In modern manufacturing, the use of specialized tools like jigs and fixtures has become a cornerstone for achieving precision and efficiency. You might be surprised to know that industries relying heavily on machining processes see a significant boost in production quality when these devices are implemented correctly.
These workholding devices play a crucial role in holding a workpiece in place, ensuring that it is machined accurately and consistently. By understanding the role of fixtures and jigs in manufacturing and engineering, you can optimize your production processes.
Understanding Fixtures and Jigs
To manufacture parts with precision, understanding the role of fixtures and jigs is crucial. These tools are fundamental in ensuring that manufacturing processes are carried out with accuracy and consistency.
What is a Fixture?
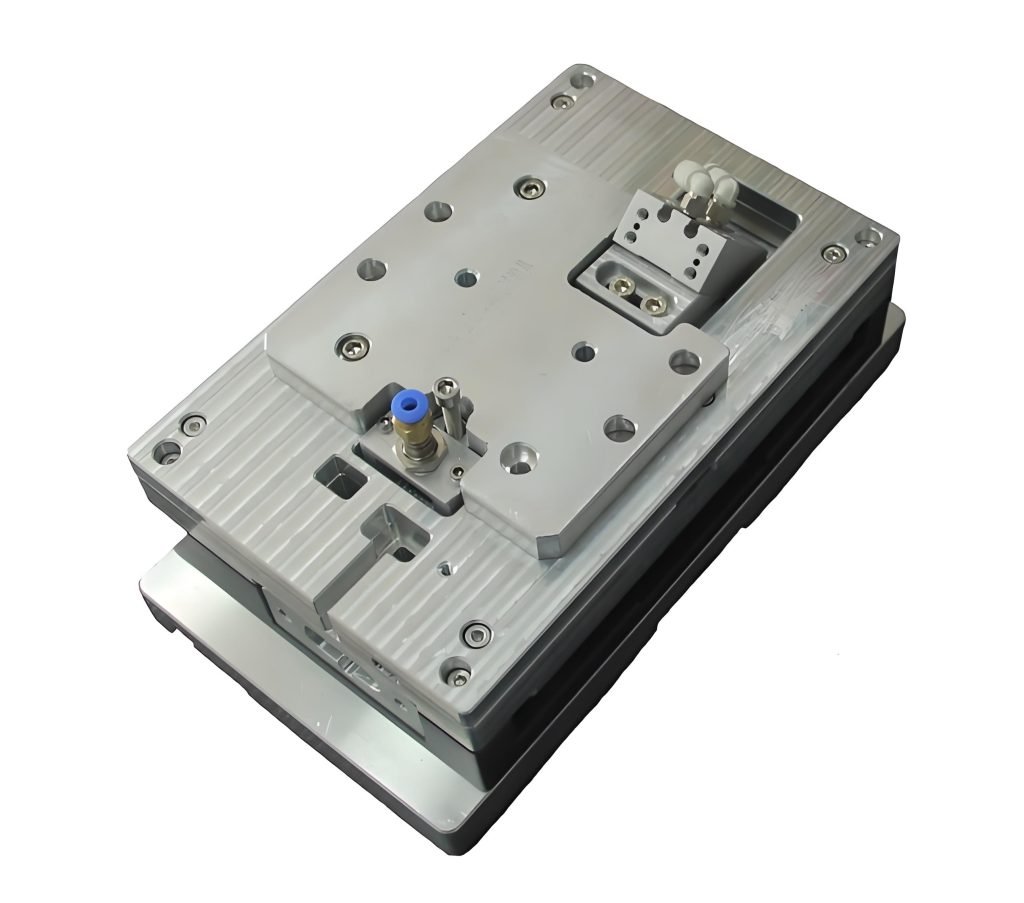

A fixture is a device that holds a workpiece in place, allowing for precise machining operations. Unlike jigs, fixtures do not guide the cutting tool; they simply secure the workpiece, ensuring that it remains stationary during the manufacturing process. This is crucial for operations where the workpiece needs to be held firmly in a specific position.
Types of Fixtures in Manufacturing
Manufacturing processes rely heavily on various types of fixtures to ensure precision and efficiency. You can improve product quality and reduce production time by using the right fixtures for your manufacturing needs.
