The injection molding industry has seen some transformative innovations over the years and the hot runner system is one of them. This fundamentally alters plastic production optimizing both manufacturing and production. The key is to maintain molten plastic throughout the process, minimizing waste and improving part quality.
This shift not only improves efficiency but also aligns with eco-friendly manufacturing practices. Lets know more about the details of hot runner technology, including its components, operational principles, and the benefits.
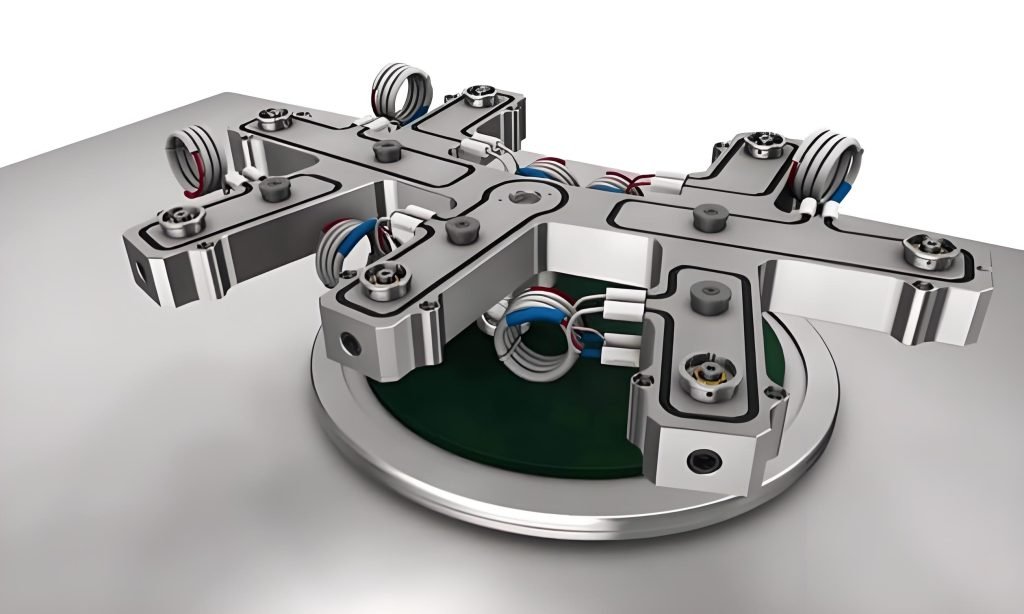

Hot Runner in Injection Molding: Design and Operation
In injection molding, a hot runner system is an assembly of different heated components. These heated components are used to inject molten plastic into the mold cavities. The primary function of a hot runner system is to maintain the molten state and temperature of the plastic.
A hot runner system works as a sophisticated channel. First, plastic pellets are melted within the machine’s barrel. The resulting molten plastic is then forced into a heated manifold. This manifold, acting as a central hub, evenly channels the plastic to multiple heated nozzles.
These heated components, including the manifold and nozzles, prevent premature cooling and ensure the plastic remains molten. The nozzles then inject the molten plastic directly into the mold cavities.
The manifold has a very critical role in the process that maintains consistent temperature and flow, guaranteeing uniform filling of the mold. This precise control ensures that the final product is free of any defect with superior accuracy and finish.
Basic Components of Hot Runner System
A hot runner system is made of different components that work together to maintain the molten state of plastic. Let’s take a look at them:
Manifold
The manifold in a hot runner system acts as a central distribution hub for molten plastic. Before reaching the nozzles, the plastic flows through the manifold’s internal channels. These channels are designed according to the specific molding process that optimize the plastic flow and minimize wastage.
Nozzles
Nozzle is a cylindrical component with a tapered tip that injects molten plastic directly into the mold cavities. They are designed to withstand and maintain high temperatures. Depending on the design, they are typically installed into the mold plate with or without a manifold. There is a wide variety of nozzles available such as threaded, support ring, single-valve gate, and sprue bushing nozzles.
