Ever scratched your head wondering what the real deal is between hot stamping and cold stamping in the wild world of making things? Whether you’re a seasoned pro in engineering or just getting your feet wet in the cool pool of precision manufacturing, getting a grip on these two processes can seriously level up your game.
Think of this article as your friendly guide to the nitty-gritty of hot stamping and cold stamping. We’ll break it down, see what makes it beat, and see how they play a role in your next idea. By the end, you will have the knowledge and tools to choose the best metal stamping process in manufacturing.
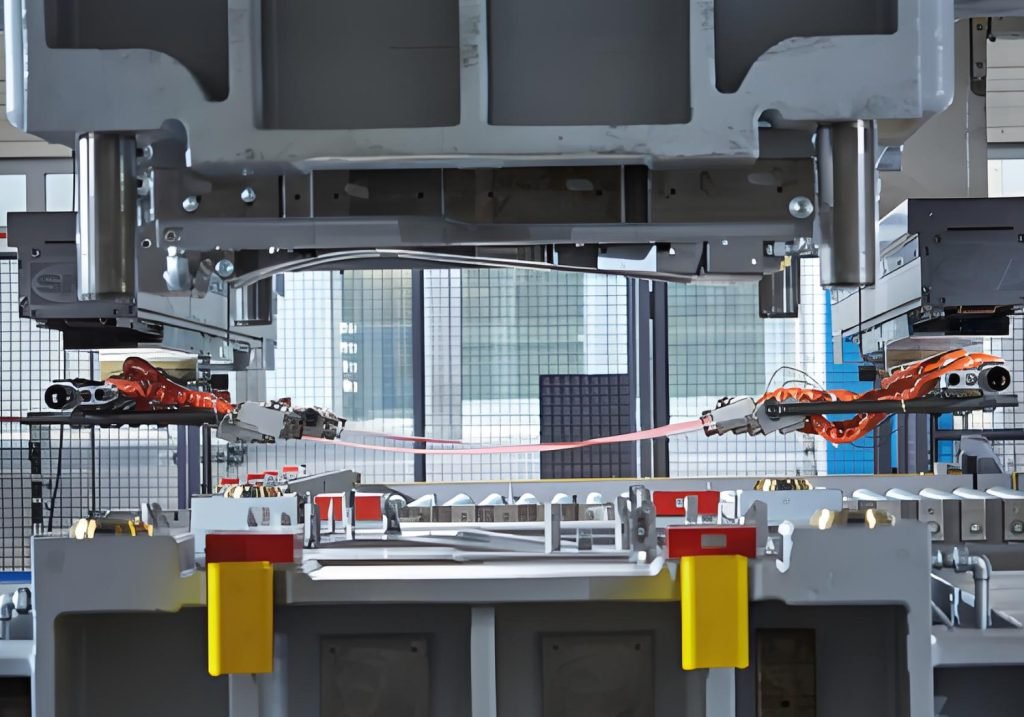
What Is Hot Stamping?
In simple terms, hot stamping is a process of using heat and pressure to transfer a very thin layer of material, usually a shiny metallic foil, with great precision to whatever substrate surface you are using. Think of it as placing a design on a t-shirt with a hot iron, but it is much more sophisticated.

The Process Unveiled:
- First, you’ve got a heated die. Think of it as a custom-made stamp with your desired design etched into it.
- This hot die then presses a special foil against the surface (the substrate). This foil isn’t just a plain sheet; it has layers, including the metallic bit you want to transfer and an adhesive layer.
- The heat from the die does its magic by activating that adhesive on the foil.
- At the same time, the stamping die applies the required pressure so that the foil adheres to precisely the location you want – the shape of your design.
- Finally, the top carrier film of the foil is removed, which is similar to taking the paper off the back of a sticker, and you have a metallic or decorative layer firmly applied to your object.
Key Benefits of Hot Stamping:
Super Versatile
Hot stamping isn’t picky! It plays well with a huge range of materials. We’re talking plastics that can handle the heat, sturdy metals, natural wood, and even luxurious leather. This makes it your go-to buddy for adding that special touch to all sorts of products.
Clean and Tidy Operation
Ditch the messy inks and complicated cleanup! Hot metal stamping process uses rolls of solid metallic foil, making for a cleaner and easier process than a traditional wet print process.
Top-Notch Quality, Every Single Time
You get consistent quality if you go hot! The adhesion of the foil is solid, and depending on the color or if you’re using a metallic foil, the finish is uniform. You can count on that professional look, batch after batch.
Built to Last
Hot stamp designs are tough! Although they will not withstand an overwhelming amount of wear and tear, they do a great job resisting scratches, fading, and other issues compared to some surface treatments.
