beneficial in medical applications. Edge Gate Nozzles eliminate cold runners for high volume production where sidewall gating is needed, increasing part consistency and reducing material waste.

3) Temperature Controllers
Temperature controllers are critical for maintaining thermal stability throughout the molding process. These devices use thermocouples or resistance temperature detectors to monitor and adjust heat levels at various locations in the system. Advanced temperature controllers use predictive algorithms to anticipate fluctuations and adjust in real time.
These come in various configurations from compact units managing 2-12 zones to large scale controllers managing up to 192 zones. Some even have integrated sequential valve gate control for fine tuned material flow, ensuring optimal performance across the entire hot runner system.
Benefits of Hot Runner Systems
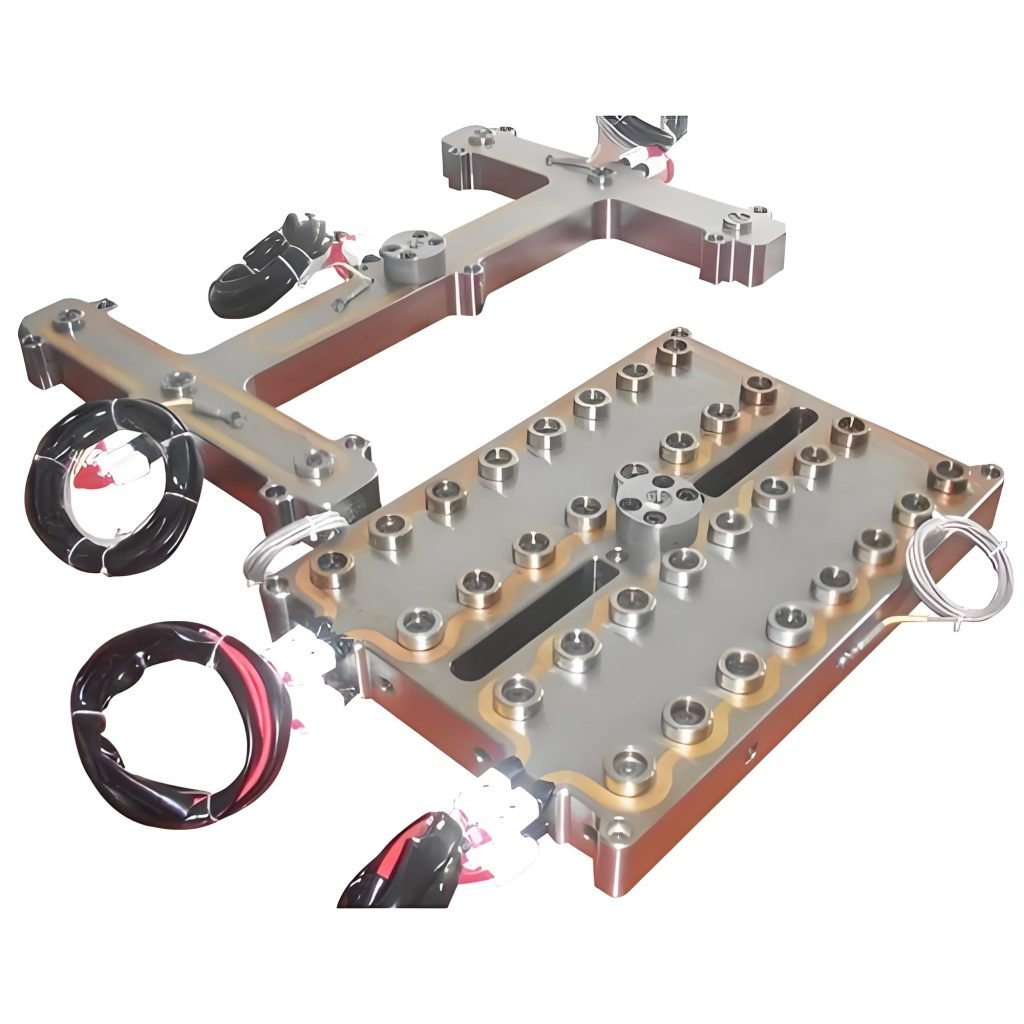
Hot runner systems offer several benefits compared to cold runner systems:
1. Reduced Material Waste
Hot runner systems eliminate the requirement for solidified plastic runners commonly found in cold runner systems. These systems prevent material waste by keeping the thermoplastic material molten throughout the injection cycle. This is especially beneficial when working with high-cost technical resins as the entire material volume is directed into part production without leftovers that need to be reground or disposed of.
