In the manufacturing industry, ensuring product quality is crucial. Did you know that a significant portion of product recalls and quality issues stem from inadequate planning during the design phase? This is where Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) comes into play.
APQP is a structured methodology that ensures your products meet customer requirements and are developed with quality in mind from the outset. Originally developed by major automotive manufacturers, this framework has become essential for industries with high-quality demands.
By adopting APQP, you can significantly reduce the risk of quality issues, minimize development time, and ensure consistent quality across production runs. This methodology bridges the gap between customer requirements and final product delivery, establishing clear communication channels and expectations between manufacturers and their supply chain partners.
Understanding Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
APQP serves as a bridge between customer requirements and the final product delivery, ensuring quality is maintained throughout the production process. This methodology is crucial for manufacturers aiming to optimize their product quality planning.
Definition and Origin of APQP
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) is a structured methodology aimed at ensuring product quality from the design phase through to production. Originating in the automotive industry, APQP has become a standard practice across various manufacturing sectors. It focuses on preventing quality issues rather than detecting them after production.
Core Principles of APQP
The core principles of APQP revolve around a proactive approach to quality planning. This involves cross-functional team collaboration, risk assessment, and the development of control plans. By adopting these principles, manufacturers can significantly reduce defects and rework, improving overall product quality.
The Significance of APQP in Manufacturing
APQP is significant in manufacturing as it provides a systematic approach to translating customer requirements into specific product characteristics and process parameters. This methodology not only enhances product quality but also reduces development time and costs. By implementing APQP, manufacturers can achieve faster product development cycles and higher customer satisfaction.
In summary, APQP transforms manufacturing operations by establishing a structured approach to quality planning, creating a common language across the organization and supply chain, and ensuring consistent quality across production runs.
When Is APQP Necessary?
The necessity of APQP arises in several key situations, particularly when changes occur in product development, manufacturing processes, or supply chain dynamics. Understanding when to implement APQP is crucial for maintaining product quality and ensuring customer satisfaction.
New Product Development Scenarios
In new product development scenarios, APQP plays a vital role in ensuring that quality is designed into the product from the outset. By applying APQP principles, you can identify potential quality issues early in the development process, reducing the risk of costly rework or product recalls. This proactive approach helps in creating a robust product design that meets customer requirements and regulatory standards.
Process and Product Changes
When making changes to existing products or manufacturing processes, APQP is essential for assessing the impact of these changes on product quality. Whether it’s modifying a product design or introducing new equipment into the production line, APQP helps you evaluate potential risks and implement necessary controls to maintain quality standards.
Supplier Changes and Technology Integration
APQP is also necessary when there are changes in suppliers or when integrating new technologies into your manufacturing process. By applying APQP, you can ensure that new suppliers meet your quality requirements and that new technologies are properly validated to prevent quality issues. This systematic approach helps in maintaining a robust supply chain and ensuring that production processes remain reliable and efficient.
Key Elements of Advanced Product Quality Planning
APQP’s effectiveness is rooted in its core elements, which are designed to enhance product quality and reliability. These fundamental components work together to ensure that your product quality planning is comprehensive and robust.
Cross-Functional Team Collaboration
Effective APQP requires collaboration among various departments, including design, manufacturing, and quality assurance. This cross-functional team collaboration ensures that all aspects of product quality are considered, from design to production.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies is crucial in APQP. This involves analyzing your process flow and product characteristics to pinpoint areas of risk and implementing controls to manage them.
Documentation and Control Plans
Comprehensive documentation and control plans are essential in APQP. Control plans detail process controls, quality checks, and response plans for out-of-control conditions, ensuring that your product meets quality standards. Proper documentation management is vital for maintaining these plans and supporting future quality planning activities.
By focusing on these key elements, you can ensure that your APQP is effective in driving product quality and reliability.
Essential APQP Techniques and Tools
Effective Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) involves utilizing various techniques and tools to drive quality and reliability. These methodologies are crucial for identifying potential failures, controlling processes, and ensuring accurate measurements.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic approach used to identify and evaluate potential failures in a product or process. By assessing the severity, occurrence, and detection of failure modes, FMEA enables proactive measures to mitigate risks, thereby strengthening APQP effectiveness.

Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a quality control technique that uses statistical methods to monitor and control processes. SPC helps detect deviations from the norm, enabling timely corrective actions to maintain process stability and ensure product quality.
Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)
Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) is a critical tool that ensures the accuracy and reliability of measurement data. MSA involves evaluating measurement systems through techniques like Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility (GR&R) studies, attribute agreement analysis, stability studies, and linearity studies. By validating measurement systems early in the APQP process, organizations can prevent invalid conclusions based on poor measurement data.
