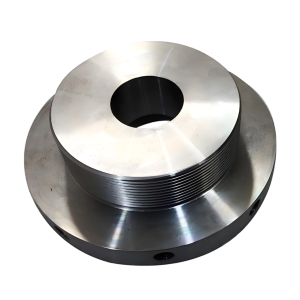
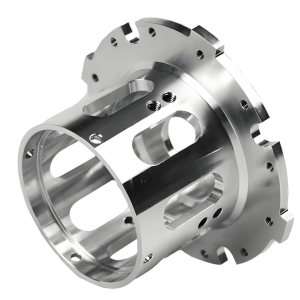
Bronze Machining Services
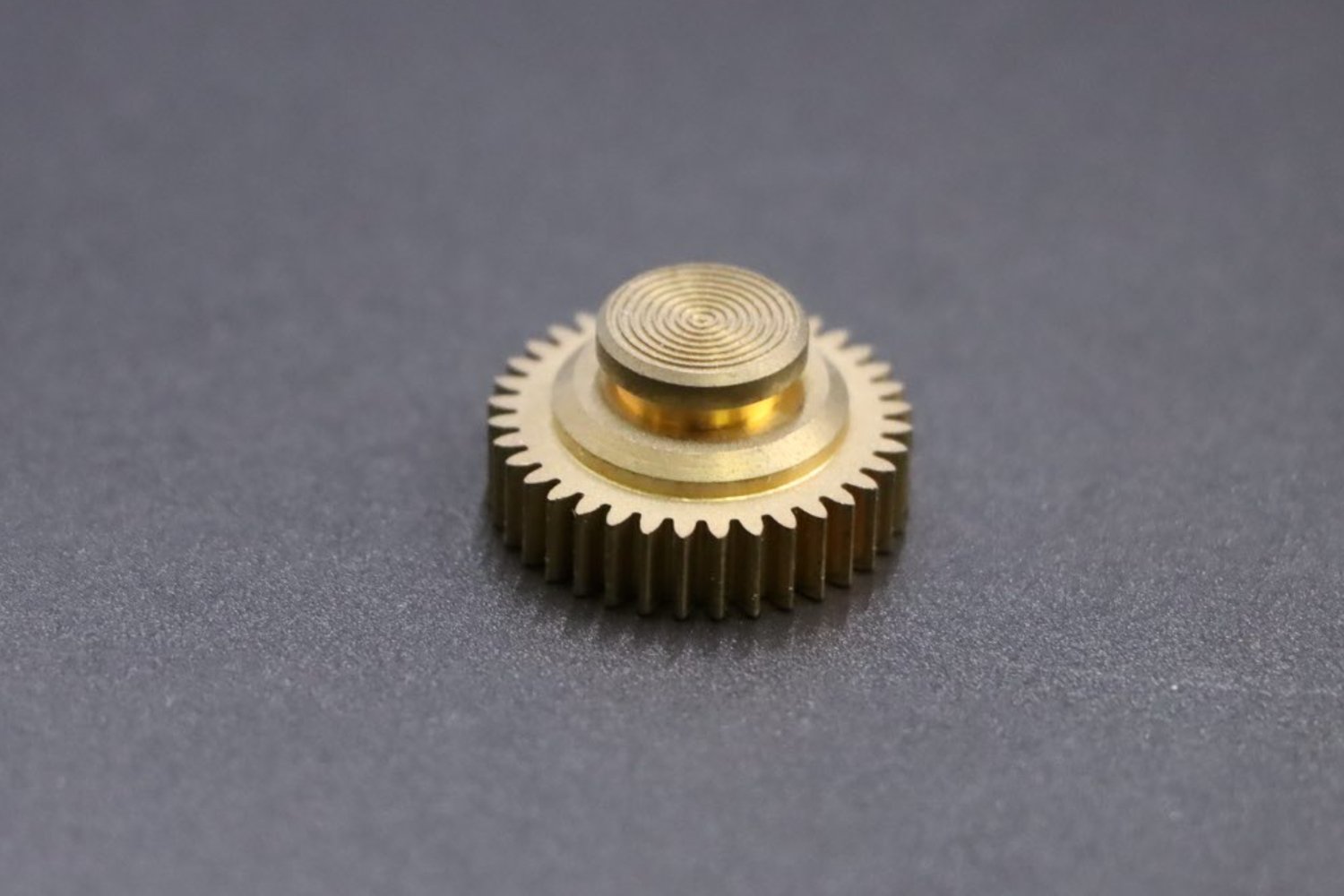
Bronze CNC machining is a precision manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control (CNC) machines to shape bronze alloys into complex, high-accuracy components. This advanced manufacturing method ensures consistent quality and tight tolerances for bronze parts used in various industrial applications.
