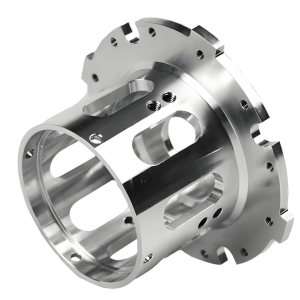
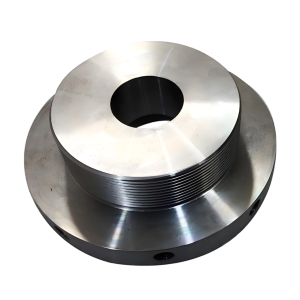
Stainless Steel Machining Services
Stainless steel CNC machining combines advanced computer-controlled precision with one of manufacturing’s most versatile and durable materials. This specialized process creates high-quality components with exceptional corrosion resistance, strength, and dimensional accuracy for demanding applications across industries.
Various Options
Functionality
Cost-effectiveness
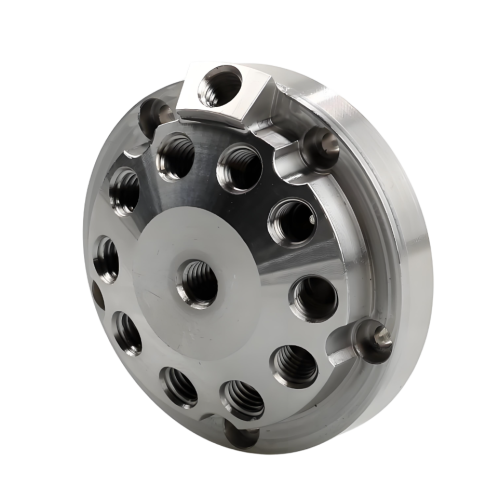


| Specification | Capability | Notes |
| Standard Tolerance | ±0.005″ (0.127mm) | General machining tolerance |
| Precision Tolerance | ±0.001″ (0.0254mm) | Available for critical features |
| Material Thickness | 0.020″ to 6.0″ (0.5mm to 152mm) | Varies by grade and application |
| Maximum Part Size | 24″ × 36″ × 18″ (610mm × 914mm × 457mm) | Larger sizes available upon request |
| Surface Roughness | Ra 0.8 to 3.2 μm | Finer finishes available with post-processing |
| Machining Equipment | 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machines | Selected based on part complexity |
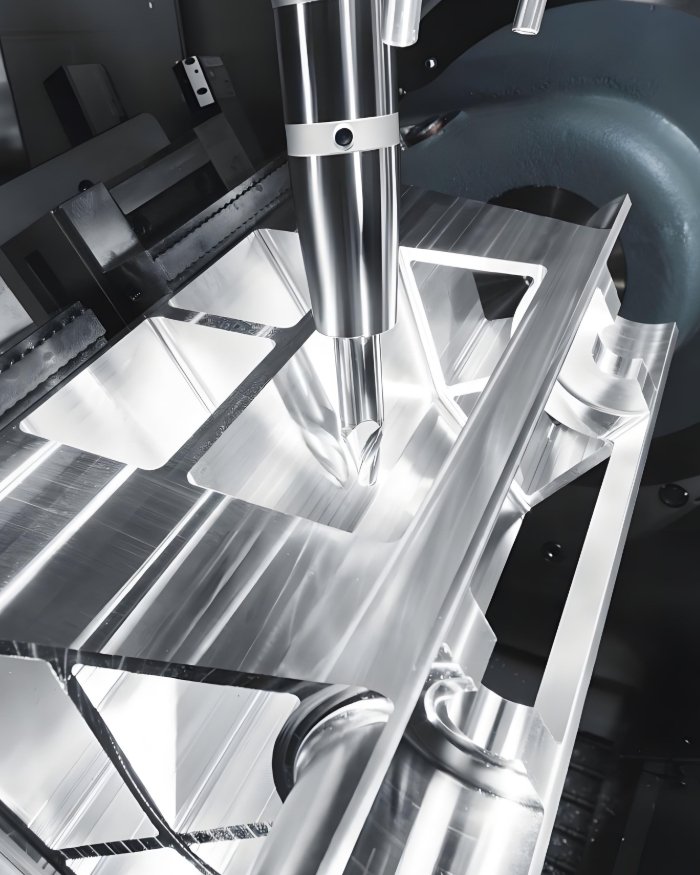
CNC Machining of Stainless Steel
Fecision stainless steel CNC machining services deliver custom components with tight tolerances, superior surface finishes, and consistent quality. Whether you need prototypes or production runs, our expertise ensures your parts meet exact specifications while maximizing the inherent benefits of stainless steel.
