Precision Compression Molding for Your Needs
Start your project now
ISO 9001:2015 Certified Processes
ISO 13485: 2016 Medical Device
IATF 16949: 2016 Automotive
AS9100 Quality Mangament
Faster Lead Time for Production Needs
In-Process Inspection with CMM
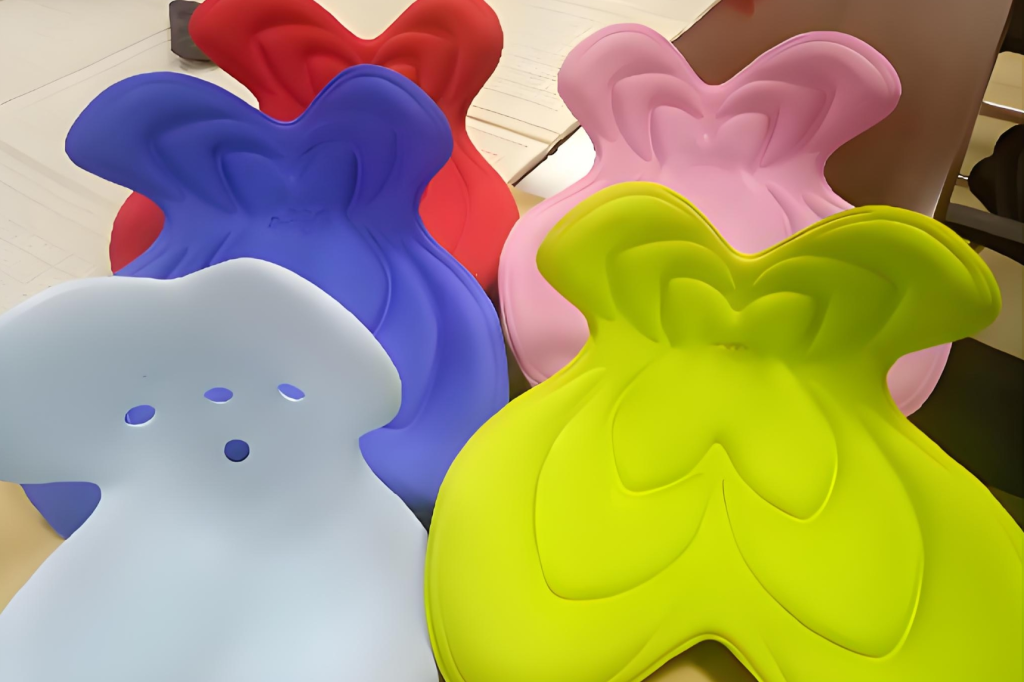

Custom Compression Molding Services
Compression molding is a manufacturing process where a preheated polymer material (thermoset or thermoplastic) is placed in an open mold cavity, then compressed and heated to form the desired shape. The mold closes under high pressure, curing the material into a solid product.
For high-precision components (e.g., automotive or aerospace parts), compression molding can be a good choice for superior dimensional stability, tooling costs, and scalability.
At Fecision, we specialize in custom compression molding services that deliver exceptional quality components for industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to consumer goods and medical devices.
Popular Features
Cost Efficiency
Ideal for large, flat parts (e.g., automotive panels) with low tooling costs and high-volume production.
Material Versatility
Compatible with thermosets (epoxy, phenolic), thermoplastics (PP, PVC), and composites (glass/carbon fiber-reinforced).
Uniform Stress Distribution
Minimizes warpage and enhances mechanical properties, critical for structural componentss.
The Compression Molding Process
The compression molding process combines precise temperature control, carefully calculated pressure, and expert material selection to create parts with exceptional structural integrity and surface finish. At Fecision, we've optimized each step of this process to deliver superior results.

Mold Design and Creation
Our engineering team designs and manufactures precision molds based on your part specifications, ensuring optimal material flow and dimensional accuracy.

Compression and Curing
The upper mold closes with controlled speed and pressure, forcing the material to fill the entire cavity. Heat and pressure are maintained for a specific time to ensure complete curing.