Superior Precision
Complex Geometry
Consistent Quality
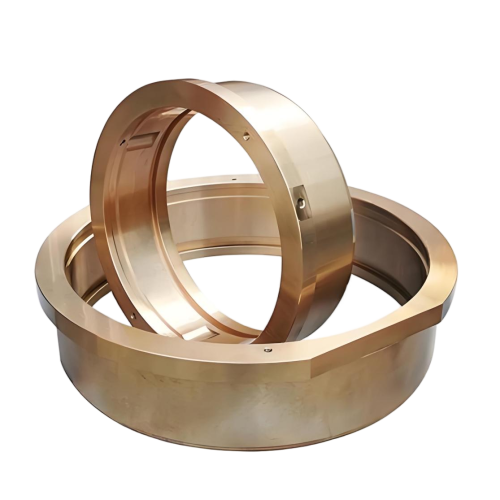
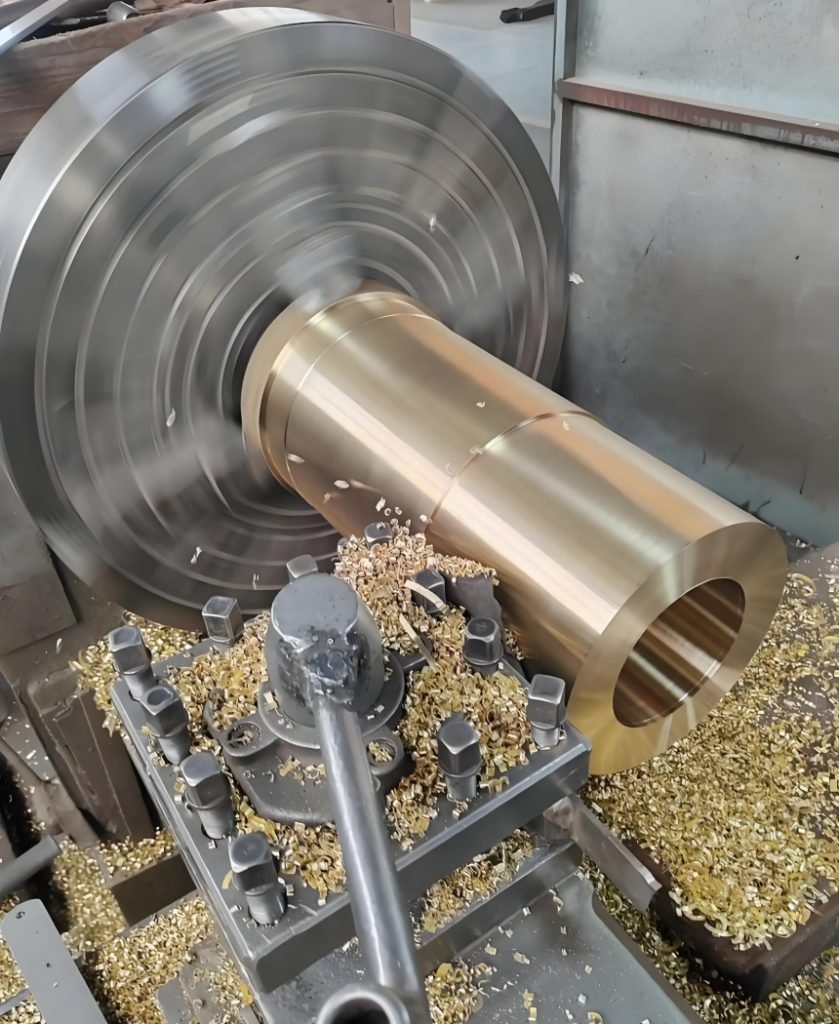


| Specification | Capabilities |
| Machine Axes | 3, 4, and 5-axis capabilities |
| Tolerance Range | ±0.0001″ to ±0.005″ |
| Maximum Part Size | 48″ × 36″ × 30″ |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.005″ |
| Surface Finish | Up to 8 RMS |
| Production Volume | Prototypes to 100,000+ units |
| Lead Times | Standard 2-3 weeks, expedited options available |
Understanding Bronze in CNC Machining
Bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper, typically with tin as the main additive, though other elements like phosphorus, aluminum, silicon, and nickel are often included to enhance specific properties. This versatile material has been used for millennia and remains a popular choice in modern manufacturing due to its unique combination of characteristics.