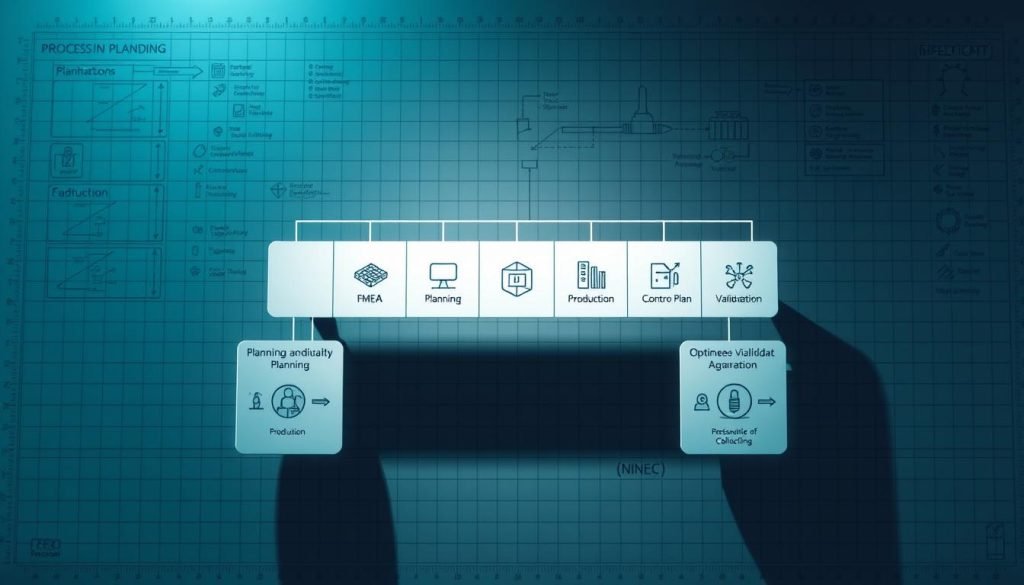
The 5 Phases of APQP
Effective product quality planning through APQP involves navigating five critical phases. These phases are designed to work together seamlessly to ensure that your product meets the highest quality standards from conception to delivery.
Phase 1: Planning and Program Definition
Phase 1 focuses on defining the project’s scope and objectives, ensuring that everyone involved is on the same page regarding “product quality planning.” This initial phase sets the foundation for the entire APQP process, emphasizing the importance of “quality” from the outset.
Phase 2: Product Design and Development
In Phase 2, the design of the “product” is developed and validated. This involves rigorous testing and analysis to ensure that the product meets customer requirements and is robust enough for production.
Phase 3: Process Design and Development
Phase 3 is all about designing and developing the “process” that will be used to manufacture the product. This includes creating detailed “process” maps and implementing controls to ensure consistency and “quality.”
Phase 4: Product and Process Validation
During Phase 4, both the “product” and “process” are validated to ensure they meet the requirements set out in earlier phases. This involves testing and “feedback” mechanisms to identify any areas for improvement.
Phase 5: Feedback, Assessment, and Corrective Action
Phase 5 closes the “feedback” loop, focusing on “continuous improvement,” “customer satisfaction,” and “assessment” of the product and “process.” It involves implementing “corrective action” when necessary and ensuring that lessons learned are documented for future “product quality planning” activities. This phase is crucial for achieving “customer satisfaction” and ensuring that the “process” remains effective over time.
By understanding and implementing these five phases, you can significantly enhance your product’s quality and your organization’s ability to meet customer needs effectively.
Implementing APQP in Your Organization
Implementing APQP in your organization requires a structured approach to ensure product quality and customer satisfaction. This involves several key steps that help in achieving high-quality products and reducing development time.
Creating an Effective APQP Team
To implement APQP successfully, you need to create a cross-functional team that includes representatives from various departments such as design, manufacturing, and quality assurance. This team will be responsible for overseeing the APQP process and ensuring that all necessary activities are completed.
Developing a Product Quality Plan
Developing a comprehensive product quality plan is crucial for APQP implementation. This plan should outline the specific quality objectives, identify potential risks, and detail the strategies for mitigating these risks. It should also include a detailed timeline and milestones for the project.
APQP Implementation Checklist
An effective APQP implementation checklist serves as a comprehensive roadmap, ensuring that all required activities are completed at each phase of the process. The checklist should include design requirements such as engineering drawings and design FMEA, process requirements like process flow diagrams and control plans, and validation requirements including measurement system analysis and production trial results.
By following these steps and utilizing a detailed checklist, you can ensure a successful APQP implementation that enhances your organization’s product quality and reduces time-to-market.
Benefits of Advanced Product Quality Planning
By adopting Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP), companies can experience substantial improvements in product quality and customer satisfaction. APQP is a structured methodology that helps organizations systematically plan and execute product development, ensuring that quality is integrated into every stage of the process.
Improved Product Quality and Customer Satisfaction
APQP focuses on understanding customer requirements and translating them into specific product and process characteristics. This approach ensures that the final product meets customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction levels. By using tools like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), organizations can proactively identify and mitigate potential quality issues, resulting in improved product reliability and performance.
