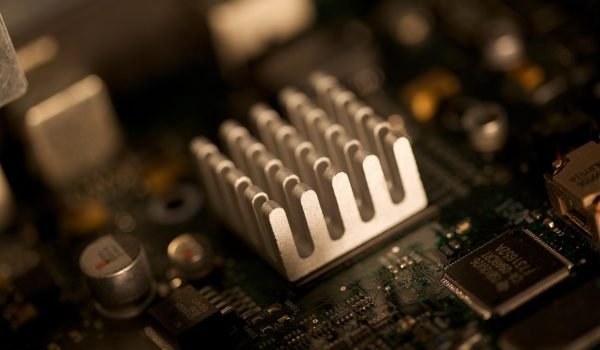
Heat sinks are widely used in all kinds of electronic devices, from computer sets to LET lighting. It is a conductive device that can absorb and transfer the heat away from components, preventing overheating and potential damage. Finding a good heat sink design is important to heat dissipation with a device, aiming to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This guide delves into the basics of heat sink design features, types, and materials. Continue reading about manufacturing techniques and helpful tips for heat sink design.
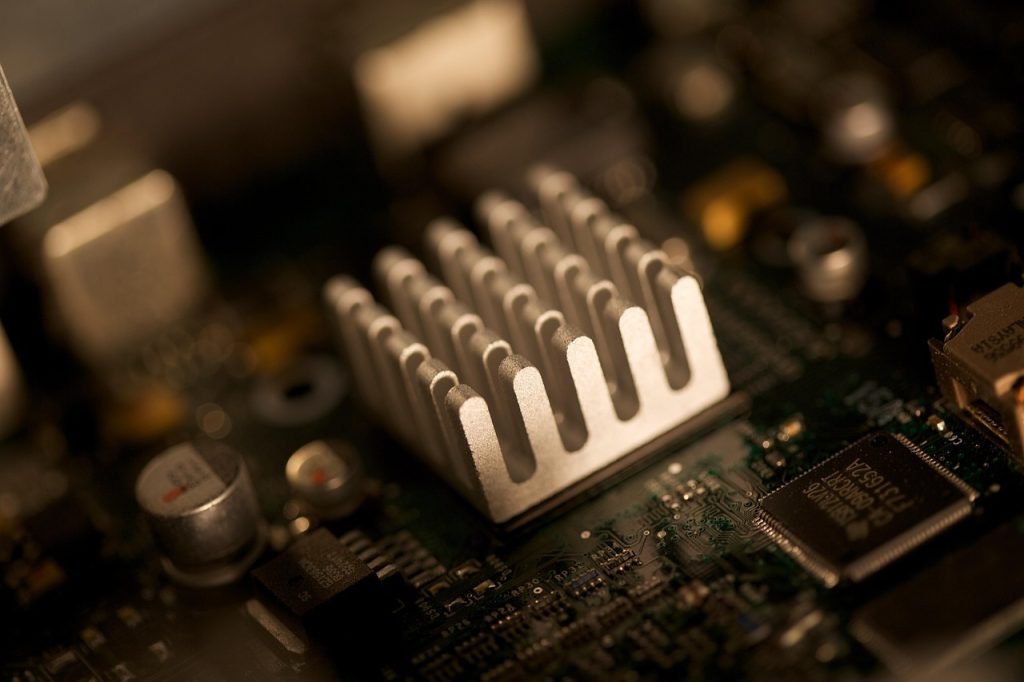
What Is a Heat Sink?
Heat sinks are mechanical devices that prevent overheating in a device using natural and forced convection. A heat sink is good for dissipating generated heat by spreading the heat across its surface and making the device cool down to a perfect temperature due to high thermal conductivity materials. Therefore, most manufacturers pay more attention to finding a suitable heat fit for the processor and transistors, preventing the temperature and the fan from being in high efficiency. These thermally radiating components are not limited to a single type; The three common types depend on how they dissipate heat from the system.