In CNC machining, bronze offers excellent machinability compared to many other metals, allowing for precise, efficient production of complex components. Its natural lubricity reduces tool wear and improves surface finish, making it ideal for parts that require both precision and durability.
Key Properties of Bronze for Machining
- Excellent Machinability: Bronze cuts cleanly with minimal tool wear, allowing for high-speed machining and tight tolerances.
- Natural Lubricity: Self-lubricating properties reduce friction, making it ideal for bearing surfaces and moving parts.
- Corrosion Resistance: Good resistance to corrosion and tarnishing, especially in marine and humid environments.
- High Thermal Conductivity: Efficiently transfers heat, making it suitable for heat exchangers and thermal management components.
- Good Electrical Conductivity: Excellent for electrical components and connectors where conductivity is important.
Speak With Our Engineering Team
Discuss your specific application needs with our CNC machining specialists.
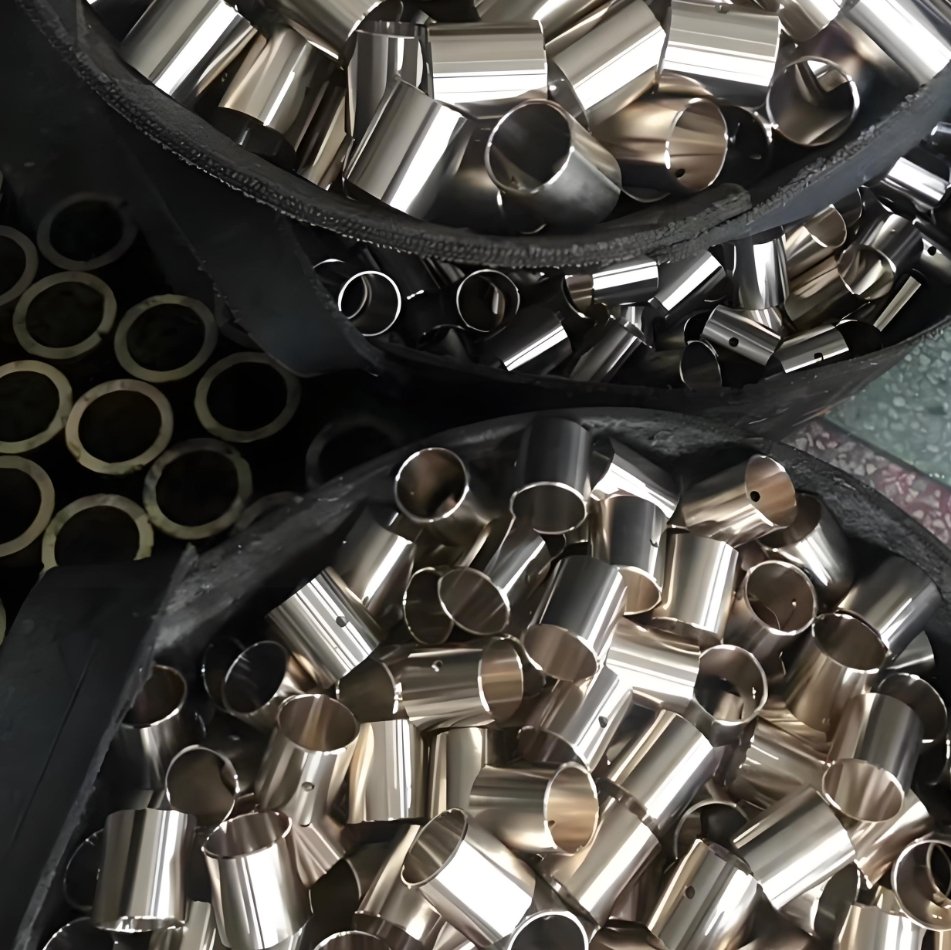

Pros and Cons of Bronze CNC Machining
Understanding the advantages and limitations of bronze CNC machining helps in selecting the right material for your specific application requirements.
