Rapid advancements in industrial and manufacturing engineering has raised the bar for heat sink design and quality. Modern applications demand more efficient and reliable heat dissipate solutions.From computers and LED lights to aircraft and industrial machinery, heat sinks are essential to maintain optimal thermal levels.
Let’s explore more details about heat sinks. What exactly they are, what they’re made of, and different types of heat sink manufacturing.
What Is A Heat Sink?
A heat sink is a thermal component designed to disperse heat away from a heat-generating source. It is used in electronic devices such as CPU, GPU, and electric vehicle coolers, where heat is a byproduct of operation.
Heat sinks work on the principle of Fourier’s Law of heat conduction. This law states that the heat naturally flows from a region of high temperature to a low temperature. Heat sinks achieve this by increasing the surface area available for heat transfer, often through the use of fins or similar structures. This increased surface area combined with its design facilitates heat dissipation and protects sensitive components from thermal damage.
Different Types of Heat Sink
Heat sinks are generally categorized into two different types i.e., passive and active. These types are based on different mechanisms they use to dissipate heat. Let’s take a look at them:
Passive Heat Sink
Passive heat sinks are the most common and traditional choice for heat dissipation. They work through a natural convection process and do not use any additional power assistance. These sinks are designed with pins or fins, increasing their surface area. The large surface area transfers heat into the surrounding air.
The best thing about passive heat sinks is they are economical and noise-free. However, their size can be a drawback, which often requires more clearance space.
Active Heat Sink
Active heat sinks use powered devices like fans, pumps, or air blowers to boost cooling capacity. The fan actively moves across the heat sink’s surface leading to more efficient heat transfer.
They work better than passive heat sinks because of their reduced size and reliance on forced air circulation. You have likely heard the whirring of such a fan while working on your laptop—that’s an active heat sink at work.
These sinks offer excellent cooling capabilities but need regular maintenance due to their moving parts.

Materials Used In Heat Sink Manufacturing
Heat sinks are commonly made from aluminum or copper. Each offers distinct advantages. Let’s explore the key differences between these two materials:
Aluminum Heat Sink
Aluminum is a popular heat sink material due to its excellent thermal conductivity and heat-proofing capabilities. The most affordable heat sinks are often made of aluminum. Depending on their specific application, these heat sinks are manufactured using aluminum alloys such as 3003, 6060, 6061, or 6063.
The versatility of aluminum heat sinks makes them suitable for diverse applications, ranging from household appliances and industrial machinery to electronics and LED lighting.
Copper Heat Sink
Copper has one of the highest thermal conductivity (393.18 W/m·K) of any engineering metal. It transfers heat better than aluminum and resists corrosion. However, copper heat sinks are more expensive and hard to manufacture.
If you are looking for high-quality heat sinks for sensitive devices such as CPUs, laptops, or gaming PCs, then copper heat sinks are a preferred choice.
Heat Sink Manufacturing: Machinery and Method
From raw materials to machinery, heat sink manufacturing involves different procedures and processes. Let’s explore these procedures one by one:
Extrusion
Extrusion is a continuous process in which heated materials ( typically aluminum) are pushed through a die to create the desired shape. The material is heated up to 540°C and then forced into the mold. It solidifies and then takes the shape of the mold.
The extruded material comes out in continuous lengths with the profile defined by the die. These lengths are then cut to the desired size, forming individual heat sink blanks.
Extrusion is a cost-effective process that is suitable for simple designs. The downside is that dimensions are restricted by the maximum width of the extrusion die.
Skiving
Skiving is a crucial but costly technique for producing thin-fin heat sinks. This precision cutting process uses a specialized blade to extract fins from solid copper or aluminum. The blade shaves off a thin layer, lifts it, and bends it vertically to form a fin. The fin thickness typically ranges up to 0.15mm for aluminum and 0.05mm for copper.
Skived heat sinks are used in demanding applications like aerospace systems, aircraft, and telecommunications equipment.
Forging
Forging is a manufacturing technique that shapes metal through hammering, pressing, or rolling. Forged heat sinks are created by compressing copper or aluminum under high pressure at relatively low temperatures. This process minimizes air bubbles and impurities, improving the material’s density and thermal properties. Forged heat sinks offer mid-range to high performance at a moderate cost.
CNC Machining
Computer numeric control ( CNC) is a manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to direct the actions of tools and machinery. These machines are capable of various functions including drilling, milling, and turning. All of them are necessary for creating the intricate shapes of complex heat sinks.
