Micro Injection Molding is a highly specialized form of injection molding that enables the production of tiny, intricate, and complex plastic parts. As the demand for smaller, more precise components increases across industries, Micro Injection Molding has emerged as an essential manufacturing process for producing miniaturized parts with high precision. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of Micro Injection Molding, including its process, materials, equipment, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. We will also compare it to traditional injection molding and discuss the cost considerations for businesses considering this technology.
1. Basics of Micro Injection Molding
Micro Injection Molding is a variation of conventional injection molding that focuses on producing miniature plastic parts, typically with weights less than one gram and dimensions smaller than a few millimeters. The process involves injecting molten plastic into tiny, highly detailed molds to create precision-engineered parts used in a variety of industries. These parts can range from medical devices to micro-components for electronics and automotive applications.
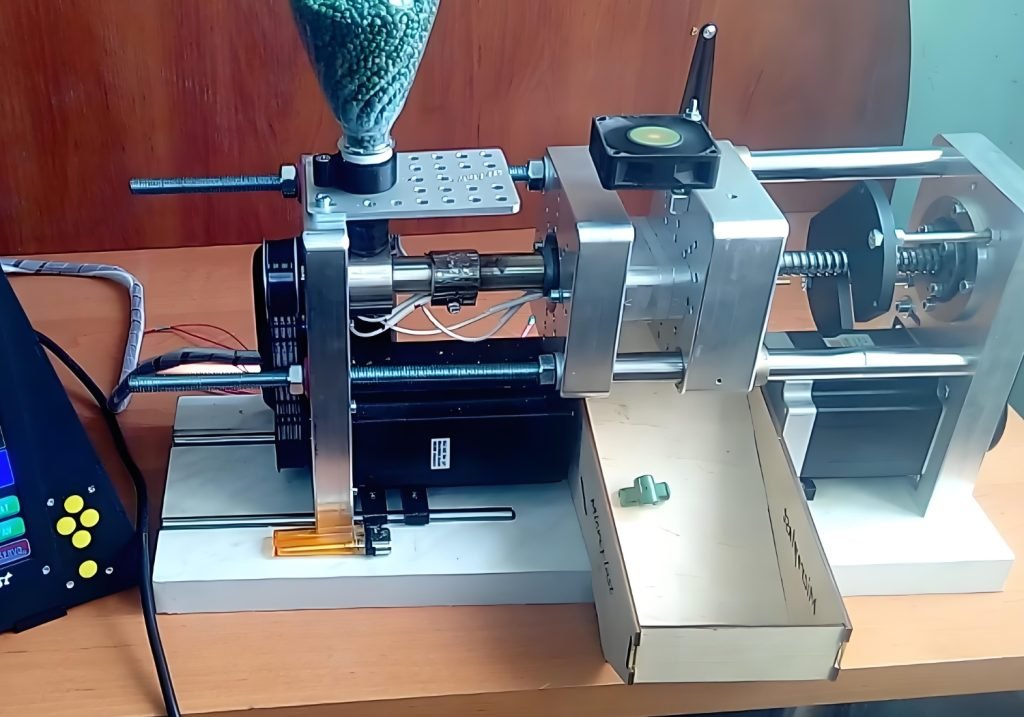

Definition and Importance
Micro Injection Molding is crucial for industries that require small and complex parts that cannot be effectively produced using traditional manufacturing methods. Due to the increasing miniaturization of electronics, medical devices, and other technological innovations, there is a growing demand for parts that are not only small but also have intricate features and high precision. This process allows for the mass production of high-quality miniature components, which is critical in industries where space and performance are paramount.
Differences from Standard Injection Molding
While standard injection molding involves producing parts that can range in size from small to large, Micro Injection Molding deals exclusively with much smaller components. The key difference lies in the level of precision and the size of the molds and machines used in the process. In traditional injection molding, parts can be several millimeters to centimeters in size, whereas in micro injection molding, parts typically weigh less than 1 gram and have complex features on a microscopic scale. The machines used in Micro Injection Molding are often much smaller, with specialized features that ensure precision during the molding process.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro Injection Molding
High Precision and Miniature Part Production
One of the primary advantages of Micro Injection Molding is the ability to produce extremely precise and complex parts. The molds used in this process are incredibly detailed, allowing manufacturers to produce parts with extremely fine features, such as micro-holes, channels, and intricate geometries. This precision makes it possible to produce highly functional and high-performance parts, which is particularly important in industries like medical device manufacturing and semiconductor production.
