We are living in an era where everything is in the hands of technology. The simplest, and even the most complicated tasks are being controlled by computers and robots. In this situation, manufacturing is not left behind. The advancements in this sector have resulted in high-speed production across an array of industries.
CNC machining is one of the enormous outcomes of this modernization. The results are exceptionally accurate, and efficient. CNC-based processes are not limited to a single type-you can get CNC milling and laser cutting. These two methods are distinguished by different purposes. Yet, people compare them due to the shaping and cutting materials. Let us highlight what CNC milling and laser cutting work is, along with their plus points and drawbacks.
What Is CNC Milling?
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process. It implies that material is eliminated from a solid workpiece by a rotating cutting tool. The machine will function under the control of a computer. This is why the results are impressive in terms of efficiency. The digital instructions (G-code) will mold the material according to the prompt you give.
This differed from the conventional manual milling procedures. CNC milling is an incredible launch that automates the cutting procedure which otherwise would demand hours or even days. Above all, the output is fascinating in terms of better accuracy. Even complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve by hand are possible through this process. The machine can move in multiple axes – these are mostly three (X, Y, and Z). Take notes that ultra-modern CNC mills will work on five or more axes for complicated shapes.
Let’s take a look at how this process actually grows. This will require a block or sheet of material, which the niche experts call as a workpiece. It is snugly fixed onto the milling table. The cutting tool that is built from high-speed steel or carbide will rotates at high speeds. As a result, it gradually removes material until you get the shape you asked for. Operators can try a plethora of tools such as end mills, ball nose cutters, and face mills.
CNC milling has been utilized in numerous industries that demand high-precision parts. This is mostly in the aerospace, automotive, medical device manufacturing, and prototyping sectors. Plus, it will work with a huge collection of materials such as aluminum, steel, and titanium metals. Even plastics, and wood are suitable. This versatility has granted CNC milling praise for a huge range of applications such as machining engine components.
Why manufacturers well-like CNC milling is owing to its ability to produce immensely accurate and durable parts with tight tolerances. The values lie within ±0.005 inches (0.127 mm) or better. Keep note that since it’s a mechanical cutting process, tool wear and maintenance cannot be ignored. It is generally less effective for thin or sensitive materials as compared to laser cutting.
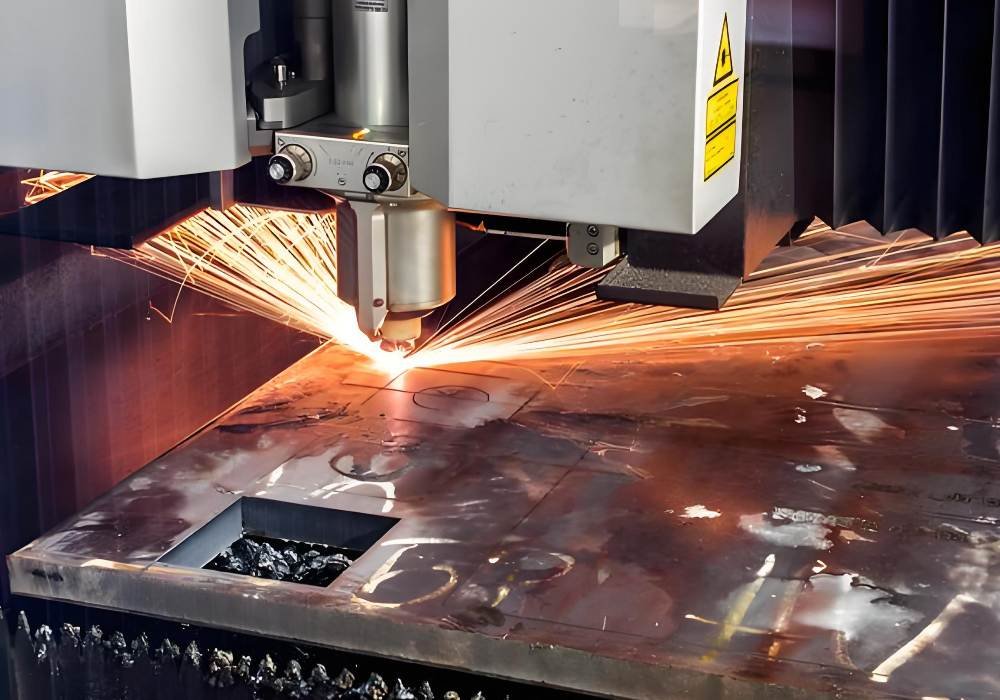

What Is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a non-contact process that utilizes a high-powered laser beam to cut through materials. It also uses thermal power. The laser will target intense heat on a small area, to vaporize, or burn away the material. It will create clear cuts with smooth edges that will impress anyone who witnesses them. CNC milling works on a different pattern. It physically removes material with a cutting tool. Thus, laser cutting relies on concentrated light energy to get impressive results.