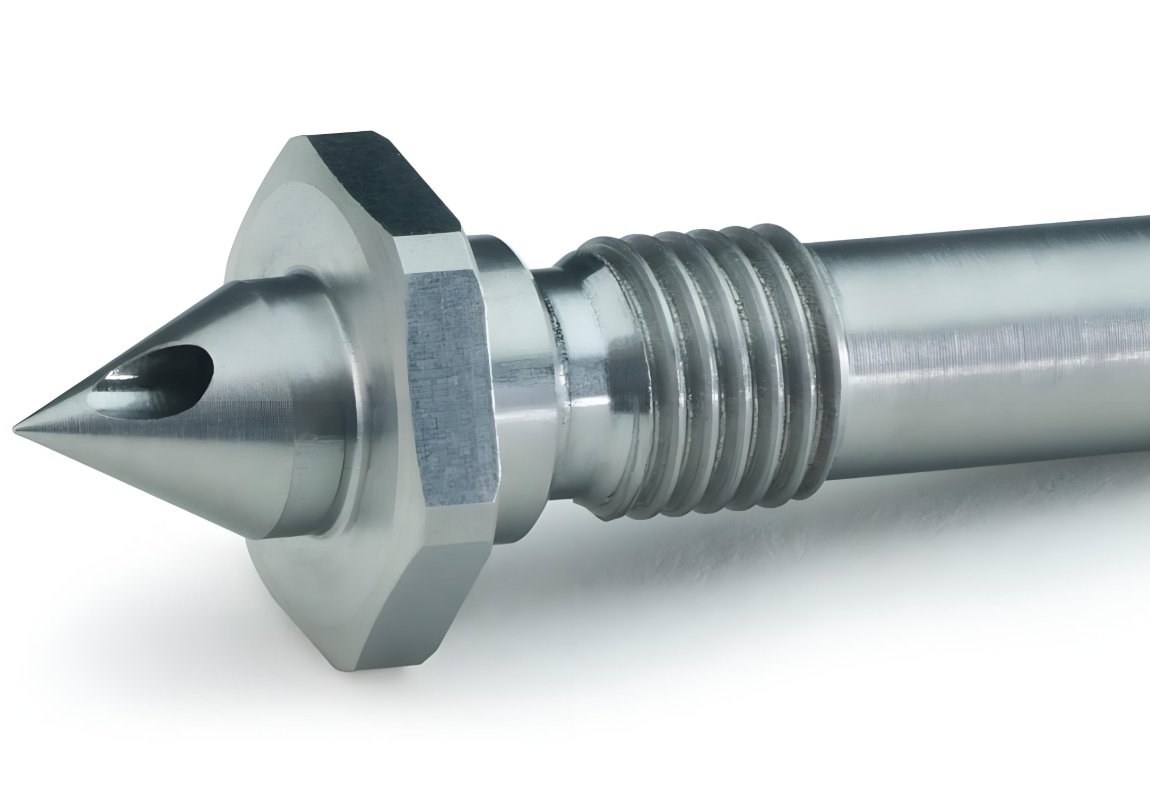

Heater Technology
Heater technology plays a key role in maintaining the optimal temperature of the molten plastic as it flows through the hot runner system. These heaters come in various types including coil heaters, nozzle heaters, and manifold heaters. Coil heaters are usually preferred as they are
compact, versatile, and provide uniform heat distribution.
Types of Hot Runner System
There are two different types of hot runner systems used in injection molding. Each is designed to address specific production needs and part requirements. Let’s take a look at them:
Open Gate Hot Runner System
An open gate hot runner system has a simple structure without any mechanical valve or pin controlling the plastic flow. The molten plastic keeps flowing until the injection cycle is complete, and is stopped by the injection molding machine’s control system. It is comparatively a low cost solution as compared to other hot runner systems.
Valve Gate Hot Runner System
The valve gate system comes with a mechanical valve or pin control, which regulates the flow of molten plastic into the mold cavity. This valve remains closed throughout the injection phase and only opens when the cavity requires filling. These systems have a more complex design and a higher cost compared to open gate systems. They provide excellent control over the entire injection molding process. .