Challenges in Material Handling
Despite its advantages, Micro Injection Molding is not without challenges. One of the primary difficulties lies in material handling. Because the parts produced are so small, it is crucial to handle the materials carefully to avoid contamination and ensure that the properties of the material are maintained throughout the molding process. The small size of the components also means that the molds need to be extremely precise, which can increase the complexity and cost of the molding process.
2. Applications of Micro Injection Molding
Micro Injection Molding finds applications in several high-demand industries, thanks to its ability to produce miniature, complex parts. Below are some of the key sectors that rely on this technology:
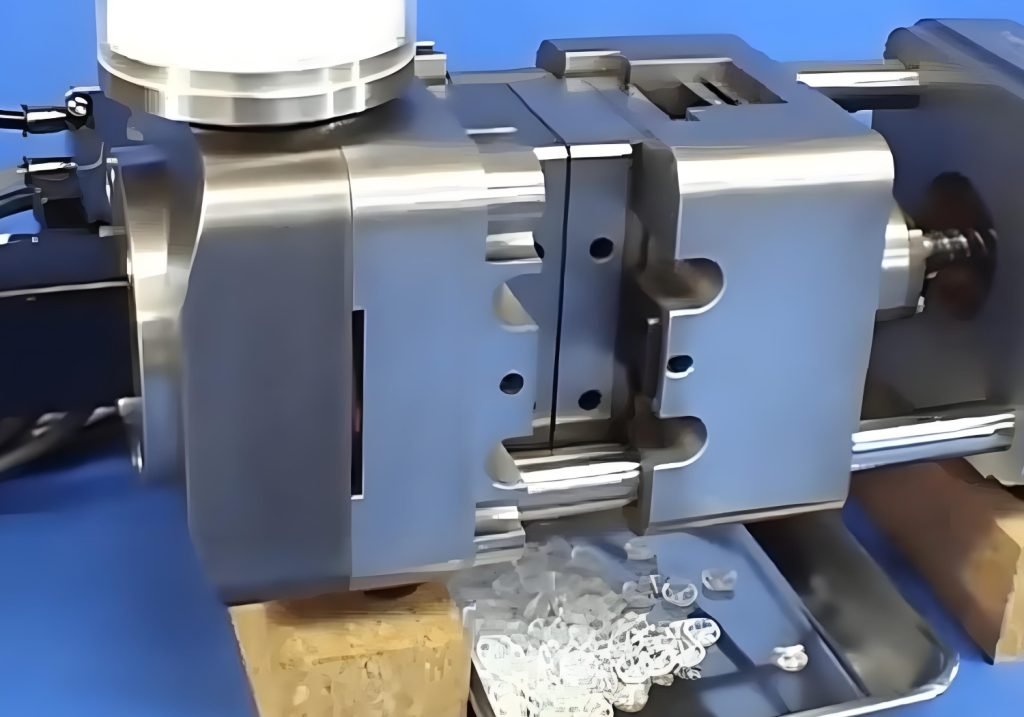
Medical Devices and Implants
The medical device industry is one of the largest sectors benefiting from Micro Injection Molding. This process enables the production of tiny components for medical implants, diagnostic devices, and surgical instruments. For instance, micro components are used in pacemakers, hearing aids, catheters, and stents, where small size and high precision are essential for performance. Additionally, Micro Injection Molding allows for the production of biocompatible materials that can be safely used inside the human body.
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
In the electronics and semiconductor industries, the need for miniaturized components is increasing due to the rise of smaller, more efficient devices such as smartphones, wearables, and sensors. Micro Injection Molding is used to create parts like connectors, housings, and components for microchips and other electronic systems. These parts need to be lightweight, durable, and able to withstand high levels of stress, all while maintaining extremely small dimensions.
Automotive Micro-Components
The automotive industry is also seeing a rise in the demand for micro injection molding, particularly for the production of micro-components used in vehicle assemblies. These can include small connectors, sensors, and actuators that are used in electronic control systems, safety devices, and other essential automotive functions. Micro Injection Molding allows for the creation of highly reliable and precise components that are necessary for modern vehicles.
