Sheet metal stamping dies to shape the products we use daily, from car parts to home appliances. These specialized industrial tools are crafted from tool steel and carbide. They turn ordinary metal sheets into precisely engineered components.
Sheet metal stamping dies require extensive expertise to create. This article explores the process of making a sheet metal stamping die. You’ll learn about material selection, component creation, and quality control measures. These steps help produce stamping dies that work effectively in manufacturing environments.
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies Overview
Sheet metal stamping dies are precision tools that shape and cut metal sheets into specific profiles. These specialized tools are built from hardened tool steel or carbide materials and operate without adding heat to the process.
What Is A Stamping Die
A stamping die is a precision-engineered tool that shapes sheet metal through cutting and forming operations. These tools come in many sizes—you’ll find compact ones small enough to hold in your palm for microelectronics, while others used for automobile body parts can span 20 square feet with a 10-foot thickness.
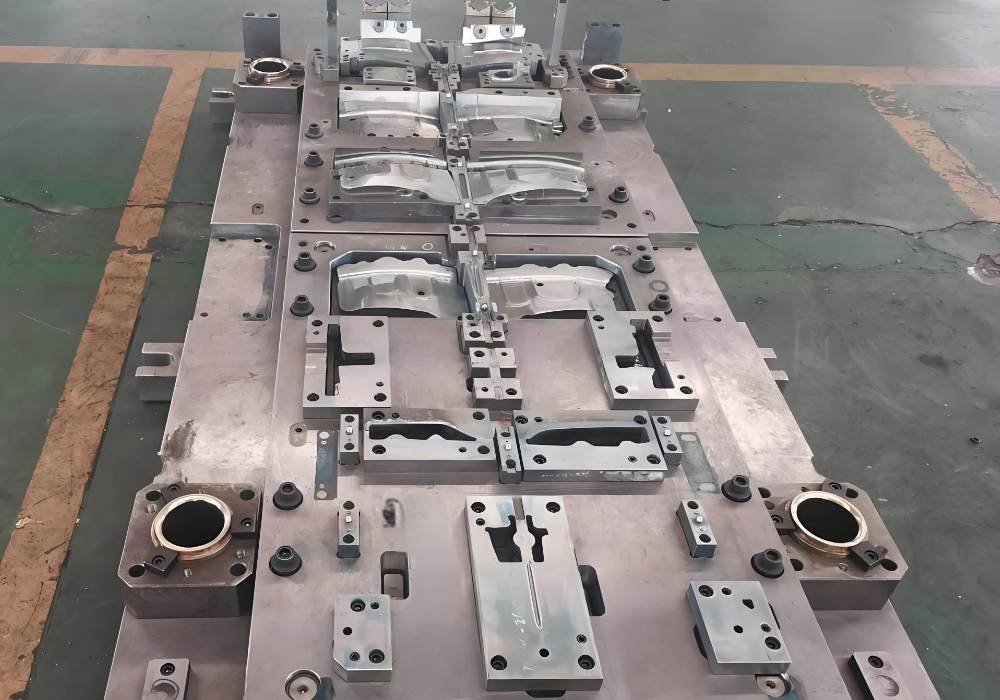

Key Components
Everything in stamping dies depends on several components that work together seamlessly:
- Die Block and Holder: The die block creates the female portion at the bottom of the assembly and contains holes and protrusions. A bolster plate secures the die holder that supports this block.
- Die Plates: These parts are the foundations for mounting other die tools. Steel or aluminum die plates need precise machining to maintain critical tolerances.
- Guide Posts and Bushings: These elements work together to keep upper and lower die components perfectly aligned. The guide posts are crafted with 0.0001 inches of precision and come as friction pins or ball-bearing-style pins.
- Die Springs: These helical, high-force compression springs hold metal sheets firmly during shaping and absorb shock and vibration.
How Does Stamping Die Work?
The process starts with the die mounted in a press. The workpiece moves through the open die and advances incrementally with each press stroke. The die follows a clear sequence:
- The press moves upward and opens the die
- The workpiece moves through the open die
- The press moves down and closes the die
- The tool shapes the workpiece as needed
Dies can create various shapes through embossing, coining, bending, and cutting. The cutting process typically needs a clearance of about 10 percent between the bypassing tool steel sections – this matches the metal’s thickness.