Advantages
- Excellent Machinability: Bronze machines easily with good chip formation, reducing tool wear and extending tool life.
- Superior Surface Finish: Achieves excellent surface finishes without extensive secondary operations.
- Wear Resistance: Excellent resistance to friction and wear, ideal for moving parts and bearings.
- Corrosion Resistance: Performs well in harsh environments, including marine and industrial settings.
- Dimensional Stability: Maintains its shape and dimensions under varying temperature conditions.
Considerations
- Higher Material Cost: More expensive than steel or aluminum, which can increase component costs.
- Weight Considerations: Heavier than aluminum, which may be a disadvantage in weight-sensitive applications.
- Lower Tensile Strength: Not as strong as steel, limiting its use in high-stress applications.
- Galvanic Corrosion: Can cause galvanic corrosion when in contact with certain other metals in wet environments.
- Temperature Limitations: May lose strength at elevated temperatures compared to some other metals.
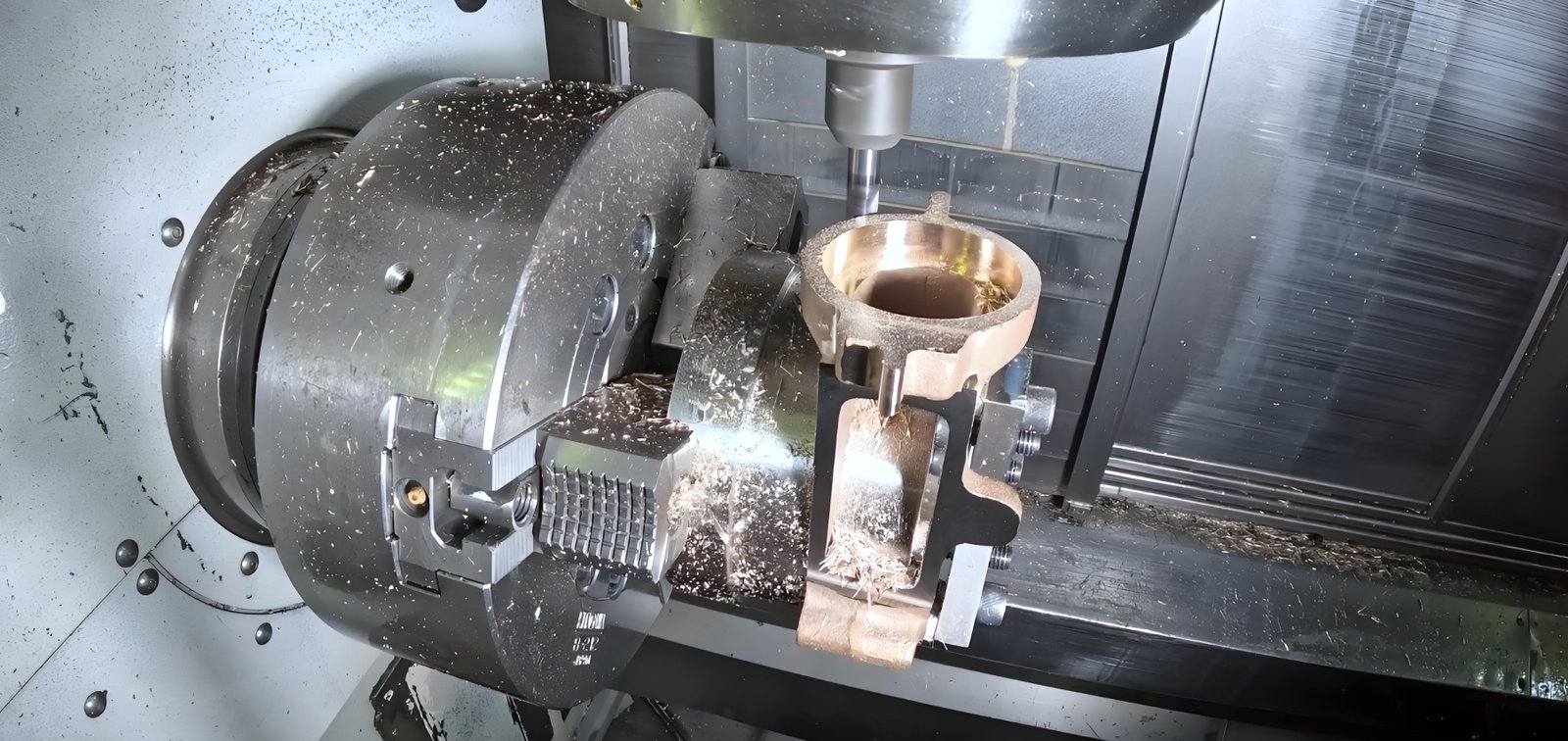

Subtypes of Bronze for CNC Machining
At Fecision, we work with a variety of brass grades to meet your specific application requirements. Each grade offers unique properties that make it suitable for particular uses.