Material Preparation
We select and prepare the appropriate material (charge) based on your performance requirements, often preheating it to achieve optimal flow characteristics.

Cooling and Release
For thermoplastics, controlled cooling solidifies the part. For thermosets, the crosslinking reaction completes before the part is released.

Material Placement
The prepared charge is carefully positioned in the heated lower mold cavity, with precise measurement to minimize waste and flash.

Finishing
Any flash is removed, and additional finishing operations are performed as needed to meet final specifications.
Compression Molding with Insert Molding & Overmolding
At Fecision, we enhance the capabilities of traditional compression molding by incorporating advanced hybrid techniques like insert molding and overmolding.
These specialized processes allow for the creation of complex, multi-material components that deliver superior performance and value.
Insert Molding
This technique is ideal for creating parts with enhanced structural integrity, electrical conductivity, or specialized functionality without secondary assembly operations.
Overmolding
Fecision's overmolding capabilities allow for creating parts with selective reinforcement, improved ergonomics, vibration dampening, or enhanced aesthetic appeal.
Materials Used in Compression Molding
Compression molding accommodates a wide range of materials, each offering distinct performance characteristics. At Fecision, we help you select the optimal material for your specific application requirements, balancing factors like mechanical properties, temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Phenolic Resin (PF)
- Properties:
- Application:
② Automotive: Brake pads, clutch plates, distributor caps
③ Industrial Equipment: Gears, pump parts, high-temperature mechanical components

Melamine Formaldehyde (MF)
- Properties:
- Application:
① Consumer Goods: Dinnerware, trays, kitchenware
② Electrical Industry: Switches, sockets, lamp holders
③ Furniture / Decorative Panels: Laminates, panels, knobs

Polypropylene (PP)
- Properties:
- Application:
① Automotive: Bumpers, interior panels, battery trays
② Consumer Goods: Storage containers, appliance housings, reusable boxes
③ Packaging Industry: Food containers, caps, industrial packaging

Polyethylene (PE)
- Properties:
①LDPE is flexible, transparent, and has good chemical resistance.
②LLDPE offers enhanced strength and toughness compared to LDPE.
③HDPE is more rigid, has higher tensile strength, and excellent chemical resistance.
- Applications:
① Packaging Industry: Bottles, containers, shrink films
② Automotive: Fuel tanks, fender liners, protective covers
③ Consumer Goods: Cutting boards, toys, appliance housings

Polyester Resin (UP)
- Properties:
- Application:
① Automotive: Body panels, bumpers, under-the-hood covers
② Electrical Industry: Switchgear housings, insulating panels
③ Construction / Furniture: Decorative panels, laminates, sanitary ware

Epoxy Resin (EP)
- Properties:
- Application:
① Electrical Industry: Insulators, switchgear housings, transformer components
② Aerospace / Automotive: Structural reinforcements, composite panels
③ Industrial Equipment: High-strength tool components, machine housings

Polyurethane (PU)
- Properties:
- Application:
① Automotive: Bushings, seals, suspension mounts
② Consumer Goods / Sports: Wheels, handles, cushioning parts
③ Industrial Applications: Conveyor rollers, gears, wear-resistant liners

Urea-Formaldehyde (UF)
- Properties:
- Application:
① Electrical Industry: Circuit breaker housings, switchgear components, insulators
② Consumer Goods: Appliance handles, knobs, small household components
③ Furniture & Decorative Panels: Laminates, drawer pulls, decorative knobs

Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
- Properties:
② Exceptional chemical and corrosion resistance
③ Naturally flame-retardant and electrically insulating
- Application:
① Electrical & Electronics: Connectors, terminal blocks, insulating components
② Automotive: Pump housings, valve components, under-the-hood parts
③ Industrial Equipment: Gears, bearings, chemical-resistant machine parts

Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
- Properties:
② Excellent wear and chemical resistance
③ Superior dimensional stability and mechanical strength
- Application:
① Aerospace & Aviation: Structural components, insulation parts, bearings
② Automotive: Fuel system components, seals, under-the-hood high-temperature parts
③ Medical & Healthcare: Surgical instruments, implants, sterilizable device components

Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
- Properties:
② Excellent chemical and thermal resistance (up to 260°C)
③ Superior electrical insulation properties
- Application:
① Chemical & Process Industry: Seals, gaskets, valve seats, liners
② Automotive & Aerospace: Bearings, bushings, high-temperature insulation parts
③ Electrical & Electronics: Cable insulation, dielectric components, connectors
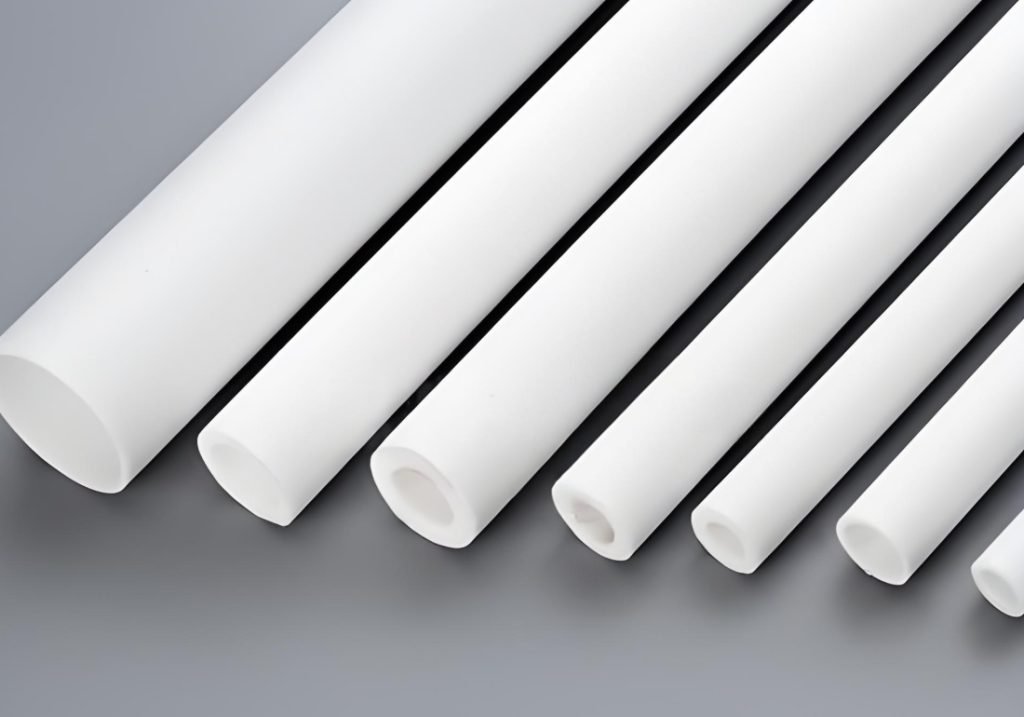

Silicone Rubber
- Properties:
- Application:
① Medical & Healthcare: O-rings, gaskets, tubing, seals for medical devices
② Automotive: Engine gaskets, seals, vibration dampers, hoses
③ Consumer Goods & Electronics: Kitchenware, appliance seals, keypads, protective covers
Need Help Selecting the Right Material?
Our materials expertise extends to specialized formulations with custom fillers, reinforcements, and additives to achieve specific performance characteristics. We can help you select materials that meet industry-specific requirements including FDA compliance, UL ratings, and automotive specifications.
Common Surface Finishes for Compression Molding

Electroplating
Depositing metal layers (e.g., chrome, nickel) onto plastic surfaces via electrolysis.
- Chrome Electroplating
- Nickel Electroplating

