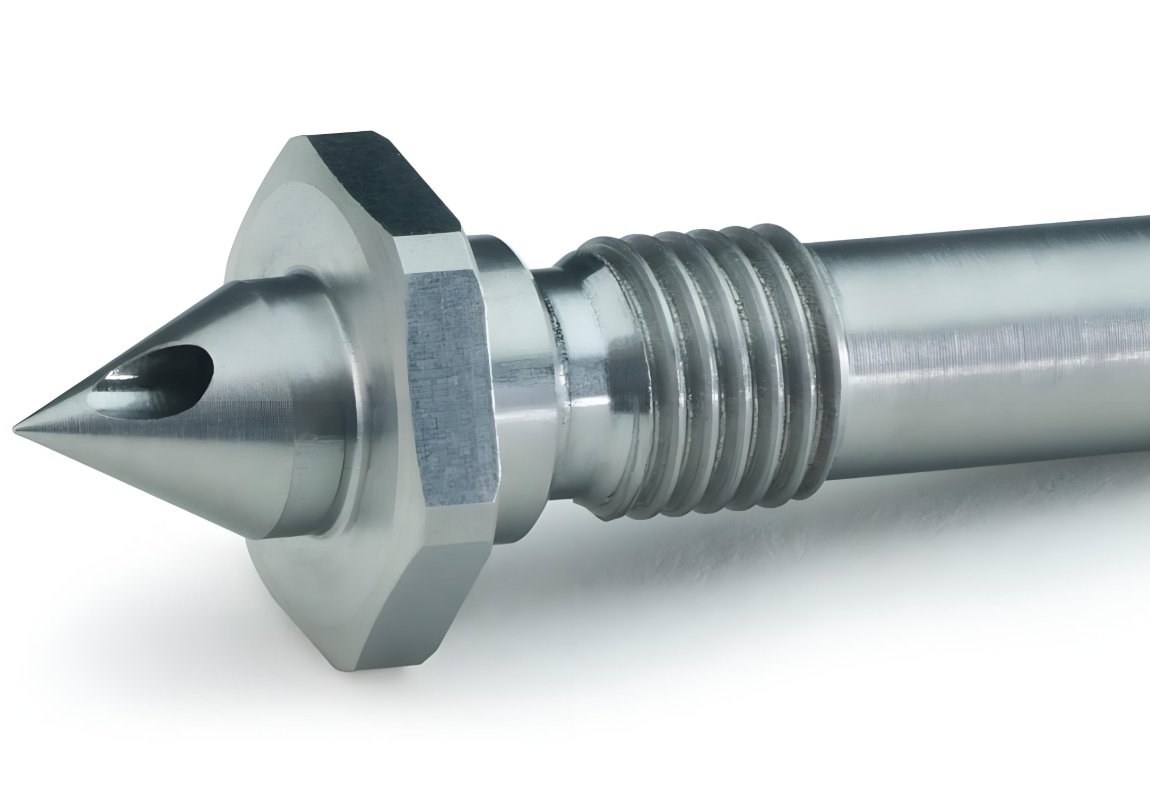
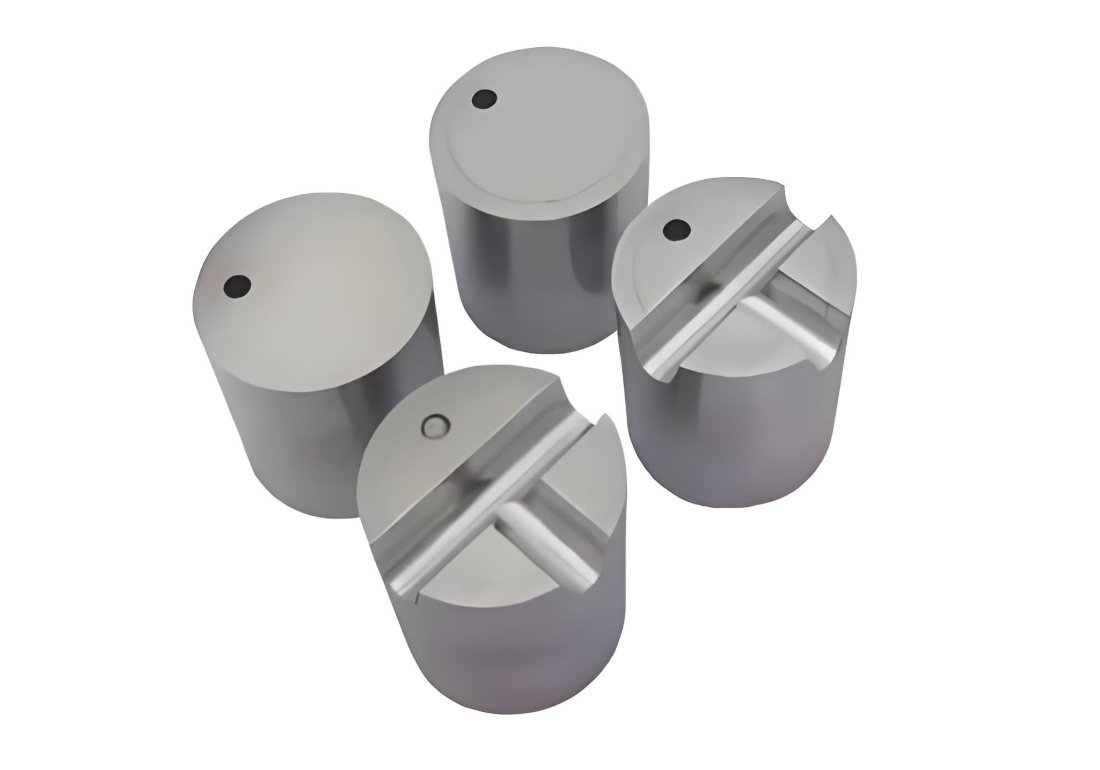
Sprue Bushings
- Thermal Efficiency: Maintains stable temperatures for consistent material flow.
- Precision Fit: Provides a leak-proof seal with the nozzle for flawless operation.
- Durability: Withstands high pressures and temperatures during prolonged use.
- Versatile Design: Adapts to various mold setups and plastic types.
Expert Craftsmanship
20+ Years of Expertise
Tailored Solutions
Custom designs
Rigorous Quality Control
ISO 9001-Certified Quality
Competitive Pricing
Cost-effective solutions
Global Support
Reliable delivery & technical assistance
ISO 9001:2015 Certified Processes
ISO 13485: 2016 Medical Device
IATF 16949: 2016 Automotive
AS9100 Quality Management
No Minimum Order Quantities
In-Process Inspection with CMM
Sprue Bushings for Precision Injection Molding