Our comprehensive approach to stainless steel CNC machining ensures consistent quality and precision through every stage of production. Each step is optimized specifically for the challenges of working with stainless steel materials.
Machining Process
- DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis
- Material selection guidance
- Tolerance optimization
- 3D model preparation
- CAM programming optimized for stainless steel
- Tool selection for specific steel grades
- Cutting parameter optimization
- Fixture design and setup
- Roughing operations with heavy material removal
- Semi-finishing to approach final dimensions
- Finishing passes for dimensional accuracy
- Feature-specific operations (threading, etc.)
- In-process inspection
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) verification
- Surface finish measurement
- Material certification verification
- Deburring and edge breaking
- Selected surface treatments
- Passivation for corrosion resistance
- Final cleaning and preparation
- Comprehensive quality documentation
- Custom packaging for protection
- Material traceability documentation
- On-time delivery logistics
Speak With Our Engineering Team
Discuss your project details with our expert CNC machining engineers.
Strengths and Limitations of Stainless Steel for CNC Machining
Strengths of Stainless Steel
- Exceptional corrosion resistance in harsh environments
- High strength-to-weight ratio compared to many metals
- Excellent heat resistance up to 1700°F (925°C) for certain grades
- Superior hygiene properties for medical and food applications
- Aesthetic appeal with various finishing options
- Long service life with minimal maintenance
- 100% recyclable material for sustainability
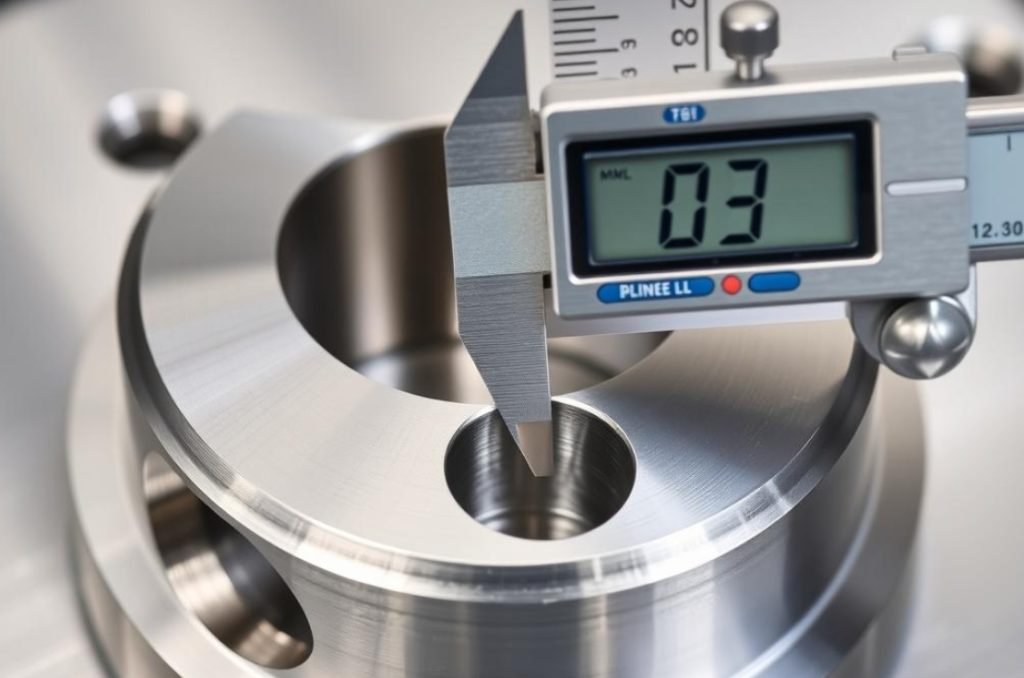
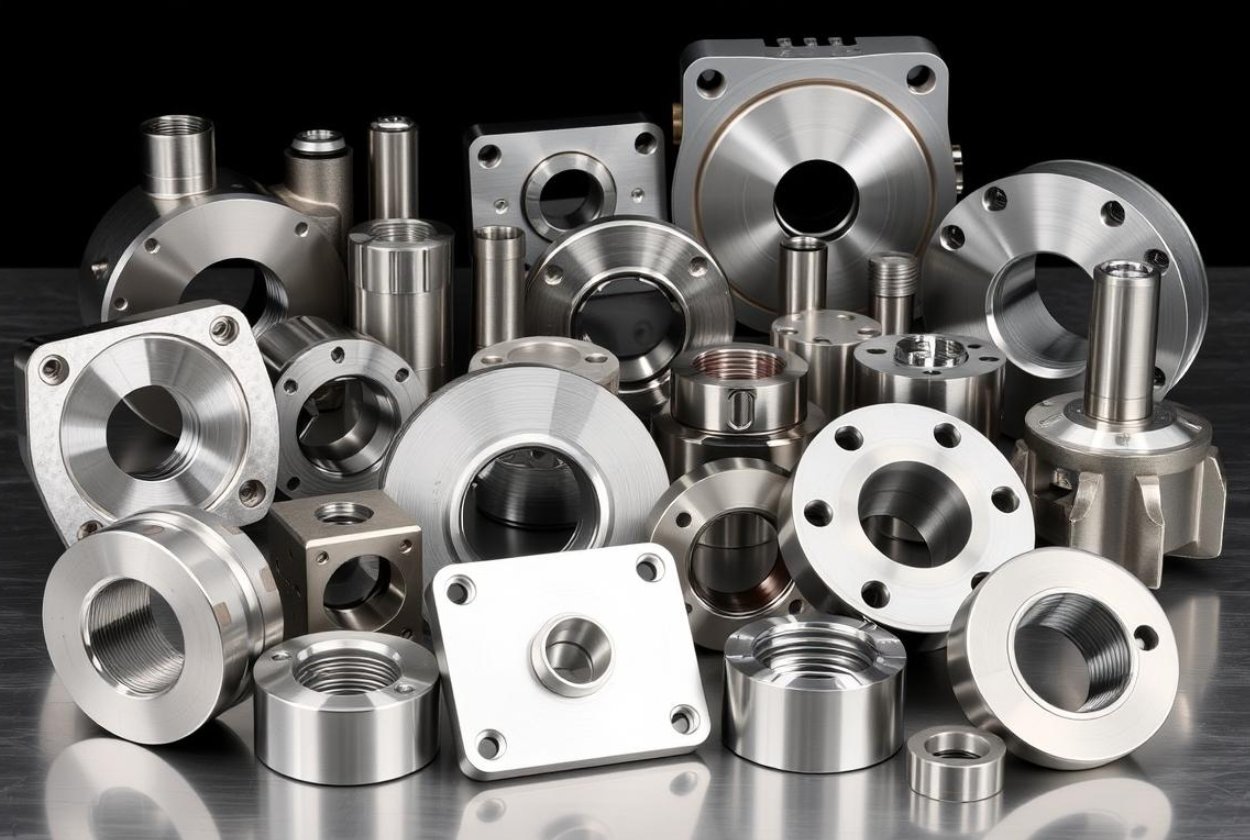


Limitations of Stainless Steel
- Work hardening during machining requires specialized techniques