Spraying Coating
Spraying or electrostatic coating applies layers.
- UV Coating: Provides scratch resistance and glossy finishes.
- Metallic Paint: Adds aesthetic appeal with reflective surfaces.
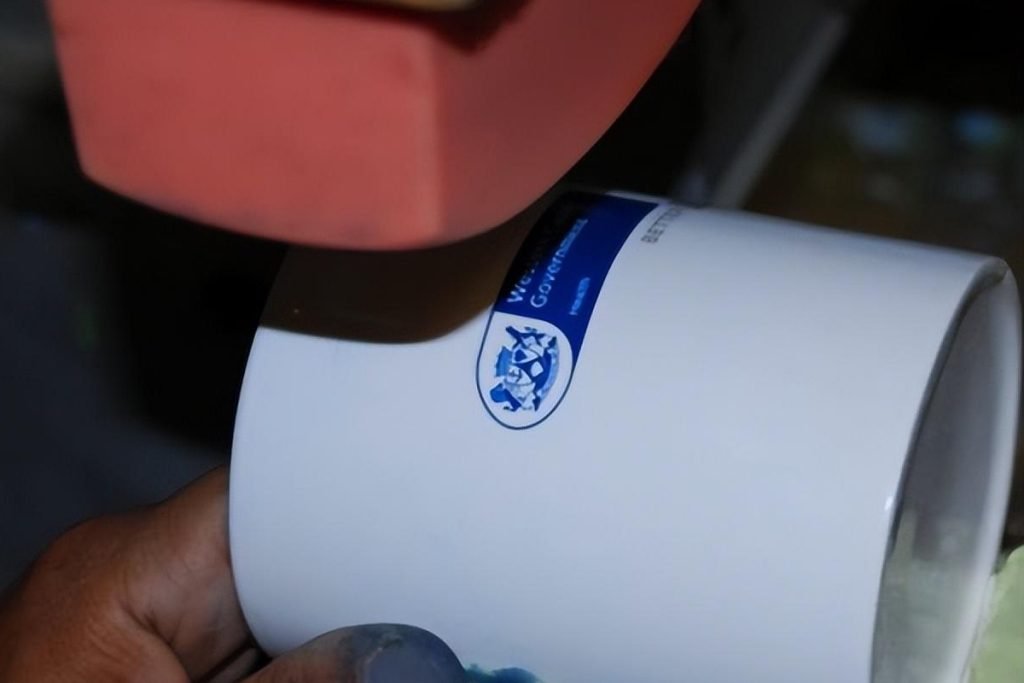

Pad Printing
Pad printing is an indirect offset printing technique that transfers ink from an etched plate (cliché) to a substrate using a silicone pad. It excels in printing on irregular, curved, or textured surfaces.

Laser Engraving
Laser ablation creates permanent markings (logos, serial numbers) without affecting structural integrity.

Hot Stamping
Hot stamping involves using heat and pressure to transfer a thin film or foil onto the surface of a substrate.