Plate and Angle-Plate Fixtures
Plate fixtures are flat, rigid plates with locating pins and clamps to hold workpieces. Angle-plate fixtures are similar but have a perpendicular surface, allowing for more complex workpiece orientations. These fixtures provide a stable base for various manufacturing operations.
Vise and Milling Fixtures
Vise fixtures are designed to hold workpieces firmly in place during milling operations. They come with jaws that can be adjusted to accommodate different workpiece sizes. Milling fixtures often include additional features like clamps and supports to ensure precise machining.
Welding and Inspection Fixtures
Welding fixtures are specialized holding devices that secure multiple components in precise alignment during welding operations. They prevent distortion from heat and ensure consistent weld quality. Inspection fixtures, on the other hand, hold parts in standardized positions for measurement and verification of critical dimensions, enabling accurate comparison against design specifications.
What is a Jig?
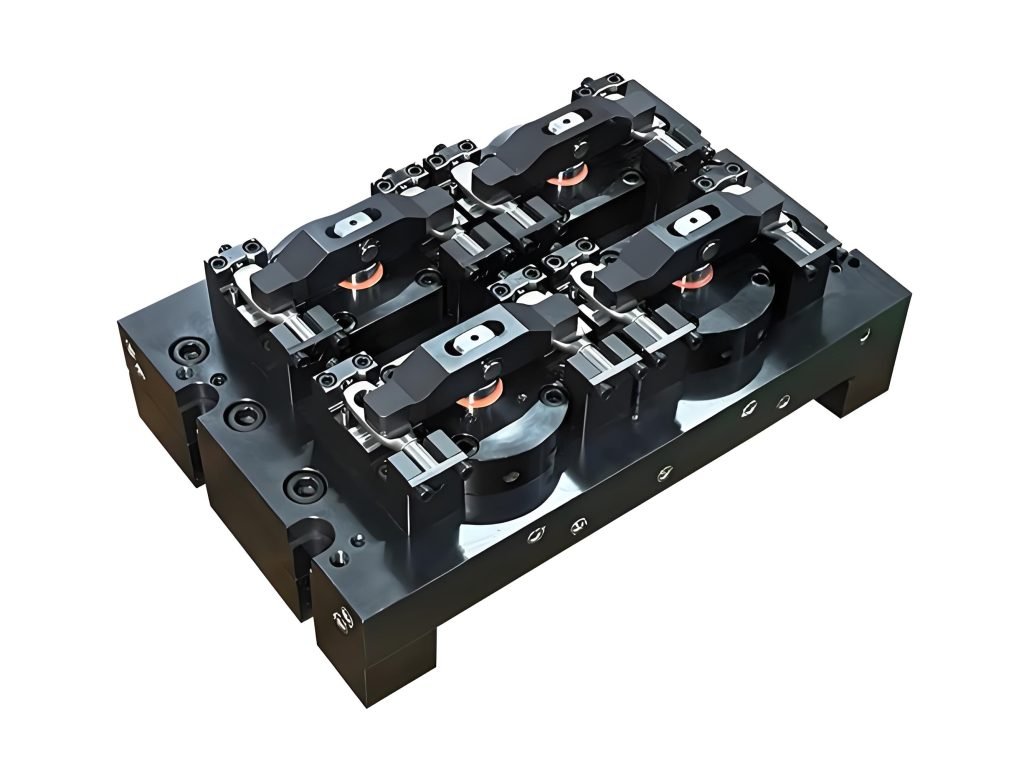

A jig, on the other hand, is a specialized tool designed to guide cutting tools, particularly drills, to precise locations on a workpiece. This ensures consistent feature placement across multiple parts. Jigs are particularly valuable for drilling operations where precise hole location is critical for part functionality and interchangeability. The design of a jig typically includes hardened bushings that guide drill bits to exact positions, eliminating the need for manual marking and reducing operator skill requirements.
By using a jig, you can dramatically improve consistency between parts while reducing the time required for setup and alignment of each workpiece. A jig acts as a template, ensuring that every part is machined to the same specifications, thereby increasing parts’ interchangeability.
Common Types of Jigs
In the realm of precision machining, various types of jigs play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and efficiency. Jigs are specialized tools designed to guide and support workpieces during manufacturing processes, particularly in drilling and machining operations.