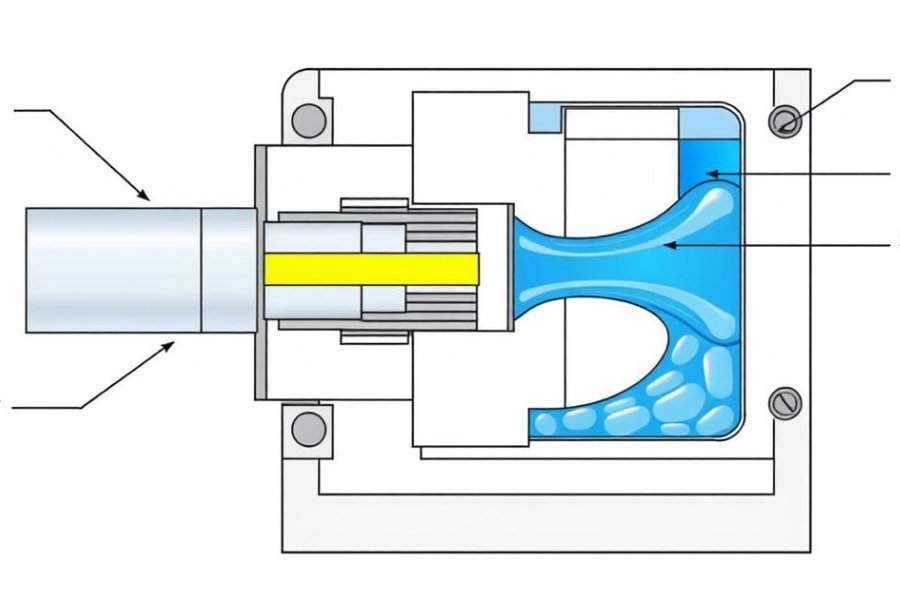
The sprue bushing consists of three key components: the nozzle seat (which interfaces with the injection machine), the melt channel (through which plastic flows), and the sprue taper (which facilitates part ejection). Its design must balance thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and precise dimensional tolerances to ensure consistent production quality.
Channels molten plastic into the runner system efficiently
Minimizes material waste with a streamlined flow path
Supports high-speed production without compromising quality
Reduces defects by ensuring uniform material distribution
How Does A Sprue Bushing Work?
During the injection molding process, the sprue bushing facilitates the critical first stage of plastic flow. When the injection cycle begins, the machine nozzle presses against the sprue bushing's spherical radius seat, creating a pressure-tight seal. As the screw advances, molten plastic material flows through the bushing's internal channel and into the mold's runner system.
The sprue bushing's tapered internal design serves two essential functions. First, it ensures smooth material flow by gradually reducing the channel diameter. Second, it creates a natural release angle that allows the solidified sprue to separate cleanly during mold opening. This taper typically ranges from 2° to 5° depending on the specific material requirements.
Thermal management is another crucial aspect of sprue bushing operation. The component must maintain proper temperature to prevent premature material solidification (which causes short shots) or excessive heat (which leads to material degradation). Many advanced sprue bushings incorporate cooling channels or specialized materials to optimize thermal performance.
Types of Sprue Bushings
Standard Sprue Bushings
Standard sprue bushings feature a simple design with a spherical radius seat that matches the injection machine nozzle. Available in various sizes and configurations, these workhorses of injection molding are suitable for most general applications.
✅ Bolt fixing or shoulder type mounting
✅ Typically made from H13 or P20 tool steel
✅ Standard taper angles for common plastics