The design of the heat sin is first created in computer-aided design software such as Autocad. It is then sent to the CNC machine for manufacturing. It is one of the most advanced manufacturing techniques that lets you create complex three-dimensional heat sinks with a single prompt.
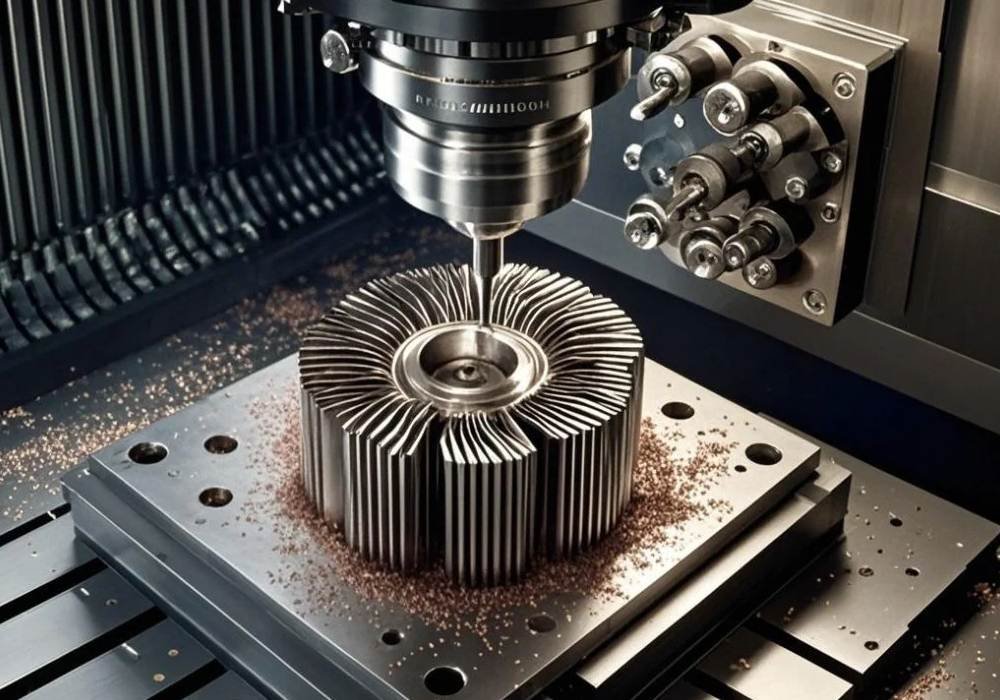

Benefits of CNC Machining for Heat Sink Manufacturing
CNC machining offers unparalleled benefits for heat sink manufacturing that set it apart from other techniques. We will discuss a few of them:
Precision and Accuracy
CNC machine’s computer-controlled precision ensures exceptional accuracy in heat sink manufacturing. You can easily achieve Intricate designs and complex layouts with optimal heat dissipation qualities.
Rapid Prototyping
It facilitates rapid prototyping which is necessary for meeting customer demands for both performance and design. Designers and engineers can quickly iterate, test concepts, and make modifications before committing to full-scale production.
Consistency and Replication
CNC machines deliver consistent, high-quality heat sinks. This consistency translates to a smooth, flawless surface finish free from scratches or imperfections. The result is uniform heat dissipation across all manufactured units.
Applications of Heat Sinks in Different Industries
Heat sinks are essential thermal management tools adopted across diverse industries. They are used in different industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications to name a few:
- LED Lights: LED lights are heat sensitive and excessive heat emission can reduce their performance and lifespan. Heat sinks in LED fixtures dissipate this heat and maintain optimal temperatures.
- Computer Systems: CPUs, GPUs, and power regulators in computers generate significant heat. Heat sinks, often with fans, transfer this heat away and keep components within a safe thermal limit.
- Automotive Electronics: Automotive electronics operate in a lot of harsh conditions. Specific heat sinks are integrated into modules that maintain reliable performance despite high temperatures, vibration, and dust.
- Industrial Machinery: Industrial equipment like motor drivers and robotics comes with built-in heat sinks to manage heat generation during operations.
Conclusion
Heat sinks are crucial for maintaining optimal thermal conditions in electronic devices. Choosing the right heat sink requires careful consideration of design needs and production volume. Aluminum offers a balance of weight and cost-effectiveness, while copper provides superior thermal conductivity for demanding applications.
From extrusion to forging and CNC machining, there are different heat sink manufacturing options available. However, CNC machining stands out due to its unparalleled precision, rapid prototyping capabilities, and ability to ensure consistent, high-quality heat sink production. Ultimately, selecting the appropriate heat sink ensures the reliability and longevity of electronic and mechanical systems.