Our engineering team can help you select the optimal brass alloy for your project.
Tin Bronze
- Tin Bronze is the “classic” bronze alloy, consisting of copper (Cu) as the base metal and tin (Sn) as the primary alloying element (typically 5–15% Sn). It may contain small additions of zinc (Zn) or lead (Pb) to improve machinability or fluidity.
- Tin enhances the alloy’s strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance compared to pure copper, while maintaining good ductility.
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
300-600
150–400
120–250 (10⁷ cycles)
60-150 HB
5-40
8.6-8.9
200-300
Aluminum Bronze
- Aluminum Bronze is a high-performance alloy where aluminum (Al: 5–12%) replaces tin as the main alloying element. Some grades include iron (Fe) or nickel (Ni) to further enhance strength and heat resistance.
- It offers exceptional strength, hardness, and wear resistance—surpassing most other bronzes.
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
500-1200
300–800
200–450 (10⁷ cycles)
100-250 HB
5-30
7.4-8.1
400-550
Phosphor Bronze
- Phosphor Bronze (also called Phosphorized Bronze) is a tin bronze variant with controlled additions of phosphorus (P: 0.01–0.35%).
- Phosphorus acts as a deoxidizer (improving casting quality) and enhances the alloy’s strength, stiffness, and fatigue resistance—especially in spring applications.
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
400-800
200–550
150–300 (10⁷ cycles)
80-200 HB
3-35
8.7-8.9
250-350
Silicon Bronze
- Silicon Bronze is a copper-silicon alloy (Si: 1–4%), often with small additions of manganese (Mn) or zinc (Zn) to optimize strength and ductility.
- It combines high tensile strength with excellent formability and weldability—properties that make it a popular alternative to stainless steel in certain applications.
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
400-750
200–500
160–280 (10⁷ cycles)
70-180 HB
10-40
8.3-8.6
250-400
Leaded Bronze
- Leaded Bronze is a tin bronze or copper-zinc alloy (brass variant) containing lead (Pb: 5–25%) as a key alloying element.
- Lead does not dissolve in copper but forms discrete particles that act as internal lubricants, drastically improving machinability (reducing tool wear and cutting forces). However, lead reduces the alloy’s strength and ductility compared to other bronzes.
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Fatigue Strength (MPa)
Hardness (Brinell)
Elongation at Break (%)
Density (g/cm³)
Maximum Temp (°C)
250-500
120–300
100–200 (10⁷ cycles)
50-120 HB
3-25
8.4-8.9
150-250
Surface Finishing Options for Bronze CNC Machined Parts
We offer a variety of surface finishing options for CNC machined bronze components to enhance their appearance, performance, and durability.
As Machined
The surface retains visible tool marks without any further processing. This represents the standard finish directly after machining.
Polishing
Creates a smooth, reflective surface finish ranging from satin to mirror-like for aesthetic applications.
Heat Treatment
Improves mechanical properties such as hardness and wear resistance through controlled heating and cooling.
Passivation
Chemical treatment that enhances corrosion resistance by forming a protective oxide layer on the bronze surface.
Painting & Powder Coating
Applied for decorative purposes and additional corrosion protection in harsh environments.