Cold Runner Sprue Bushings
Cold runner sprue bushings are designed for traditional molding systems where the runner solidifies with each cycle. These bushings often feature optimized cooling and ejection characteristics to ensure clean sprue separation.
✅ Enhanced cooling designs for faster cycles
✅ String eliminator options available
✅ String eliminator options availablev

Hot Runner Sprue Bushings
Hot runner sprue bushings incorporate heating elements to maintain plastic in a molten state throughout the runner system. These specialized components eliminate the need for sprue and runner recycling, reducing material waste and cycle times.
✅ Integrated or external heating options
✅ Thermal isolation from surrounding mold
✅ Specialized materials for thermal conductivity

Premium Material Options for Sprue Bushings
Selecting the right material for your sprue bushing is critical for optimal performance and longevity.
While standard tool steels like H13 and P20 are suitable for most applications, specialized materials offer significant advantages for challenging molding scenarios.
P20 Tool Steel
Best for large molds with standard requirements
H13 Tool Steel
Best for general purpose applications
420 Stainless Steel
Best for corrosive materials, medical applications
Beryllium Copper
Best for high thermal conductivity needs
Tungsten Carbide
Best for abrasive materials, extended wear life
Not Sure Which Material Suits Better?
Speak with our engineering team and discuss your specific project needs.
Advanced Surface Treatments
The right surface treatment can extend sprue bushing life while significantly reducing maintenance requirements and improving part quality.

Nitriding
This thermochemical process diffuses nitrogen into the surface of the sprue bushing, creating a hard case layer with excellent wear resistance. Nitrided sprue bushings typically achieve surface hardness values of 65-70 HRC while maintaining core toughness.
★Benefits: Increased surface hardness, improved wear resistance, enhanced corrosion protection, and minimal dimensional change.
DLC Coating
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings provide an ultra-hard, low-friction surface that significantly reduces wear and prevents material adhesion. This thin film coating (typically 2-4 microns) offers exceptional performance for challenging materials.
★Benefits: Extremely low coefficient of friction, outstanding wear resistance, excellent chemical resistance, and improved material flow.
Polishing
Precision polishing creates an ultra-smooth surface finish that enhances material flow and prevents sticking. For sprue bushings, mirror-like finishes with Ra values below 0.1μm are often specified for optimal performance.
★Benefits: Improved material flow, reduced sticking, easier part ejection, and enhanced appearance of molded parts.
Design Tips for Optimal Sprue Bushing Performance
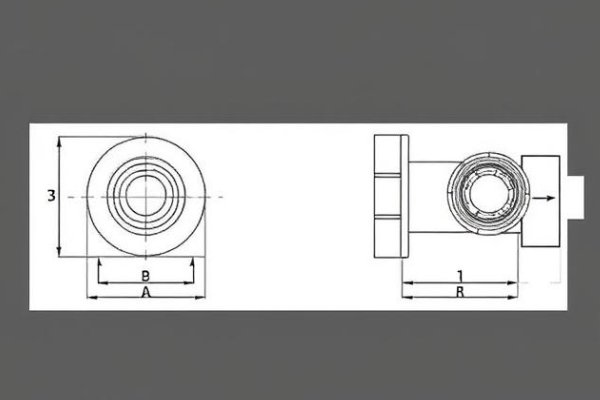
Proper Sizing
The sprue bushing orifice diameter should be sized according to the part volume and material characteristics. As a general rule, the minimum diameter should be 1.5mm larger than the maximum wall thickness of the part, but never less than 3mm to prevent premature freezing.
Optimal Taper Angle
The internal taper of the sprue bushing should be designed with a draft angle between 2° and 5°. This range provides the ideal balance between material flow and part release. For crystalline materials like PP or PA, use angles closer to 5° to facilitate easier ejection.
Nozzle Seat Radius
The spherical radius of the sprue bushing seat must match or be slightly larger (0.5-1mm) than the injection machine nozzle radius. This ensures proper sealing during injection while preventing damage to either component.
Cooling Considerations
Effective cooling around the sprue bushing is essential for cycle time optimization. Design cooling channels to maintain consistent temperature without creating hot spots or excessive cooling that could cause premature freezing.
Material Selection
Match the sprue bushing material to your specific application requirements. Consider factors like thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and compatibility with the plastic material being processed.
Mounting Method
Choose between bolt-fixed or shoulder-type mounting based on your mold design and maintenance requirements. Bolt-fixed designs offer easier replacement, while shoulder types provide better alignment stability.
Fecision Mold Component Tooling Network
In response to different service types and diverse business needs, we have deployed suppliers with different manufacturing capabilities.