While stamping is a cold-forming process, the friction from cutting and forming often makes parts hot as they exit the dies. Modern stamping dies are incredibly efficient – some types can make more than 60 parts every minute.
Planning Your Die Design
Sheet metal stamping die creation starts with smart planning. You really need to think over multiple factors to make sure the die performs well and lasts long.
Analyzing part requirements
Engineers must get into the part print details and focus on part geometry, specified tolerances, and material specifications. A detailed evaluation helps determine if sheet metal stamping is the best manufacturing method for the component. Stamping becomes budget-friendly for high-volume production. Low-volume parts might work better with alternative methods like press brake bending or welding.
Material selection criteria
The right die materials substantially impact the tool’s performance and how long it lasts. Tool steels are the most common choice because they’re affordable and easy to machine. Aluminum die sets weigh just one-third of steel and are great for high-speed stamping operations. They also absorb shock better.
Key factors in material selection include:
- Tensile strength and hardness requirements
- Formability and machinability characteristics
- Thermal conductivity properties
- Cost considerations within the project budget
Design considerations
Die design process needs attention to several vital elements:
Designers must ensure proper clearance between punch and die components. Standard clearance equals 10% per side for mild steel. Higher-strength steels might need clearances above 20% per side.
On top of that, the design must account for:
- Die set thickness based on required tonnage and support requirements
- Balanced work distribution across the tool that ensures even closure on all corners
- Strategic placement of holes and grooves while keeping minimum distances of twice the material thickness to prevent deformation
- Cooling channels for heat dissipation, especially when you have hot stamping operations
Modern die design uses computer-aided design software and analytical programs to create highly accurate, clear designs. These tools let you test and simulate virtually before physical production, which reduces potential problems.
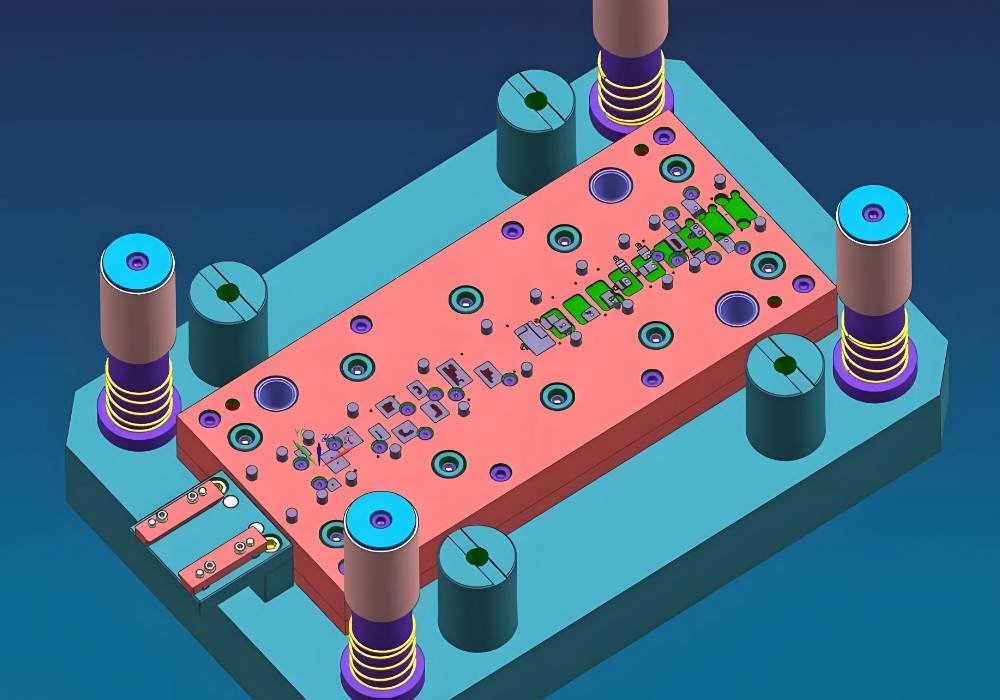
Creating the Die Components
Sheet metal stamping dies to blend precision engineering with expert craftsmanship during component creation. Each part needs careful attention to detail. The components must perform flawlessly under high-pressure conditions.
