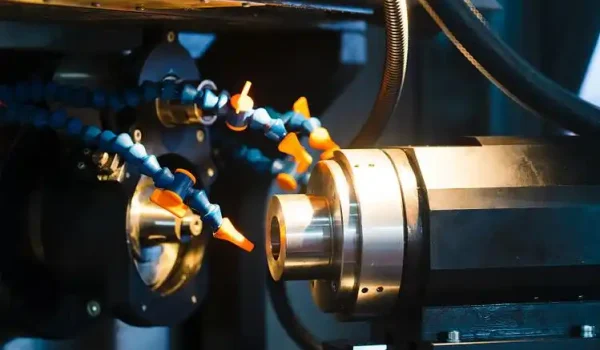
Motion control is a critical component of computer numerical control (CNC) machines in modern manufacturing. In the past, engineers typically handled motion control manually. However, today’s industry requires far less human intervention, allowing companies to save time and money by using automated motion control to optimize CNC operations.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting with CNC machines, this guide covers everything you need to know about CNC motion control – including how it works, its applications, and the best motion control kits available. Keep reading to gain a clear understanding of this essential technology.
What Is CNC Motion Control?
CNC machining its full name as computer numerical control, is a manufacturing method through computer that uses a pre-written computer to manipulate manufacturing equipment. Compared with operations by hand, machine-controlled devices controlled by computers are more accurate and stable. They include lathes, milling machines, plasma cutters, grinders, and so on, aiming to protect humans from dangerous working environments.
The design of this machine is along two moving axes to move the manufacturing object:
- Linear axis – Along with the straight line to cut
- Rotary axis – Along with the round piece to cut.
This axis is moving control is more accurate to carve, weld or cut and size and shape that you need. Precision in the complicated and detailed shape and angle is not a question. Automation makes different objects match.
Uses of Motion Controls
Motion control offers many advantages and is a far better choice than traditional hand-operated machines. The most significant benefit is its ability to reduce human errors. Even though operators are well-trained and perform their tasks carefully, manual operations are still prone to mistakes. Even a slight deviation can result in inconsistencies, causing two identical products to be cut differently.
Another key advantage of CNC motion control systems is their production speed. Since the machine’s speed depends on its electrical settings, every part is cut, carved, or welded at a consistent rate, ensuring predictable and efficient output.Thanks to these benefits, CNC motion control – especially in plasma cutting tables—is widely used across industries, including:
- Assembly
- Packaging
- Printing
- Semiconductor production
- Textile production
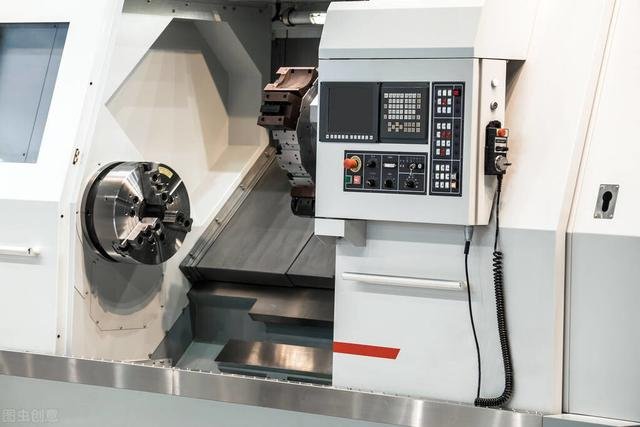

Which Do CNC Machines Use to Control Tool Motion?
CNC machines are made of several complex components, and these components make the machine operate and produce precise components. Here are the CNC motion control kits below.
- Input Device
This is basically how the NC program is loaded into the machine. It could be as simple as using a keyboard (typing G-code commands directly), or using a USB flash drive that has been pre-written with a full program, or some wireless communication if you want to download a program from another computer.
- Machine Control Unit (MCU)
This component refers to a collection of software and hardware that takes the G-code from the input device and converts it into actual instructions that the machine and all of its tools can follow. Arguably, the microcontroller (MCU) is one of the most important components in the entire machine, as it causes the servo motors to run along the various axes. It also ensures that the tool is in the correct position after the movement is completed and controls the tool changer and the start of the coolant.
- Driving System
This part says the different types of motors that move the tools. In the traditional CNC milling machine, the table is along with the X-axis and the Y-axis. The cutter moves up and down the Z axis. In the CNC lathe, the moving tools and the cutter move in the same direction and along with the edge of the workpiece. Servo motors, screw of balls and liner are in run at the same time.