Common Mistakes to Avoid with Sprue Bushings

Best Practices
- Match bushing material to processing requirements
- Ensure proper nozzle-to-bushing radius matching
- Implement adequate cooling around the bushing
- Maintain proper venting to prevent air traps
- Use appropriate surface treatments for material type
- Schedule regular inspection and maintenance
- Document specifications for future replacement
Common Mistakes
- Incorrect sizing of sprue orifice diameter
- Mismatched nozzle and bushing radius
- Insufficient draft angle for material type
- Poor cooling design causing cycle time issues
- Using standard materials for abrasive plastics
- Neglecting maintenance until failure occurs
- Improper installation causing misalignment
Custom Sprue Bushing Solutions
While standard sprue bushings work well for many applications, custom designs can significantly improve performance for specialized requirements.
Our engineering team develops custom sprue bushing solutions that address specific challenges in your injection molding process.
Thermal-Optimized Bushings
Custom cooling channel designs that maintain ideal material temperature throughout the injection cycle, preventing premature freezing while optimizing cycle times.
Wear-Enhanced Bushings
Specialized material combinations and surface treatments designed specifically for highly abrasive materials, offering 5-10x longer service life than standard options.
Application-Specific Designs
Custom geometries, special mounting configurations, and unique features tailored to your specific mold design and production requirements.
FAQs for Sprue Bushings
Ready to Optimize Your Injection Molding Process?
Contact our engineering team to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our custom sprue bushing solutions can improve your production efficiency.
Why Fecision for Mold Components?

Precision and Accuracy
Using state-of-the-art CNC machining, EDM, and other advanced manufacturing techniques, Fecision ensures all mold components meet tight tolerances and high-quality standards.
Customization
Fecision understands the unique needs of each project. Our team works closely with customers to provide tailored solutions, ensuring that each component fits perfectly within the target mold system.
Rapid Prototyping
Fecision offers rapid prototyping for mold components, enabling customers to test and refine designs quickly before moving into full production.
End-to-End Services
From initial design and DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis to final mold assembly and testing, Fecision handles every aspect of the mold component manufacturing process.
Process for Manufacturing Mold Components
Manufacturability Evaluation
The initial step involves assessing the manufacturablity of the mold component. If it's deemed feasible, we proceed with production immediately. If not, we will provide a detailed DFM (Design for Manufacturability) report to the customer. If necessary, mold flow analysis is performed to simulate the flow of molten material within the mold.
Material Selection
Next, choose the right material for mold parts. Common materials for mold components include steel alloys, aluminum, stainless steel, specialty alloys, etc. If needed, a prototype may be made using rapid prototyping techniques (e.g., 3D printing, CNC machining) to test the design for fit, function, and manufacturability.
Mold Components Manufacturing
Once the design and materials are finalized, the mold component undergoes CNC machining. If required, the mold component may undergo heat treatment, depending on the material and intended application. For certain components, surface hardening methods such as nitriding or carburizing are applied to increase wear resistance.
Shipping
For molds with multiple components, such as multi-cavity molds or molds with inserts, the individual components are carefully assembled into the final mold system. Once our engineers confirm the product meets all requirements, it will be shipped. We maintain ongoing communication to ensure the customer is fully satisfied with the product they receive.
Expert Sprue Bushing Solutions
With over 20 years of experience in injection mold component design, our team can help you select or create the perfect sprue bushing for your application.