Beyond Just Looks
In the automotive business, hot stamping can reduce malleability in steel at higher temperatures. This is crucial for forming complex, high-strength parts that are essential for vehicle safety.
Limitations and Considerations of Hot Stamping Process:
Small Lettering Troubles
If your design includes super small lettering, hot stamping might not be the best choice. Fine details can sometimes lose their crispness during the heat and pressure process. You want your message to be clear, not blurry!
Material and Die Choices Matter
Foils are not universal. Some materials, such as leather, may require specialty foils to get the best result. The material used in the die (brass, copper, magnesium, steel, etc.) has a bearing on its longevity and cost for your project. Just like using the right tool for a precision cut, using the proper die is paramount.
Tricky with Complex Shapes
While hot stamping excels on relatively flat or gently curved surfaces, really irregular or complex shapes can present a challenge. Getting consistent pressure and heat transfer across a bumpy surface can be tricky. However, clever solutions like silicone dies can sometimes come to the rescue, conforming better to those unusual shapes.
What Is Cold Stamping?
Next on our list is cold metal stamping. Opposite of hot stamping, cold stamping uses a pressure-sensitive adhesive to make the metallic foil transfer to the designated area. This kind of process is more like “stick and press”.
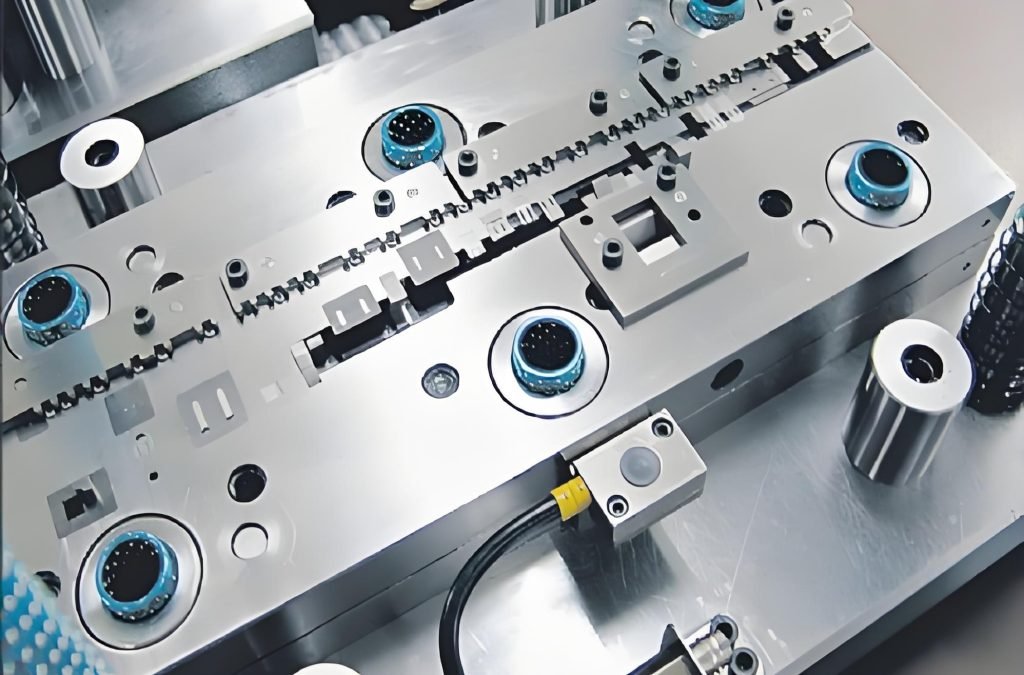
The Process Unveiled:
- First, a pressure-sensitive adhesive is applied to your chosen surface (the substrate) in the exact pattern of your desired design. Think of it like printing a sticky outline.
- Next comes the metallic foil that is pressed to the adhesive area with a die or roller.
- The amount of pressure required is what fixes the foil to the adhered surface.
- Like hot stamping, the foil’s carrier film is peeled off, but now you have a cool metallic design that is bonded to the surface.
Key Benefits of Cold Stamping:
Wallet-Friendly (Especially in the Long Run)
A big benefit of cold stamping is cost savings. The absence of heat creates a massive energy saving. When you consider a large run of stamping, these savings can add up tremendously!
Speedy Production
Cold stamping is a speed demon! It boasts fast production rates, making it perfect for when you need to churn out a high volume of parts in a relatively short amount of time. Think efficiency on overdrive.
Material Strength
Because you’re not messing with the metal’s temperature, it retains its original hardness and strength. This is crucial for applications where the structural integrity of the part is paramount. You get strong parts without any heat-induced changes to the metal’s properties.