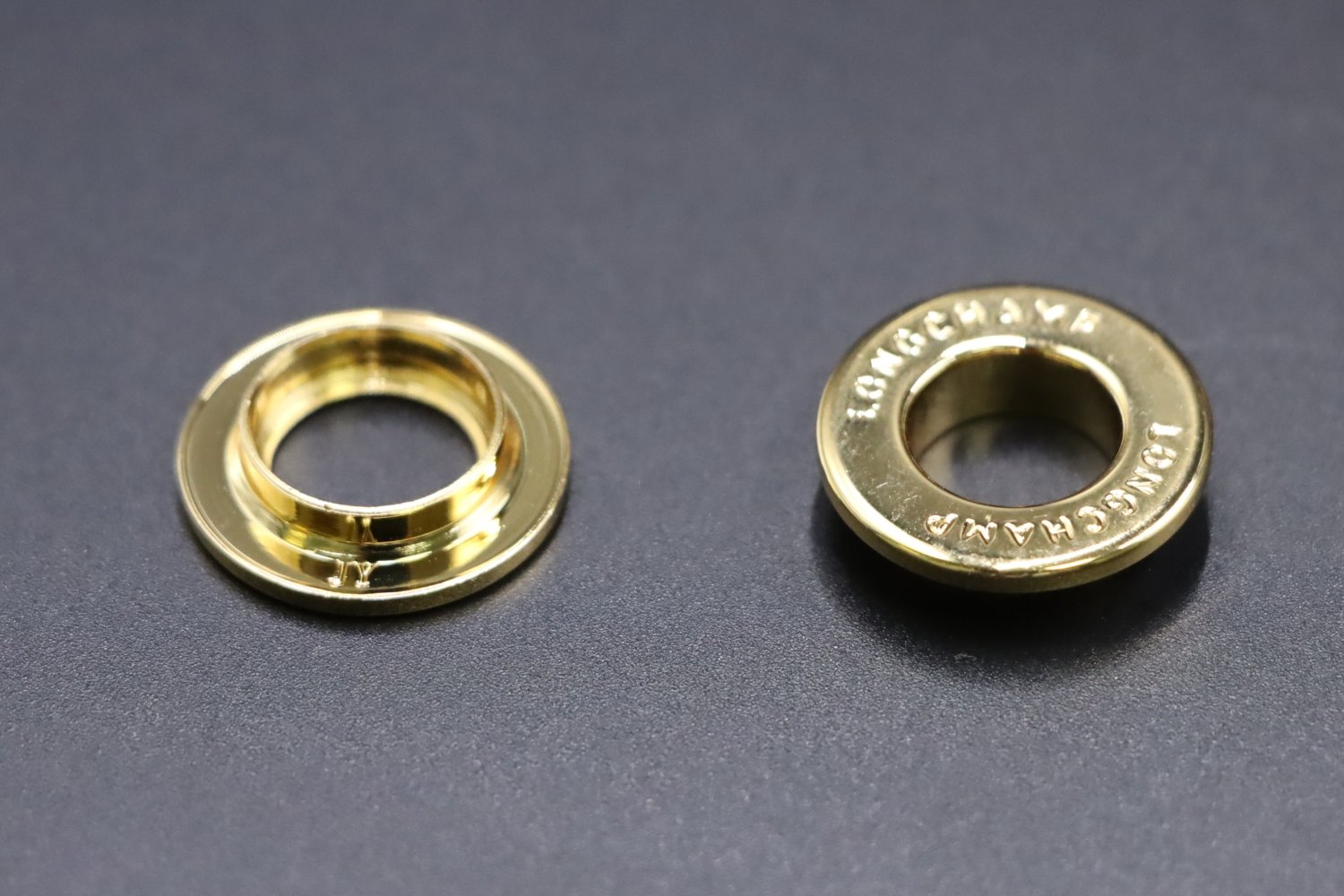
Electroplating
Chrome, nickel, or gold plating for enhanced corrosion resistance, conductivity, or decorative purposes.