3. Micro Injection Molding Process and Techniques
The Micro Injection Molding process consists of several crucial steps that ensure the creation of high-quality miniature parts. These steps include mold design, material selection, and micro-machining for mold fabrication.
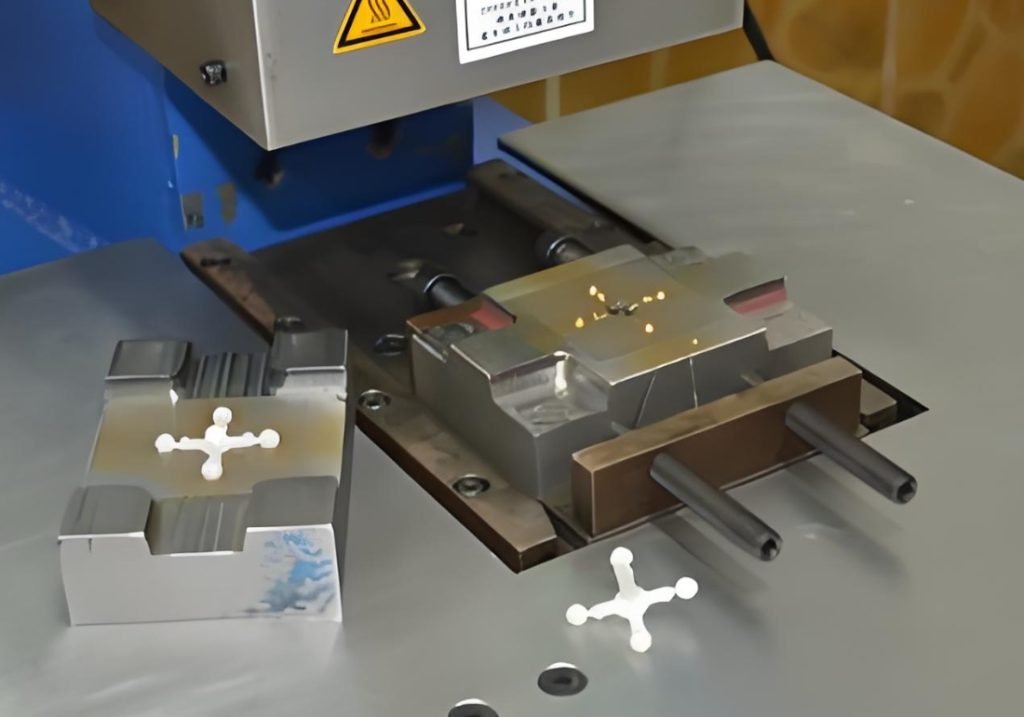
Mold Design and Material Selection
The first step in the micro injection molding process is designing the mold. Because micro components are highly detailed, mold designs must be incredibly precise. Additionally, material selection plays a significant role in determining the final part’s properties. Common materials used in Micro Injection Molding include thermoplastics like PEEK, LCP, and polycarbonate, as well as biocompatible materials for medical applications.
Micro-Machining for Mold Fabrication
Mold fabrication in Micro Injection Molding often involves micro-machining techniques, such as electrical discharge machining (EDM) or laser ablation, to achieve the necessary precision. These techniques allow manufacturers to create molds with extremely fine details and features. The ability to produce complex shapes with micron-level precision is one of the key factors that make Micro Injection Molding so effective.
4. Equipment Used in Micro Injection Molding
Micro Injection Molding requires specialized equipment to handle the tiny parts and high-precision molds. These include:
Specialized Micro Injection Molding Machines
Unlike traditional injection molding machines, micro injection molding machines are smaller and designed to handle miniature parts. These machines offer high levels of precision, allowing for the control of variables such as temperature, pressure, and speed, all of which are critical for producing tiny parts with accurate dimensions. Specialized nozzles and injection units are also used to ensure that the plastic is injected in the correct amount and at the proper speed.
Importance of High-Precision Molds
The molds used in Micro Injection Molding need to be highly precise to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. These molds are typically made of durable materials such as steel or tungsten and are often created using advanced micro-machining techniques to achieve the necessary level of detail. The precision of the mold is a critical factor in determining the overall quality of the molded part.