For this type, you will need a digital design file. It will be the guide for the laser cutter to make accurate movements in the material. Here is an astonishing fact: the laser itself can be generated using different technologies. Mostly, carbon dioxide and fiber lasers are used. CO₂ lasers are utilized for non-metal materials such as acrylic, and fabric. Fiber lasers are appropriate for cutting metals owing to its high energy efficiency and intensity.
Laser cutting is a must-have for industries such as electronics, signage, textiles, and manufacturing engineering. It has a unique ability to create complex patterns and engravings. In simple words, it is applicable for decorative applications. The high-speed cutting capability is valuable for industrial-scale production.
One of the paramount advantages of laser cutting is its pinpointness. The laser beam can be as narrow as 0.1 mm. Thus, incredibly detailed cuts that are impossible with CNC machining are accomplishable through this technique. Plus, it is a contactless process. There is minimal risk of material deformation so it is suitable for sensitive and thin materials.
Here is another benefit: it gives a smooth finish on the cut edges. The laser melts the material as it cuts. It eliminates the demand for post-processing in many cases. CNC milling may require additional finishing to remove tool marks. Yet, this was just the positive side. Laser cutting has multiple drawbacks as well. It is less effective for thicker materials, as the laser may struggle to penetrate beyond a certain depth without a compromise on quality. Even though laser cutters are suitable for a plethora of materials, some highly reflective metals such as copper and brass can be challenging.
CNC Milling vs. Laser Cutting: What is the Difference?
CNC milling and laser cutting are used to mold materials, but the process is much different. You should know the major difference to select the suitable one for your project.
1. Cutting Technique
CNC milling is a mechanical process. It uses rotating cutting tools to remove material. The machine crates out the design by shaving off layers.
Laser cutting is a thermal process. It uses a high-powered laser to cut or engrave materials. The laser beam melts or vaporizes the surface.
2. Contact vs. Non-Contact
CNC milling is a contact-based process. The cutting tool will physically touch the material. This can cause wear and tear on the tool over time.
Laser cutting is non-contact. The laser never touches the material. It means that wear and tear is negligible and the machine’s lifespan would be better.
3. Material Compatibility
CNC milling works best with metals, plastics, wood, and composites. It is appropriate for tough materials such as steel and titanium.
Laser cutting is better for thin materials. It works well with metals, acrylic, fabrics, and wood. It struggles with very thick or highly reflective metals.
4. Detail in Making
Laser cutting is more detailed. The laser beam is extremely thin so complicated cuts can be possible. It can create fine details that milling cannot.
CNC milling is accurate but not as expert for tiny details. However, it produces solid parts with complex 3D shapes.
5. Edge Finish
Laser cutting leaves smooth, and clean edges. The heat melts the material to seal the edges as it cuts. No extra finishing is demanded in most cases.
CNC milling can leave rough edges. The tool marks may require sanding or polishing. Finishing steps depend on the material and tool used.
6. Speed
Laser cutting is faster for thin materials. The laser will rapidly cut through sheets in seconds. It is perfect for mass production and rapid prototyping.
CNC milling is slower. The cutting tool must gradually remove material layer by layer. It will demand immense time but it is necessary to mold solid materials.
7. Depth of Cutting
CNC milling can cut deep into thick materials. It can create deep cavities, and 3D shapes.
Laser cutting has some restrictions in terms of depth. It works best for flat sheet materials. The laser struggles with deep cuts in thick metals.
8. Charges
Laser cutting machines can be expensive, but they demand less maintenance. The non-contact process decreases tool wear which will decrease the long-term costs.
CNC milling machines is highly variable in cost. The tools wear out and need frequent replacement. Take notes that milling is better for large, and complex parts.
9. Loss of Material
Laser cutting produces negligible waste. The thin laser beam removes very little material. It is efficient and eco-friendly.
CNC milling creates more waste. The cutting tool shaves off chunks of material. The outcome is a lot of scrap, yet it depends on the design.
10. Applications
CNC milling is used for making strong parts. It is common in aerospace, and medical industries. It is best for mechanical components that demand durability.
Laser cutting is utilized for decorative and lightweight designs. It is suitable for signage, electronics, engraving, and textile industries. It is best for complex but highly-detailed projects.
Bottom Line!
CNC milling and laser cutting are products of advancing technologies, and they are highly recommended for modern construction. Milling is highly recommended for solid, and durable parts. On the other hand, laser cutting is suitable for extremely fine details. You must select a suitable method that depends on material, and application demands.