Active heat sink relies on the device’s power source. A force convection mechanism is used to make the fluid or air move across the hot area to achieve heat transfer into the component. The manufacturers usually use one or two fans to for the air across to the component, making it cool down the temperature.
The passive heat sink is a common alternative. However, it is not as effective at dissipating heat as an active heat sink. Nevertheless, passive heat sinks are widely used because of cheap and do not require electricity. But when you choose the passive heat sink. Passive heat exchangers include microcontrollers, microprocessors, chipsets, etc.
The hybrid heat sink is the type that uses passive and active heat-transferring methods. In the condition of low heat waste, it does not use the fan. The heat can transfer away from natural convection. But if the temperature is extremely high, the fan will open autumnally so that the heat will transfer out quickly and efficiently.
Suitable Materials for Heat Sink Design
High thermal conductivity, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness are helpful for better heat elimination. Some of the suitable materials for heat sink design include:
- Aluminum
Aluminum is widely used due to its extreme thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and cost-effective price. It is the common option in electric devices. For example, LED often choose aluminum as in heat sink.
- Aluminum Alloys
Combining aluminum with other metals will have a better performance in strength than working with a pure form of aluminum. Aluminum alloys maintain a lightweight profile. The common alloy used is Aluminum 1050.
- Copper
Copper offers higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, and it suits devices and components due to its better exchange properties. CPUs often use copper as a sensitive component in heat sinks due to its working efficiency.
- Graphite
Compared to copper, graphite has higher thermal conductivity. Besides, it is extremely lightweight. Graphite is applied in some situations that require lightweight heat elimination it is more expensive and fragile.
- Ceramics
This material has lower thermal conductivity than other metals. Therefore, ceramics only can be used in some specific applications due to their properties of thermal and electrical insulation.
Common Manufacturing Techniques for Heat Sinks
Various types and materials are needed for different methods of constructing heat sinks. For example, some advanced techniques are often used the CNC machining while die casting is suited for simple processes.
For the complex construction of a heat sink, CNC machines are the ideal option for going through the part of a heat sink efficiently. These types of machines have functions for drilling, milling, and turning. A design just needs to be made in the CAD software and transferred to the making to make the components. A precise method to design structural parts of the heat sink, including the dressing of the bottom surface.
Extrusion is ideal for constructing simple and uniform heat sinks in large quantities. Although it can not handle the complex heat sink design, its cost-effective production may be attractive to you. Aluminum 6063 are common material in heat sink extrusion because of is a good thermal conductor.
If you know the injection molding process, you may find it easy to understand die casting. These two techniques are similar. In die casting, aluminum is heated to a high temperature and it becomes liquid and poured into the mold to make the component of the heat sink. When finishing die casting, a completed final product is produced. This technique is widely used and can mend more complex structural designs.
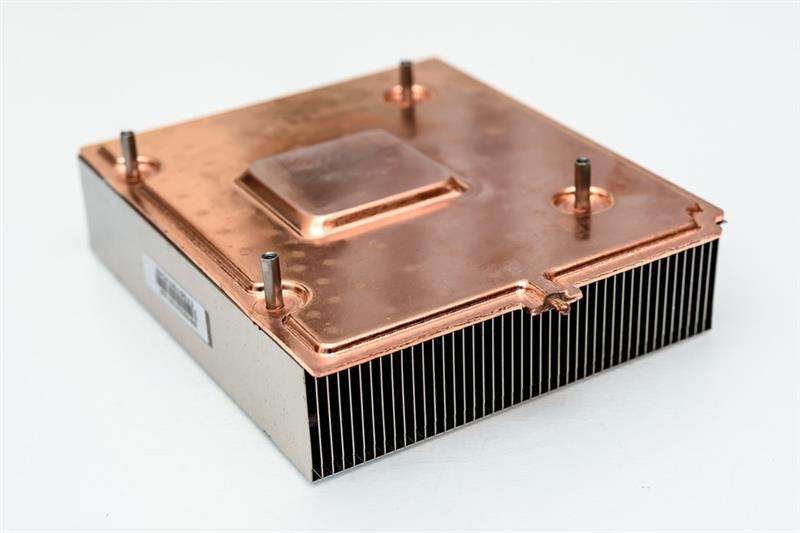

Tips to Consider During Heat Sink Design
The right heated sink design is really important to make an efficient thermal management solution. The following factors can be considered during the heat sink design:
- Shape and Arrangement of Heat Sink Fins
Fins are the essential parts in a heat sink that can help to transfer the heat to the surrounding air efficiently and quickly. The shape and arrangement of the fins affect the flow of the heat. Besides, the sheer number and size also influence it. Therefore, the design and layout of the fins need to be considered so that the air can circulate smoothly and efficiently. To achieve the best heat dissipation, it had better to optimize the shape, size, and arrangement of the heat sink, so the electrical component can be conducted and dissipated well.
- Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance is the key factor in how efficiently heat transfers from the semiconductors to the environment via the heat sink. Choosing the right thermal resistance for your heat sink is important. Therman resistance influences the temperature and how well it cools in the heat sink.
Finding Heat of Convection:
Qc = 2hA(Tcompent – Tambient ) Where
h = 1.42[( Tcompent – Tambient )/H ] ^0.25
A = HL + t(2H + L)
Qc : 2hA( Tcompent – Tambient )
You’ll notice that there is a separate surface at A2 where heat can be transferred, which determines the convective calorific value here:
Qc = 2h2A2(Tcompent – Tambient ) Where
s = 2.71 [ gβ(Tcompent – Tambient )/Lαv ]
A2 = L[2( H – b) + sb] + tL
The calculation for finding the heat generated through radiation:
Qr2 = 2ϵσA2( T4compent – T4ambient )
Qr = 2ϵσA1( T4compent – T4ambient
Where
A2 = L(t + s) + 2(tH + sb
The total number of fins is calculated by:
Fn = 1 + [(Q – Qr2 – Qc2) / (Qr1 + Qc1)]
The width of a fin is calculated by:
W = (N – 1) + Nt
- Heat Sink Attachment Methods
Heat sink are used in different devices, which mainly are the mechanical components, The heat sink attachment method has a great influence on the dissipating heat. Before you choose the method for heat sink attachment, please consider the device’s mechanical and thermal requirements. Common methods for heat sink attachment include:
Plastic Clips
Wire Clips
Push Pins
Thermal Tapes
Epoxy

Common Applications of Heat Sinks
The range of heat sinks is widely used, and they are mainly used as electronic devices. The is that the electric device will generate much high heat when it functions and it can cool its temperature. These devices impact the performance of the semiconductor. Therefore, a heat sink can continuously regulate the temperature of the device when working. Applications of heat sinks are concluding:
- Power Amplifiers
The heat generated by the power transistor can cause current to leak. An increase in collector current causes more power to dissipate. This may cause the temperature to rise. What’s worse, sometimes a thermal runaway cycle may appear that damages the transistor. However, heat sinks can prevent this damage by reducing heat quickly on their surfaces.
- CPUs
During computer operation, the CPU chips and graphics card are overlocked and generated the huge heat. The heatsink can swap the heat in the CPS quickly away for the chip, conducting it along the surface and dissipating it around the air.
- Optoelectronics
One common application for heat sink are the Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and lasers. For the reason that these devices do not have enough ability to minimize operational temperature levels. The cooling medium plays much important to the device, which can ensure longevity because the working temperature infects the lifespans.
Start to Design Your Heat Sink Easily
The design of the heat sink is important to ensure that the heat sink can adequately perform. In all electronic devices, heat sinks are indispensable. Therefore, designing the heat sink can not have something wrong. Before you take this project, you had better understand the basics. Also, it need to continue improving your heat sink design based on your needs.
Fecision, as your best reliable manufacturing company, can help you handle the heat sink design and make it a better performance. Fecision has many experienced engineers in the team who have been highly trained many times. They can help you to handle something that you are confused. Do not hesitate, to contact Fecision and we will give you an instant quote today.