- Accelerated tool wear compared to softer materials
- Higher machining costs versus aluminum or mild steel
- Poor thermal conductivity creates heat management challenges
- Stringy chip formation can complicate the machining process
- Some grades have limited machinability ratings
- Requires proper coolant and cutting strategies
Types and Grades of Stainless Steel for CNC Machining
Different applications require specific stainless steel grades to achieve optimal performance.
Our stainless steel CNC machining capabilities extend across all major types, each offering unique properties and machining characteristics.
Austenitic
Stainless Steels
- Characteristics: Non-magnetic, excellent corrosion resistance, high toughness, weldable and formable. Contains high chromium (16-26%) and nickel (8-25%). Most widely used stainless steel category.
- Common Applications: Food processing equipment, architectural trim, medical devices, chemical containers, marine components.
Grade
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
201
520-750
275
180
≤241
40
7.86
815
301
515-1380*
205
170-240*
≤207-430*
40-10*
7.93
870
303
515-655
205
170
≤201
40
7.93
870
304
515-720
205
170
≤201
40
7.93
870
304L
485-690
170
150
≤201
40
7.93
870
316
515-720
205
170
≤217
40
8.0
870
316L
485-690
170
150
≤217
40
8.0
870
Ferritic
Stainless Steels
- Characteristics: Magnetic, low cost (low or no nickel), good oxidation resistance, but limited toughness and weldability. Chromium content: 10.5-30%.
- Common Applications: Automotive exhaust systems, household appliances (refrigerator panels), decorative trim, heat exchangers.
Grade
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
403
415-635
240
170
≤183
20
7.7
815
409L
380-550
205
140
≤170
18
7.7
650
Martensitic
Stainless Steels
- Characteristics: Magnetic, heat-treatable (via quenching/tempering) for high hardness, moderate corrosion resistance. Chromium: 11-17%; higher carbon content than ferritics.