2. Faster Cycle Times
Hot runner systems shorten the molding cycle time because there’s no need to wait for runners to cool and solidify. This allows manufacturers to produce more parts per hour, increasing throughput. The faster cycle time also optimizes machine utilization making it ideal for high volume production.
3. Better Part Quality
Hot Runner systems improve part quality through better temperature control and balanced melt flow. This reduces weld lines, improves surface finish and provides better dimensional accuracy. The ability to apply holding pressure at the gate results in better packed parts with minimal shrinkage and warpage.
4. Smaller Machine Requirements
Hot Runner systems eliminate bulky runners so the overall shot volume required per cycle is smaller. This means lower clamping force requirements and manufacturers can use smaller, more energy efficient machines. Over time this means lower equipment costs and energy consumption.
5. More Automation and Efficiency
Hot Runner systems simplify the demolding process as there are no solid runners to remove or trim. This speeds up production and reduces labor costs and improves consistency in automated environments. The absence of post processing steps like gate trimming makes for smoother workflows especially in automated or lights out manufacturing.
6. More Design Flexibility
Hot Runner systems allow for precise gate placement so engineers can optimize flow paths and mold complex geometries. This enables advanced molding techniques like multi-material co-injection and stack molding. Manufacturers can design more intricate high performance parts without the limitations of traditional cold runner designs.
Hot Runner Injection Molding Applications
Hot Runner injection molding is used in:
Automotive is the largest hot runner market accounting for 33.1% of all implementations in 2024. The automotive industry relies on hot runner injection molding to manufacture essential components like dashboards, interior trim pieces, bumpers, and intricate engine parts. Specifically they use hot runners for electrical connectors, headlight housings, taillight assemblies and sealing gaskets. The precision melt delivery and faster cycle times of hot runners is crucial for high volume automotive production.
Medical manufacturing is another key application area. Hot Runner injection molding enables the production of syringes, vials, surgical instruments and diagnostic devices with high precision. In medical applications hot runners ensure uniform melt distribution for high quality parts with minimal defects – especially important when producing components that need to meet strict regulatory standards for biocompatibility and sterility. Currently hot runners are used to produce various medical products from orthopedic devices to drug delivery systems.
Consumer electronics production benefits from Hot Runner system injection molding. Phone casings, laptop components and countless small precise plastic parts rely on hot runner technology. The ability to produce intricate designs with tight tolerances makes these systems essential for modern electronics manufacturing.
Packaging applications use hot runners for bottle caps, closures, containers and thin walled packaging solutions. The reduced waste and faster cycle times make hot runner systems economical for high volume packaging production.
Other applications include toy manufacturing, aerospace components, household products and furniture production. These industries mainly benefit from the consistency, efficiency and quality that only Hot Runner injection molding can deliver.
When Not to Use a Hot Runner System
While hot runners are great in many cases they are not always the right choice.
1. Low Volume or Prototype Production: The high upfront cost and complexity of hot runner systems don’t justify their use for short production runs or one off prototyping.
2. Thermally Sensitive Materials: Some plastics (like PVC or certain flame retardant materials) degrade when held at high temperatures for too long, making hot runners a bad choice.
3. Highly Variable Part Design: If part design changes frequently the fixed nozzle locations in a hot runner system can become a constraint, leading to expensive mold rework.
4. Limited Budget or Cost Sensitive Projects: Hot runner systems require a higher initial investment in tooling and maintenance. For budget constrained operations cold runners might be more viable.
5. Technical Requirements: If the parts are simple, hidden and produced in low to moderate volume a cold runner system will do at a lower cost.
Conclusion
Hot Runner injection molding is a game changing technology that has changed the way manufacturers produce high precision plastic parts at scale. By keeping the plastic in a molten state until it reaches the mold cavities hot runner systems eliminate waste, reduce cycle times and improve part quality.
Every component from the heated manifold and nozzles to the advanced temperature controllers plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient high quality production. While the system has higher upfront costs and complexity, its long term advantages make it essential for industries like automotive, electronics, medical and packaging.
When deciding between a Hot Runner in an injection mold system or a cold runner approach, consider your production volume, design complexity, material usage and maintenance capabilities. Hot runners often deliver the best ROI for high volume precision based manufacturing.