Hot Runner System vs Cold Runner System
Both hot runner systems and cold runner systems are two distinct methods for injecting plastic, each with different operational principles. A hot runner system utilizes heated components to maintain the plastic in a molten state as it travels from the injection molding machine to the mold cavities. This eliminates the need for solid runners and significantly decreases plastic waste.
On the other hand, the cold runner system allows the plastic to cool and solidify within the runners. Consequently, these runners must be ejected along with the finished part, leading to a greater amount of plastic paste.
While both hot and cold runner systems serve the same purpose of delivering plastic to a mold, they differ significantly in their operation and resulting outcomes. This detailed breakdown will help you determine which system best suits your specific injection molding needs.
| Feature | Hot Runner System | Cold Runner System |
| Plastic State | Maintain molted during transit | Solidified in runners |
| Waste Generation | Minimal (no runners ejected) | Significant (runners ejected) |
| Cycle Duration | Shorter | Longer |
| Eco-Friendliness | More eco-friendly | Less eco-friendly ( as it produces more wastage) |
| Cost | Higher (complex system, heating components) | Lower (simpler system) |
| Best For | High volume production, complex geometries and expensive resins. | Low volume production, simple part designs |
Advantages of Using a Hot Runner System
Each running system has its own unique advantages which makes them suitable for different applications. Let’s talk about the benefits of a hot runner system:
Reduces Material Waste
Hot runner system reduces material waste by eliminating the need for runners to solidify and be ejected. This translates to cost savings as the mold system generates little to no material waste, making it a more economical process.
Improves Cycle Time And Efficiency
Since the hot runner system injects plastic directly into the cavity, no additional material needs to be cooled. This short cycle time not only increases production efficiency but also reduces energy costs associated with the molding process.
Enhances Product Quality And Consistency
Parts made using hot runner molds exhibit better final quality due to the excellent filling profile and injection pressure. Cosmetic and structural conditions like stress lines and sin marks are also minimized because the plastic no longer travels through a cold runner in the mold.
Design Flexibility
Hot runner systems provide better flexibility in the placement of the gate using hot tip, valve gate, or edge gate options. This increased flexibility improves part appearance and ensures complete mold filling, enabling the creation of more intricate designs.
Disadvantages and Challenges
Just like any other manufacturing technology, hot runner systems have their drawbacks and challenges:
Higher Initial Cost
Hot runner systems demand a high upfront investment due to the complex mold design and specialized components. However, this higher cost is justified by long-term savings from reduced material waste and shorter cycle times.
Complex Maintenance And Troubleshooting
Due to their intricate design and numerous heated components, hot runner systems require specialized knowledge and skills for maintenance and troubleshooting. This can lead to longer downtime and increased repair costs if in-house expertise is limited.
Requires Precise Temperature Control
Maintaining optimal performance needs high precision temperature control equipment. Any deviation from the required temperature range can lead to part defects and compromise quality.
Applications of Hot Runner Systems
Hot runner systems are used across various industries due to their efficiency and precision. Here are some prominent applications of hot runner systems:
Automotive Industry
Hot runner systems are crucial for producing large, complex automotive parts like dashboards and bumpers. Their precision ensures consistent quality and reduces wastage.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, hot runners enable the precise molding of intricate components for devices like smartphones and laptops, for high aesthetic and finishing standards.
Medical Devices
Hot runners are vital for medical equipment like syringes and sterile containers. They provide precise, consistent molding for accurate dosing and maintain material integrity for medical-grade plastics. This minimizes contamination and enables the production of safe and reliable medical devices.
Conclusion
Hot runner systems represent a considerable advancement in injection molding, offering substantial advantages in efficiency and quality. While it may need a high initial investment and specialized maintenance, it delivers long-term benefits through reduced waste, shorter cycle times, and improved part consistency.
Choosing between hot and cold runner systems depends on specific production needs. Hot runners are ideal for intricate parts, expensive materials, and large-scale operations whereas cold runners remain a cost-friendly solution for simple designs. Ultimately, hot runner technology remains a powerful tool for manufacturing aiming to optimize their injection molding processes.