- Common Applications: Knives, valves, pump shafts, surgical instruments, bearings.
Grade
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
410
517-725
275
205
≤207
20
7.7
650
420
725-1035
485
275
≤235
12
7.7
600
440C
1790-2000
690
345
≤269
5
7.7
120
2Cr13
635-830
345
240
≤217
18
7.75
600
3Cr13
735-930
440
270
≤235
15
7.75
550
4Cr13
835-1080
540
300
≤255
12
7.75
500
Duplex
Stainless Steels
- Characteristics: Combined austenitic-ferritic structure (≈50% each), high strength (twice that of austenitics), excellent resistance to stress corrosion. Chromium: 21-27%; nickel: 4-7%.
- Common Applications: Oil/gas pipelines, desalination plants, chemical processing equipment, offshore structures.
Grade
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
2205
620-850
450
290
≤290
25
7.8
315
2507
800-1000
550
345
≤310
25
7.8
315
Precipitation Hardening
Stainless Steels
- Characteristics: High strength (via aging treatment to form precipitates), good corrosion resistance, moderate toughness. Used where strength-to-weight ratio is critical.
- Common Applications: Aerospace components (aircraft frames), high-pressure valves, precision molds, springs.
Grade
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
17-4 PH
860-1310
725-1100
380
270-388
10–15
7.8
315
17-7 PH
930-1380
760-1170