- Feedback System
This system is a bit like a backup system at work. The drive system is extremely accurate, but this closed-loop control system is a way to verify that parts have moved where they should be. If they deviate slightly, it adjusts them utilizing an encoder (a sensor that measures the position of each component). Probes also play a role; They measure the actual workpiece and make sure everything is going according to plan. If any adjustments need to be made, the machine will do them automatically.
- Display Unit
This is explained fairly plainly and simply. It’s a display that shows all the important information (such as the machine’s settings, G-code, and current operating status) while the work is in progress. Some machines come with huge high-definition displays with a wealth of information, but others may be small and show only the most basic necessary information.
- Tailstock
This is a part of the lathe that supports one end of a long cylindrical workpiece, while the chuck clamps and drives the other end to turn. It is an important component of the machine and prevents the material from bending and deforming during processing. It can be moved up and down in the Z-axis direction to accommodate different lengths of material and is particularly suitable for products such as shafts or screws.
- Tailstock Quill
This guide rod is located inside the tailstock and is a tapered structure that is aligned with the spindle and chuck. It can rotate freely and keep the material in a central position. For longer parts, a blind hole is usually drilled at the end of the part so that the guide rod can be inserted into it to get some support. When the tailstock is in place – close to the workpiece, the guide rod is pushed in by pneumatic or hydraulic pressure.
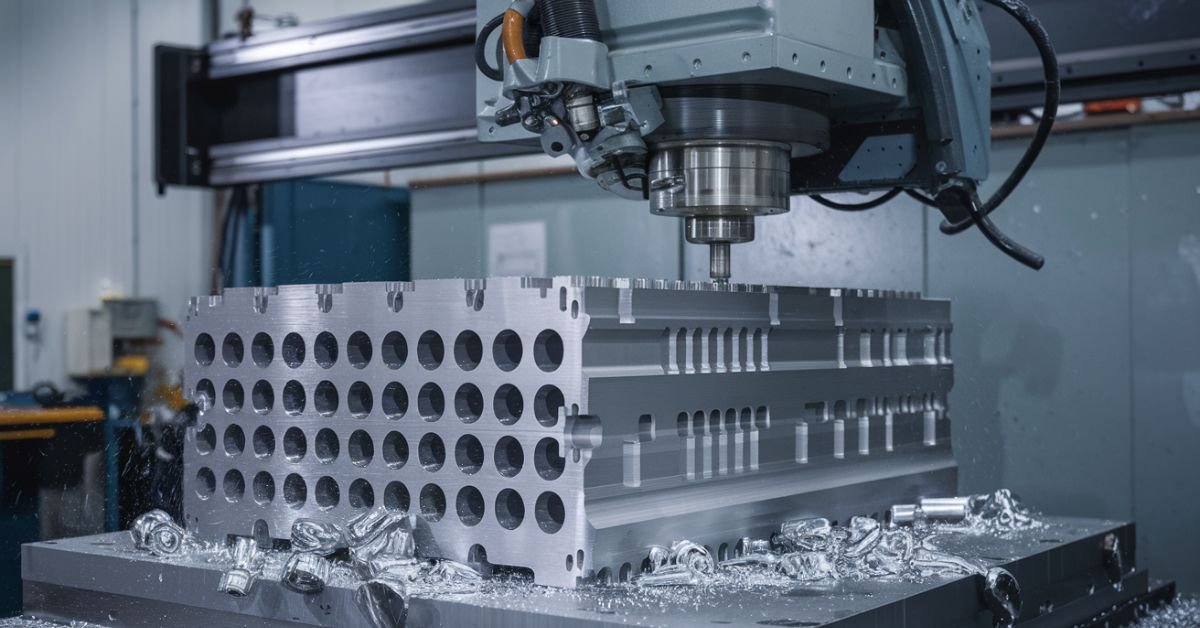

Conclusion
CNC motion control systems provide a powerful and precise machining method, delivering high accuracy, automation, and versatility across industries.
Fecision’s CNC motion controller achieves ±0.001″ precision thanks to our engineers’ focus on smarter motion control. You don’t need to worry about cycle times—our motion control solutions can reduce cycle times by 20% or more while anticipating tool wear.
Upgrade to unwavering precision—request a demo today!