Making the die block
The die block forms the stamping tool’s foundation and needs the right material choice and precise machining. Most manufacturers choose high-strength steels like A2 or D2 tool steel because they last exceptionally long. CNC machining starts the process by cutting the die block to match the design’s exact specifications.
Die inserts fit strategically within the block after the original shaping creates specific features. These hardened steel inserts need perfect positioning within preset locations to keep tight tolerances. The whole die block then goes through heat treatment. This critical process makes the block stronger and more durable through controlled heating followed by rapid cooling.
Crafting punch elements
Punch components act as the male portion of the die assembly and need equally precise manufacturing methods. Hardened steel or tungsten carbide creates these elements that must keep exact dimensions. The proper clearance with corresponding die cavities depends on this precision.
Punch creation focuses on these important aspects:
- Material selection matches specific application needs
- Precise nose shapes come in round, oblong, square, rectangular, or hexagonal forms
- Die springs integrate to distribute force optimally
- Retainers are installed to hold components firmly
Specialized fasteners and dowels mount these components onto die plates. Hardened, precision-ground dowels ensure accurate positioning. High-quality alloy steel creates die retainers that secure the cutting and forming components while preventing stacking tolerance errors.
Quality control measures remain strict throughout component creation. Every element is inspected thoroughly to check dimensional accuracy and surface finish quality. All components must work perfectly together since small deviations could affect the stamping operation’s success.
Testing and Quality Control
Quality assurance is the lifeblood of successful sheet metal stamping die manufacturing. Each die undergoes testing procedures after assembly to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Original testing procedures
Sample sheet metal runs verify accuracy and consistency in the testing phase. Operators must confirm proper die setup by checking key parameters. They need to verify die shut height, stop block lead readings, press tonnage readings, and ensure the die stays flush against positive location stops.
Manufacturers use specialized tools like solder strips and set blocks with grooved surfaces to calibrate precisely. Set blocks ground to specific heights to help measure and adjust die-shut heights accurately. Pressure-sensitive films reveal detailed pressure distribution data that helps technicians identify areas needing adjustment.
Common defects to check
Inspectors need to watch for several critical defects:
- Structural Issues: These cover splits, cracks, nonconforming part geometry, and excessive burrs
- Surface Problems: Including scratches, dents, slug depressions, and score marks
- Material Flow Issues: These show up as wrinkling, loose metal, or unrestrained parts
A pressure-sensitive Mylar-based sensor film captures pressure distribution between mating surfaces and pinpoints areas that affect tool balancing. This data is a great way to get information about potential wear points and pressure imbalances.

Making adjustments
Technicians implement systematic corrections when they detect issues. They get into the die to establish root causes. Adjustments might involve:
- Modifying component positions within the die
- Adjusting stamping machine settings
- Refining die surface characteristics
The die goes through re-testing to confirm improvements. Unbalanced pressures can cause the die to “kick,” which leads to premature fatigue and component breakage. The die needs careful attention to pressure readings to maintain optimal balance. Technicians often achieve this by varying stripper pressures between infeed and output die ends.
Conclusion
Sheet metal stamping dies are everything in modern manufacturing. They just need precision at every step of their creation. The process might seem complex, but success depends on three basic pillars: full design planning, precise component creation, and strict quality control.
Each stamping die needs a most important investment of expertise and resources. The right material selection and exact machining processes will give these tools the ability to work through thousands of production cycles. Quality testing plays a vital role. Manufacturers can spot and fix potential risks before they impact production runs.
Stamping die creation needs close attention to detail from start to finish. Fecision sticks to proper design principles and maintain high quality standards to create reliable, long-lasting dies. Our systematic testing approach helps deliver consistent results. Contact us today to discuss your sheet metal stamping die projects!