415
280-390
10-15
7.8
370
Surface Finish Options for Stainless Steel
The appearance and performance of stainless steel machined parts can be significantly enhanced through various finishing processes.
We offer comprehensive surface treatment options to meet aesthetic, functional, and corrosion resistance requirements.
Mechanical Finishes
- Polishing: Mirror (Ra 0.1μm) to satin (Ra 0.5μm) finishes
- Bead Blasting: Uniform matte texture (Ra 1.6-3.2μm)
- Brushing: Directional grain pattern for aesthetic appeal
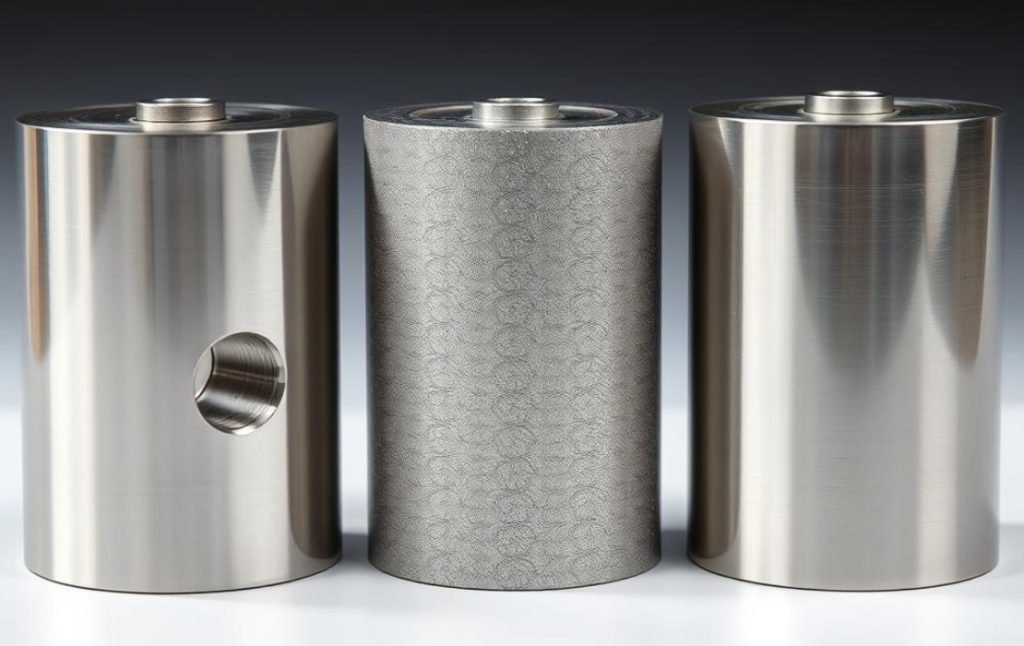

Chemical Treatments
- Passivation: Enhanced corrosion resistance
- Electropolishing: Microscopic smoothing and brightening
- Chemical Etching: Surface texturing and marking
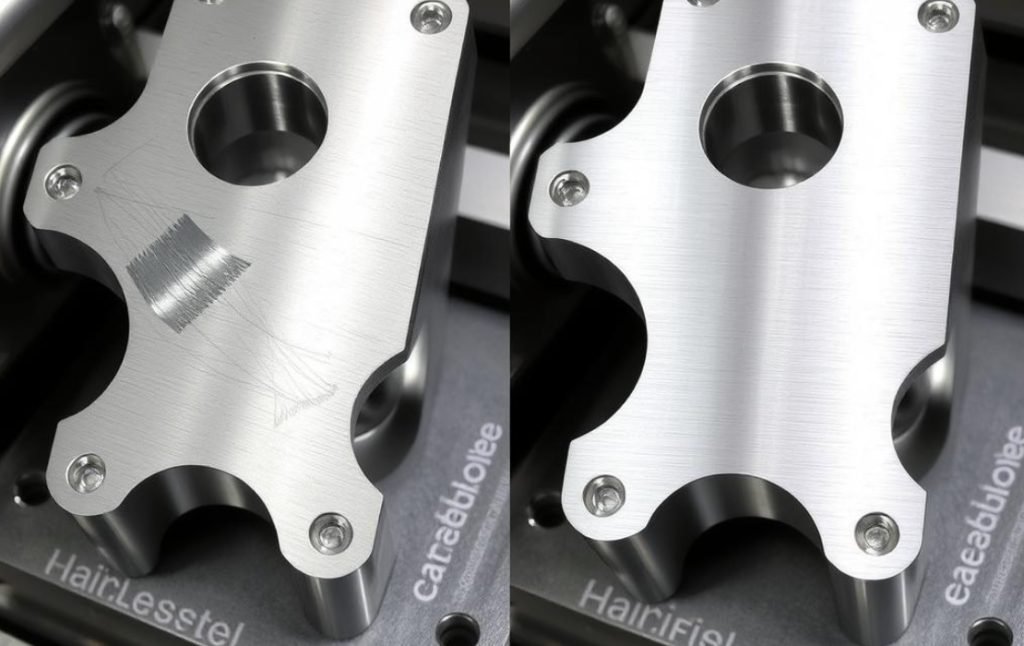

Coating Applications
- PVD Coating: Decorative and wear-resistant layers
- Powder Coating: Colored protective finishes
- Teflon Coating: Non-stick and chemical resistance
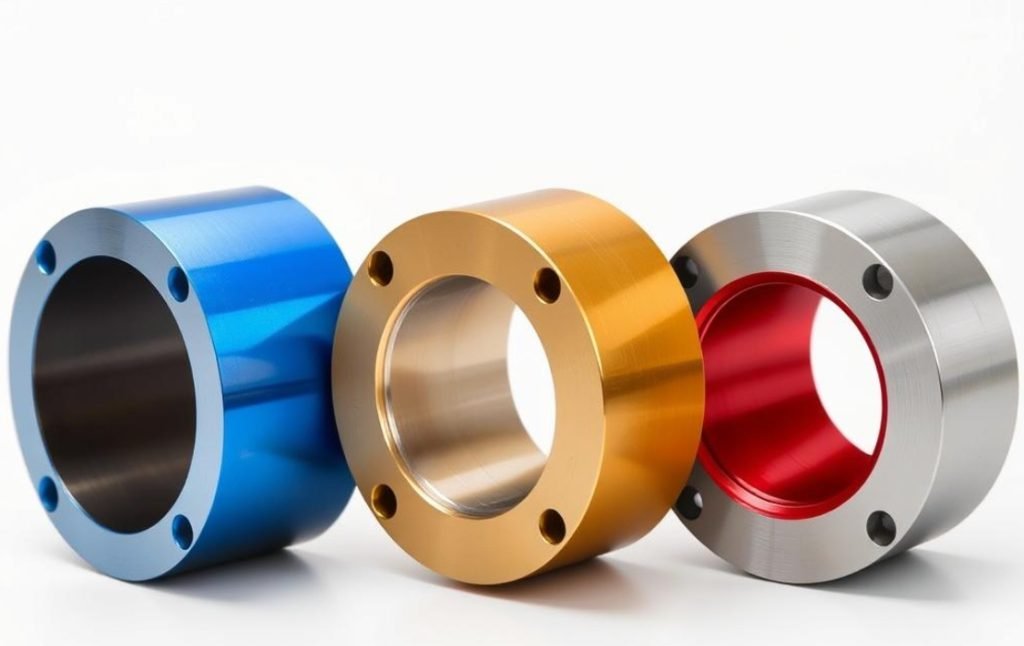

Applications of CNC Machined Stainless Steel Parts
The exceptional properties of stainless steel make it ideal for demanding applications across numerous industries.
Our CNC machining stainless steel expertise delivers precision components for critical applications where reliability and performance are essential.