Reduced Development Costs and Time-to-Market
The structured nature of APQP helps organizations streamline their product development processes, reducing the likelihood of costly rework and delays. By identifying potential issues early in the development cycle, companies can avoid expensive corrections later on. This proactive approach enables businesses to bring high-quality products to market more quickly, giving them a competitive edge.
Enhanced Risk Management and Communication
APQP provides systematic risk assessment tools like FMEA, enabling organizations to identify potential failure modes in both product design and manufacturing processes. The methodology’s structured approach to risk prioritization ensures that resources are focused on addressing the most critical quality risks. Additionally, APQP establishes clear communication channels between different functional groups, breaking down silos and ensuring that all perspectives are considered in quality planning decisions. This leads to faster decision-making, better alignment between departments, and more efficient problem-solving throughout the product development process.
Common Challenges and Solutions in APQP
The successful implementation of APQP requires overcoming several common challenges that organizations typically encounter. Effective APQP implementation demands a strategic approach to address these hurdles.
Resource Constraints and Management Support
One of the primary challenges is resource constraints and lack of management support. Organizations must allocate sufficient resources and ensure top management is committed to the APQP process. This involves dedicating necessary personnel and budget to support APQP initiatives.
Communication Barriers Between Departments
Communication barriers between departments can hinder APQP success. To overcome this, organizations should establish clear communication channels and foster collaboration among cross-functional teams. Regular meetings and updates can help ensure that all stakeholders are aligned.
Documentation Management and Best Practices
Documentation management is another significant challenge. Deploying electronic document management systems and establishing clear naming conventions and version control procedures can help. Standardized templates and formats for APQP documentation ensure consistency across projects. Best practices include regular documentation audits and electronic signature capabilities for approvals.
APQP Applications Across Industries
The versatility of APQP is evident in its widespread adoption across multiple industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As you explore the applications of APQP, you’ll find that its principles are adapted to meet the unique needs of each sector.
Automotive Industry Applications
In the automotive industry, APQP is used to ensure the quality and reliability of vehicles. It involves rigorous testing and validation processes to meet stringent safety and performance standards. By applying APQP, automotive manufacturers can reduce recalls and improve customer satisfaction.

Aerospace and Defense Implementations
Aerospace and defense industries utilize APQP to manage complex product development processes. The methodology helps in identifying and mitigating risks associated with the production of critical components. This ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and enhances overall product quality.
Medical Device and Electronics Manufacturing
Medical device manufacturers adapt APQP principles to meet FDA requirements and ISO13485 standards, focusing on patient safety and regulatory compliance. Electronics manufacturers apply APQP to manage rapid technology evolution and complex manufacturing processes. In both industries, APQP helps manage complex supply chains, ensuring that critical components meet precise specifications.
Conclusion
You now understand that Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) is a comprehensive framework that ensures product quality from concept to production. This methodology provides a structured approach to translating customer requirements into consistently manufactured products.
The APQP process emphasizes proactive quality planning, delivering significant benefits such as improved product quality, reduced development costs, faster time-to-market, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Its principles and tools have been successfully adapted across various manufacturing sectors, demonstrating the universal value of structured quality planning.
To successfully implement APQP, you need organizational commitment, cross-functional collaboration, and systematic application of quality planning tools throughout the product development process. As manufacturing complexity increases and customer quality expectations rise, APQP provides a proven methodology for managing these challenges and maintaining a competitive advantage through superior product quality and reliability.
By adopting APQP, you can ensure that your products meet customer requirements and are delivered on time, ultimately driving business success.
FAQ
What is the primary goal of Advanced Product Quality Planning?
The primary goal is to ensure that your product meets customer requirements and is produced with a robust process, minimizing the risk of defects and improving overall customer satisfaction.
How does Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) contribute to APQP?
FMEA is a critical tool used in APQP to identify potential failures in your product or process, assess their impact, and implement mitigation strategies to reduce risk.
What is the significance of Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) in APQP?
MSA is essential in APQP as it ensures that your measurement systems are accurate and reliable, providing a solid foundation for data-driven decision-making.
How does APQP impact product development costs and time-to-market?
By identifying and mitigating potential issues early on, APQP helps reduce development costs and accelerates time-to-market, ultimately improving your competitiveness.
What are the key elements of a successful APQP implementation?
A successful APQP implementation relies on cross-functional team collaboration, thorough risk assessment, and robust documentation and control plans to ensure that your product meets customer requirements.
Can APQP be applied to industries beyond automotive?
Yes, APQP has been successfully applied in various industries, including aerospace, defense, medical devices, and electronics manufacturing, to improve product quality and customer satisfaction.
How do you ensure effective communication between departments during APQP implementation?
Effective communication is achieved by establishing a cross-functional team, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and fostering a culture of collaboration and open feedback.
What are the benefits of using Statistical Process Control (SPC) in APQP?
SPC helps you monitor and control your process, identifying variations and enabling data-driven decisions to improve product quality and reduce waste.