Materials Used in Micro Injection Molding
A wide range of materials can be used in Micro Injection Molding, depending on the application and the required properties of the final part. Some of the most commonly used materials include:
Thermoplastics (PEEK, LCP, Polycarbonate)
Thermoplastics are frequently used in Micro Injection Molding because of their versatility and ability to be molded at high precision. Materials such as PEEK (Polyetheretherketone), LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer), and polycarbonate are popular choices due to their strength, durability, and resistance to high temperatures.
Biocompatible Materials for Medical Use
For applications in the medical field, biocompatible materials are often required to ensure that the parts do not cause adverse reactions when used in or on the human body. Materials like medical-grade polyethylene, silicone, and other specialized polymers are commonly used in these applications.
5. Cost Considerations in Micro Injection Molding
Factors Affecting Cost (Tooling, Machine Type, Material)
The cost of Micro Injection Molding can vary depending on several factors. One of the primary cost drivers is the tooling or mold fabrication process, which can be expensive due to the high precision required. Additionally, the type of machine used and the material chosen will influence the overall cost of production. High-quality materials, such as PEEK or biocompatible materials are more expensive than standard thermoplastics, and the specialized machines used for micro injection molding come with a higher upfront cost.
Cost Comparison with Conventional Injection Molding
While Micro Injection Molding tends to be more expensive than conventional injection molding due to the need for specialized equipment and molds, it is often more cost-effective for producing high-precision, miniature components. The ability to produce small parts in large quantities can offset the higher initial costs over time.
6. Micro Injection Molding vs. Traditional Injection Molding
The primary difference between Micro Injection Molding and traditional injection molding lies in the scale and precision of the parts produced. Micro Injection Molding is used to create parts that are much smaller and more intricate than those produced using traditional methods. The precision required in Micro Injection Molding is far greater, making the process more specialized.
Cost and Efficiency Comparisons
While traditional injection molding can be more cost-effective for producing larger parts, Micro Injection Molding is ideal for industries that require small, highly detailed components. The efficiency of Micro Injection Molding improves as the production volume increases, especially when producing high-precision parts in large quantities.
7. FAQ’s
What is Micro Injection Molding?
Micro Injection Molding is a specialized version of injection molding that produces miniature plastic parts, typically weighing less than one gram and with dimensions smaller than a few millimeters. It is used to manufacture high-precision, miniature components for industries like medical devices, electronics, and automotive.
How does Micro Injection Molding differ from standard Injection Molding?
Micro Injection Molding differs from standard injection molding primarily in the size and precision of the parts produced. While traditional injection molding can produce parts of varying sizes, Micro Injection Molding focuses on very small, highly detailed components. Additionally, the machines and molds used in Micro Injection Molding are specially designed to handle the precision required for miniature parts.
What are the main applications of Micro Injection Molding?
Micro Injection Molding is commonly used in industries such as:
- Medical devices and implants (e.g., pacemakers, catheters, and surgical instruments)
- Electronics and semiconductors (e.g., connectors, microchips, and housings for small devices)
- Automotive micro-components (e.g., sensors and small connectors in vehicles)
These applications require small, highly precise, and durable components.
What materials are commonly used in Micro Injection Molding?
Common materials used in Micro Injection Molding include:
- Thermoplastics such as PEEK (Polyetheretherketone), LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer), and polycarbonate, known for their strength and durability.
- Biocompatible materials for medical applications, including medical-grade polyethylene and silicone, which are safe for use in or on the human body.
These materials offer the necessary properties for the demanding applications of Micro Injection Molding.
Is Micro Injection Molding more expensive than traditional Injection Molding?
Yes, Micro Injection Molding is generally more expensive than traditional injection molding due to the need for specialized machines, molds, and high-precision techniques. However, it is often more cost-effective for producing small, intricate parts in high volumes, especially in industries where miniaturization and precision are critical. The higher initial costs can be offset over time through mass production of high-quality components.
8. Conclusion
Micro Injection Molding offers numerous benefits, including the ability to produce highly precise, miniature parts for various industries, including medical devices, electronics, and automotive applications. The process is essential for manufacturing parts that require fine details, high durability, and high-performance characteristics. When considering Micro Injection Molding for your manufacturing needs, it’s important to assess factors such as the required precision, material properties, cost considerations, and production volume. While it may have higher initial costs than conventional injection molding, its ability to produce small, complex parts makes it a crucial technology for industries that demand miniaturization and high-performance components.