Precision and Polish
Cold stamping is all about accuracy. It allows for tight tolerances and an excellent surface finish on the final parts. You get consistent, high-quality components that meet demanding specifications.
Less Waste, More Efficiency
Well-designed dies in cold metal stamping are all about minimizing material waste. By carefully planning the cutting and forming process, you can get more parts out of each sheet of metal. It’s like being a super-efficient recycler from the get-go.
Limitations and Considerations of Cold Stamping Process:
Thickness Limitations
Cold stamping works best with thinner metal sheets. It can be difficult to form very thick materials at room temperature and may require very high forces and specialized equipment. There is certainly a limit to how much you can shape and bend without heating the material.
Tooling Costs
The robust dies used in cold stamping can be expensive and require a considerable initial capital investment. They need to be very strong and engineered precisely for use under high pressure. Nevertheless, these strong tools are made to last, and for high production volume, the cost is worthwhile.
Simpler Shapes are the Sweet Spot
Cold stamping is perfect for making part shapes in all manner of shapes but could be considered not the best option in cases with very complex shapes (many curves and undercuts). Hot stamping will tend to give more versatility in making complex geometries.
The Risk of Work Hardening
Cold stamping will strengthen the metal and increase its hardness, but it can also increase the brittleness of the part over time. This is called work hardening, which we need to manage during the cold stamping process, and in some cases, intermediate steps of annealing (heating and cooling) need to be performed to fully shape the part or for more complicated formed materials.
Differences Between Cold Stamping vs Hot Stamping
Alright, let’s get to the basic differences between these two metalworking heavyweights in a simple-to-understand table:
| Feature | Hot Stamping | Cold Stamping |
| Temperature | High temperatures (around 900-950°C) | Room temperature |
| Material Properties | High-strength materials like boron steel | Variety of metals (steel, aluminum, copper, brass) |
| Product Strength & Hardness | Higher strength and hardness due to phase transformation | Lower strength and hardness, no significant phase change |
| Equipment | Requires heating and cooling setups | Simple hydraulic or mechanical presses |
| Production Cycle Time | Longer due to heating and cooling cycles | Faster, no temperature changes needed |
| Applications | Safety-critical components, automotive, aerospace | General metal parts, electronics, appliances |
| Material Thickness | Can handle thicker materials more readily | Best suited for thinner metal sheets |
| Tooling Costs (Initial) | Can be lower for simpler designs | Can be higher due to the need for robust, precise dies |
| Design Complexity | More flexible for complex shapes | Better suited for simpler to moderately complex shapes |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to heating requirements | Lower, as no heating is involved |
| Surface Finish | Can achieve decorative finishes and markings | Typically focuses on functional surface finish |
| Work Hardening | Less of a concern due to high-temperature processing | A potential concern that needs to be managed |
Making the Right Choice: Hot or Cold?
So, with the key differences laid out, how do you decide which metal stamping method is your best bet? In cases where the visual appearance of something and a unique decoration are part of the key, it is hot stamping. The unique opportunity to apply brilliant metallic finishes and embossed effects and work across many materials makes hot stamping a perfect fit when used as a marketing tool (branding, packaging, and decorative). When you add your special touch to create a unique, premium feel, hot stamping may be the ideal technique to achieve durable impressions.
On the other hand, if you’re producing high volumes of durable metal parts with tight tolerances, cold stamping is a better option. Because it works quickly and is cost-effective for larger runs, all while maintaining the metal’s natural strength, it is practical and effective in various applications: automotive, electronics, and appliance industries. If speed and structural soundness are critical to your metal parts, cold stamping is a practical, repeatable process capable of higher volumes.
Conclusion
Hot stamping and cold stamping are both essential metal stamping processes in manufacturing. Hot stamping produces high-strength parts and looks good while doing it for safety-critical applications. Cold stamping is economical and fast for making large amounts of metal parts that are precise and material efficient, making it the workhorse of many industries, from automotive to electronics. Ultimately, it will depend on your project and whether it requires maximum strength and unique shapes or the ability to produce a large volume at a cost-effective price.
And guess what? When it comes to bringing your metal part visions to life, Fecision has you covered! Here’s why our metal stamping services are your winning ticket:
- Expertise You Can Trust: Not just that we do, we are experts in both hot stamping and cold stamping.
- Customize for Your Needs: Whether your project is complex, simple, large, or small, we can provide customized metal stamping solutions for you.
- Cutting-Edge Tech: We utilize the latest technology so we can provide you with the highest precision and quality in metal stamping.
- Seamless Journey: From your initial design ideas to when we deliver you finished parts, we will focus on making your manufacturing experience smooth and easy.
Let Fecision be your partner in precision metal stamping!