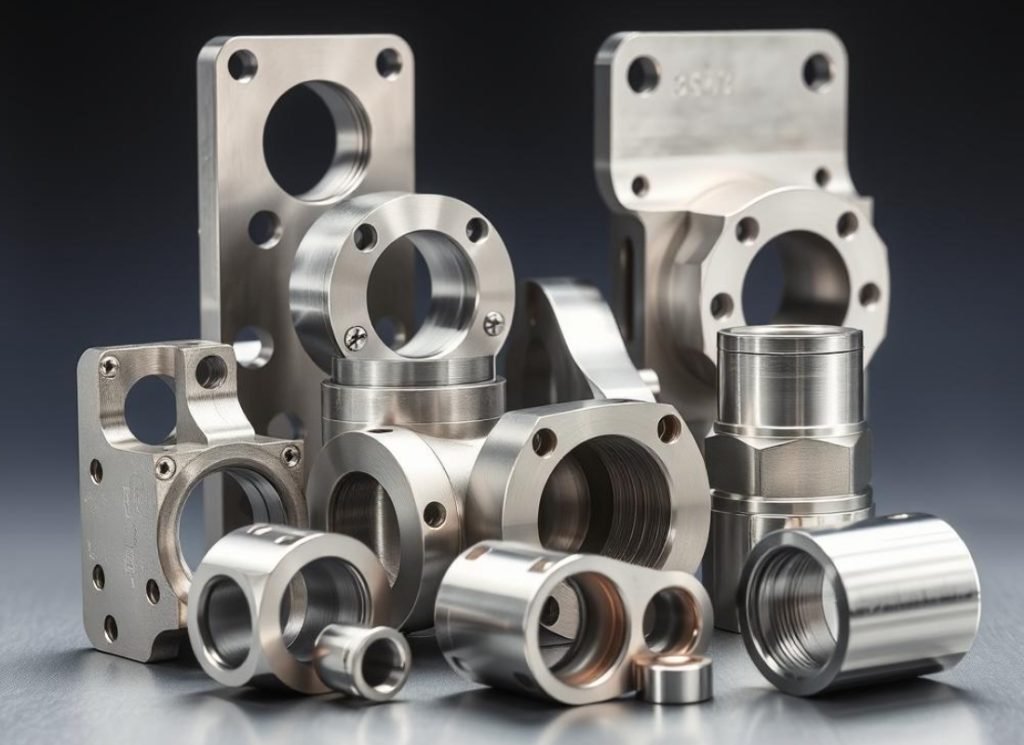

Aerospace & Defense
- Hydraulic system components
- Structural fasteners and brackets
- Fuel system components
- Navigation and control hardware
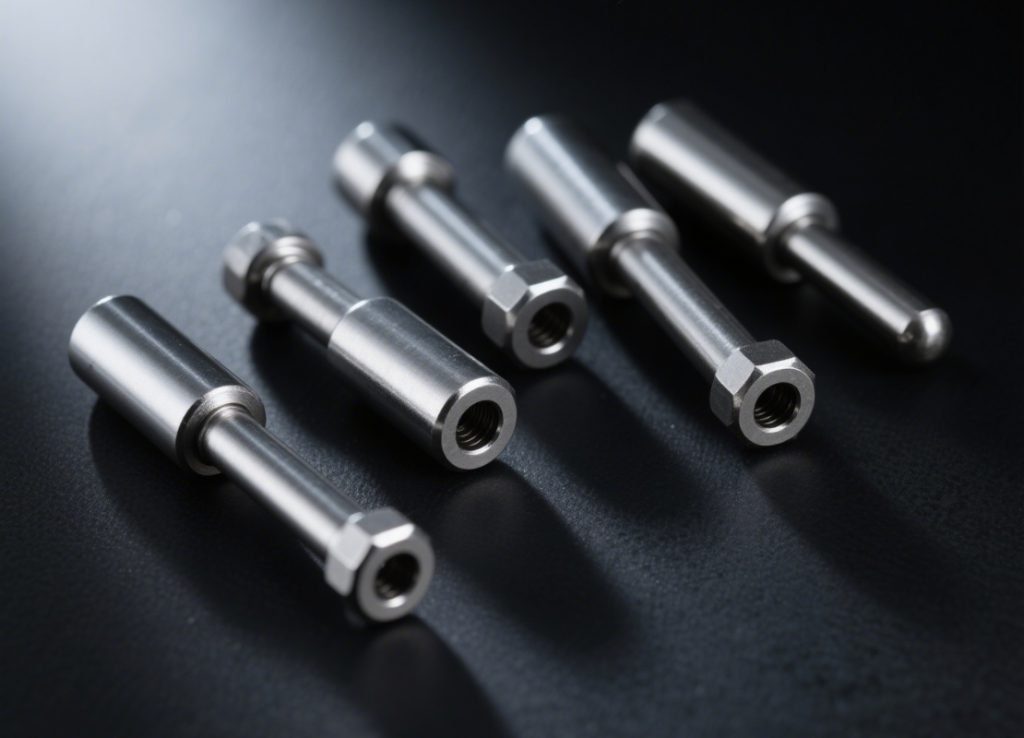

Automotive
- Exhaust system components
- Fuel delivery systems
- Turbocharger components
- Structural brackets and mounts

Medical
- Surgical instruments and implants
- Laboratory equipment components
- Pharmaceutical processing equipment
- Medical device housings and frames