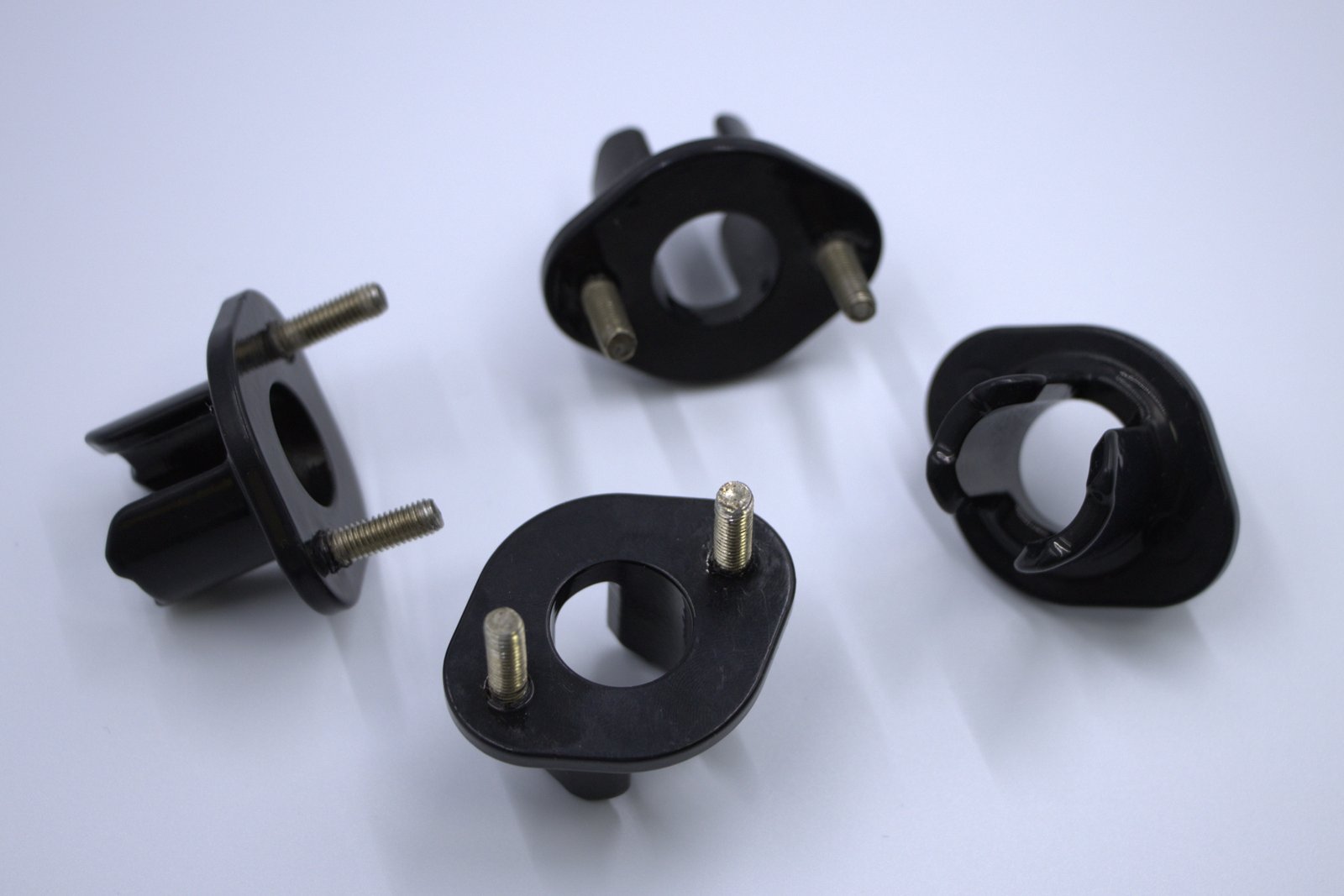
Bronze CNC Machining Application
Industries We Serve
Bronze CNC machined components are valued across numerous industries for their unique combination of properties, including wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability.