Vacuum Metallization (PVD/CVD)
Deposits thin metal or ceramic coatings (e.g., aluminum, titanium nitride) in a vacuum chamber.
Compression Molding Applications
Industries We Serve
Compression molding's versatility makes it ideal for a wide range of applications across multiple industries. At Fecision, we've developed specialized expertise in compression molding solutions for diverse market sectors.
Medical & Healthcare
Surgical instrument parts
Diagnostic equipment components
Laboratory equipment and fixtures
Orthopedic and prosthetic components
Automotive
Under-hood components
Interior trim and structural elements
Electrical housings and insulators
NVH (noise, vibration, harshness) components
Aerospace & Defense
Flame-retardant interior components
Electrical insulators and connectors
Radomes and antenna housings
Thermal protection components
Consumer Products
Appliance components and housings
Sporting equipment components
Tool handles and housings
Furniture components and fixtures
Electrical & Electronics
Switch and breaker housings
Terminal blocks and connector bodies
EMI/RFI shielding components
Heat-resistant electronic enclosures
Industrial Equipment
Wear plates and bushings
Chemical processing equipment parts
Conveyor system components
Heavy equipment guards and covers
Compression Molding Design Guide
Successful compression molded parts begin with design that accounts for the unique characteristics of the process.
Our engineering team works closely with clients to optimize designs for manufacturability while maintaining critical functional requirements.
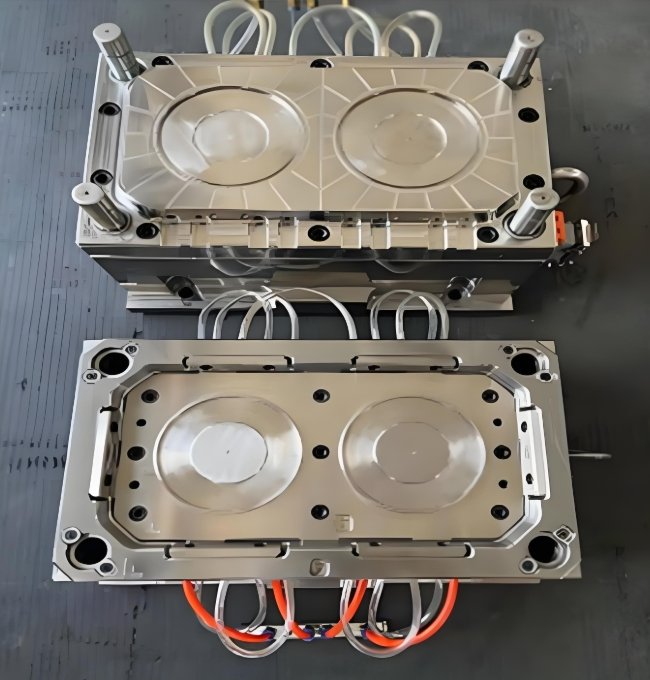

Key Design Considerations for Compression Molding
| Design Element | Recommendation | Rationale |
| Draft Angles | 2-5° minimum for thermosets 1-3° for thermoplastics | Facilitates part release from the mold without damage |
| Wall Thickness | Minimum 1.5mm (0.060″) Maximum 25mm (1.0″) | Ensures proper material flow and curing while preventing sink marks |
| Corner Radii | Minimum 0.8mm (0.030″) | Prevents stress concentration and improves material flow |
| Ribs & Gussets | 50-70% of wall thickness | Provides structural support while preventing sink marks |
| Undercuts | Avoid when possible Limited to 0.5mm (0.020″) max | Simplifies mold design and part ejection |
| Parting Line | Place at widest part cross-section | Optimizes material flow and minimizes visible flash |
Design Optimization Services
Fecision offers comprehensive design for manufacturability (DFM) services to optimize your parts for the compression molding process.
Review existing designs for compression molding compatibility
Recommend design modifications to improve quality and reduce costs.
Perform material flow and structural analysis simulations
Develop prototypes to validate design concepts
Create detailed mold designs optimized for your specific part requirements
Advantages of Compression Molding
- Superior Structural Integrity – Creates parts free of knit lines and flow-induced stress, resulting in exceptional strength and durability.
- Excellent for Fiber Reinforcement – Preserves fiber length and orientation, maximizing the mechanical properties of reinforced materials.
- Cost-Effective Tooling – Lower pressure requirements allow for less expensive tooling compared to injection molding, especially for large parts.
- Minimal Material Waste – Precise charge preparation results in very little material waste, reducing overall production costs.
- Large Part Capability – Well-suited for manufacturing large, flat, or slightly curved components that would be challenging with other processes.
- Excellent Surface Finish – Can produce Class A surfaces directly from the mold, reducing finishing requirements.
- Low Internal Stress – Parts exhibit minimal residual stress, resulting in better dimensional stability and performance.
- Material Versatility – Compatible with a wide range of thermosets and thermoplastics, including highly filled and reinforced compounds.
Limitations of Compression Molding
- Longer Cycle Times – Generally requires longer processing times compared to injection molding, affecting production rates.
- Design Constraints – Less suitable for parts with complex geometries, deep draws, or intricate details.
- Limited Undercuts – Significant undercuts are difficult to accommodate without complex mold designs.
- Flash Removal – May require secondary operations to remove flash from parting lines.
- Material Preparation – Requires precise measurement and preparation of the charge material.
- Thickness Variations – Can be challenging to maintain uniform wall thickness in complex parts.
- Initial Setup Time – Process parameter optimization may require more extensive setup time.
- Less Automation – Typically requires more manual operations compared to fully automated injection molding.
Compression vs. Injection Molding
While compression molding and injection molding are both effective plastic forming processes, they have distinct characteristics that make each better suited for specific applications. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the optimal manufacturing method for your parts.
| Characteristic | Compression Molding | Injection Molding | Best For |
| Process Principle | Material placed in open mold, compressed with heat | Molten material injected into closed mold cavity | Depends on part design and material |
| Suitable Materials | Excellent for thermosets, reinforced materials, and high-viscosity compounds | Best for thermoplastics and materials requiring precise flow control | Thermosets: Compression Thermoplastics: Either |
| Part Size | Well-suited for large, flat, or slightly curved parts | Better for smaller, more complex geometries | Large parts: Compression Small parts: Injection |
| Complexity | Limited complexity, minimal undercuts | Handles complex geometries, fine details, and undercuts | Complex parts: Injection Simple parts: Either |
| Cycle Time | Longer (typically 1-5 minutes) | Shorter (typically seconds) | High volume: Injection Low/medium volume: Either |
| Tooling Cost | Lower due to simpler mold design and lower pressure requirements | Higher due to complex mold design and high pressure requirements | Budget-sensitive: Compression High volume: Injection |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste, typically 2-5% | Higher waste from runners and sprues, typically 5-10% | Material efficiency: Compression |
| Structural Integrity | Superior, with no knit lines or flow-induced stress | Good, but may have knit lines at flow convergence points | Structural applications: Compression |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volumes | Medium to high volumes | High volume: Injection Low volume: Compression |
At Fecision, we offer both compression molding and injection molding capabilities, allowing us to recommend and implement the optimal manufacturing process based on your specific part requirements, production volumes, and budget considerations. Our engineering team can help evaluate your project needs and determine which process will deliver the best combination of quality, cost-effectiveness, and performance.
Why Fecision for Compression Molding?