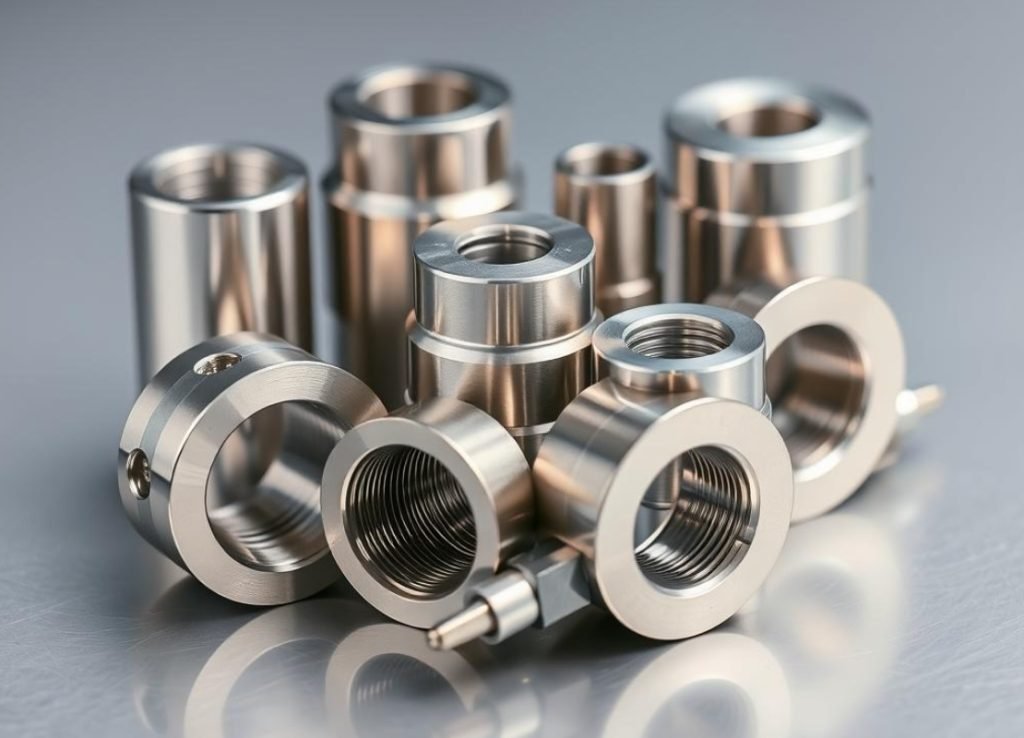
Chemical Processing
- Valve bodies and trim
- Pump components and impellers
- Heat exchanger parts
- Pressure vessel components
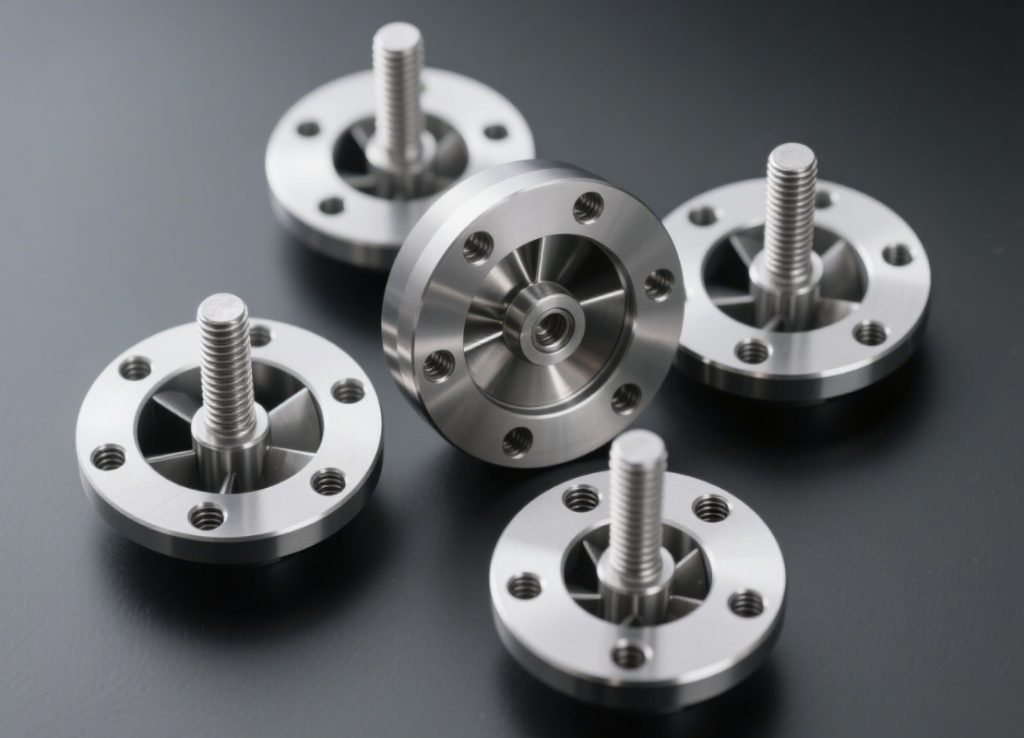

Marine & Offshore
- Pump and valve components
- Propeller and shaft hardware
- Deck equipment and fittings
- Underwater sensor housings
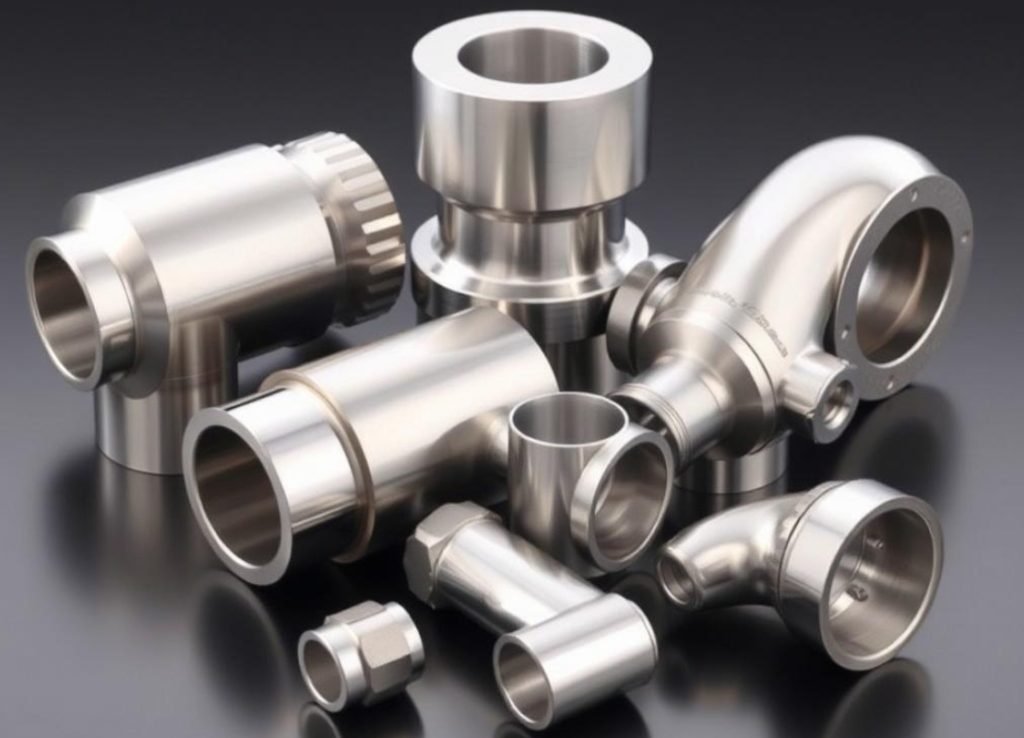

Food & Beverage
- Processing equipment components
- Sanitary fittings and valves
- Mixing and blending equipment
- Conveyor and handling systems
Stainless Steel Machining FAQs
Need to discuss stainless steel machinig project?
Our team of experts is ready to help you achieve exceptional results with your stainless steel components. From material selection to final delivery, we provide comprehensive support throughout your project.





Ready to Start Your Stainless Steel Machining Project?
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our specialized stainless steel machining capabilities can help you achieve your manufacturing goals with confidence.