Automotive Industry
• Bearings and bushings
• Valve guides and seats
• Gear components
• Fuel system parts
• Hydraulic system components
Marine Industry
• Propellers and propeller shafts
• Pump components
• Valve bodies and fittings
• Rudder components
• Marine hardware and fasteners
Industrial Machinery
• Bearing sleeves and thrust washers
• Gear blanks and worm gears
• Hydraulic cylinder components
• Pump rotors and stators
• Valve stems and seats
Aerospace & Defense
• Landing gear components
• Hydraulic system parts
• Actuator components
• Instrumentation parts
• Bearing assemblies
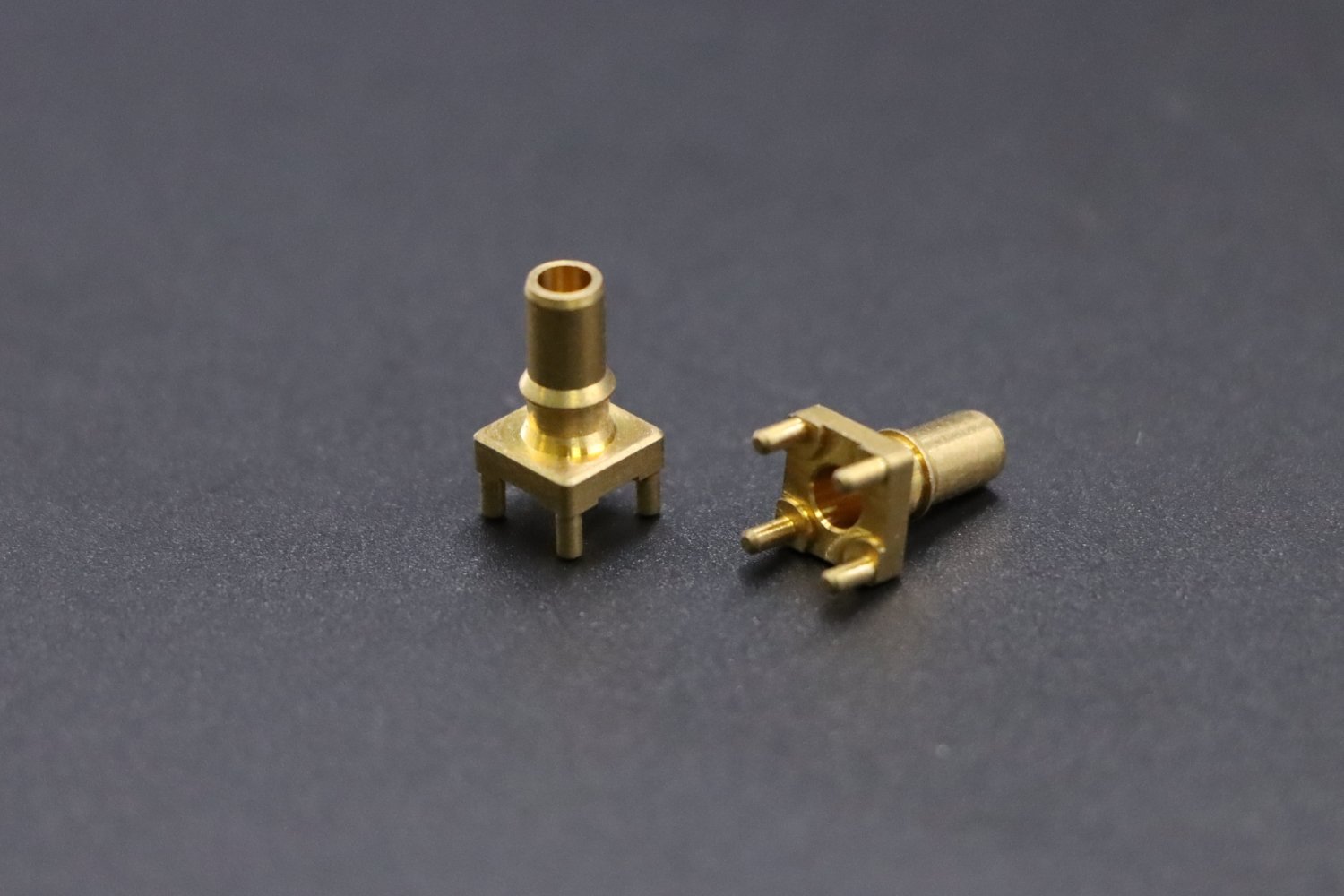
Electrical & Electronics
• Electrical connectors
• Switch components
• Terminal blocks
• Heat sinks
• Motor components
Plumbing & Hydraulics
• Valve bodies and stems
• Fittings and couplings
• Pump components
• Pressure regulators
• Pipe connectors
Bronze Machining FAQs
Ready to Start Your Bronze CNC Machining Project?
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a free quote for your bronze CNC machining project.






Contact Us for Bronze CNC Machining
Contact us today to discuss your bronze CNC machining requirements.
Discover how Fecision can help bring your designs to life with precision and quality.