Industry Expertise
Our team has years of experience across multiple industries, including automotive, medical, consumer goods, electronics, and packaging. We understand the unique challenges of each sector and offer expert solutions tailored to your needs.
Quality Assurance
Our products are trusted by high-profile customers from industries across Japan, Germany, the United States, and beyond, meeting strict and complete quality standard. Access to ISO 9001: 2015 quality certification and our manufacturing partners certified to ISO 13485: 2016, ISO 14001: 2015, and IATF 16949: 2016.
Sustainable Practices
We are committed to sustainability and offer eco-friendly plastic options, as well as processes that minimize waste and energy usage, making us a responsible partner for your business.
How to Work with Us
Submit Drawings
For a free quote, please submit a product description along with a technical drawing. We also offer reverse engineering services to assist you.
DFM & Quotation
We will provide a DFM (Design for Manufacturability) report or mold flow analysis report. Please be aware that further discussions may be needed during the process.
Mold Manufacturing
Upon your confirmation to the mold design, our team will begin making mold components, which will then be sent for inspection and assembly.
Compression Molding
Once the mold is complete, we will initiate the plastic molding process. A T1 sample will be provided for you to check whether the product details align with your specifications. After approval we will continue massive production.
Delivery
Your custom-designed plastic parts undergoes thorough inspection, will be carefully packaged, and delivered to you.
Recent Projects






Partner with Fecision for Your Compression Molding Needs
From concept development through production, our team provides comprehensive support for your custom compression molding projects. With state-of-the-art equipment, material expertise, and decades of manufacturing experience, we deliver high-quality parts that meet your exact specifications.
Compression Molding FAQs
Compression uses preheated material in an open mold, while injection forces molten material into a closed mold.
Low-viscosity thermoplastics (e.g., PET) may leak from molds.
Limited to moderate complexity; undercuts require specialized tooling.
Yes, robotic systems handle preform placement and part ejection.
Yes, for multi-material parts (e.g., rubber grips on plastic handles) .