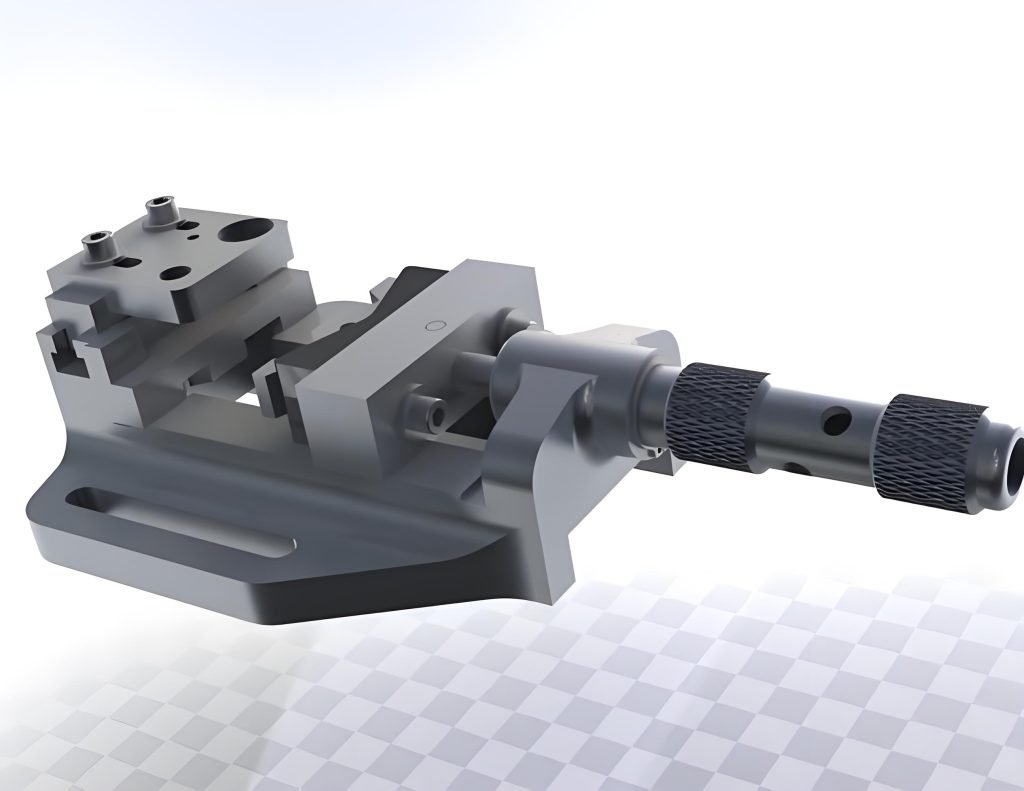
Template and Plate Jigs
Template jigs are used to guide tools along a specific path, ensuring consistent results across multiple workpieces. Plate jigs, on the other hand, are flat plates with holes or slots that guide drills or other tools to precise locations on the workpiece.
Box and Channel Jigs
Box jigs enclose the workpiece on multiple sides, providing comprehensive support and guidance for complex machining tasks. Channel jigs are designed with a channel or groove that guides the tool along the workpiece, useful for operations requiring linear motion.
Indexing and Drill Jigs
Indexing jigs allow for the precise rotation of workpieces to facilitate drilling at multiple angles or positions. Drill jigs, specifically designed for drilling operations, guide drill bits to exact locations on the workpiece, ensuring high repeatability and accuracy.
Indexing jigs incorporate rotational capabilities, enabling the workpiece to be positioned at multiple predetermined angles. This functionality is particularly valuable for creating evenly spaced hole patterns around cylindrical or circular features.
Drill jigs are perhaps the most common type, used extensively in high-volume production environments. They typically incorporate hardened steel bushings to prevent drill bit wandering, ensuring consistent hole placement across production runs.
Jigs vs. Fixtures: Key Differences
Jigs and fixtures, though both used for workholding, serve distinct purposes in manufacturing operations. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right tool for your specific manufacturing needs.
Functional Differences
The primary functional difference between jigs and fixtures lies in their design and application. Jigs are designed to guide tools during operations such as drilling, reaming, and tapping. They incorporate guiding elements that ensure precise tool positioning, making them ideal for applications where accuracy is critical. On the other hand, fixtures are focused on securely holding the workpiece in place during operations like milling, turning, and grinding. They provide the necessary stability and support, ensuring that the workpiece remains stationary and secure.
Application Differences
The application domains of jigs and fixtures differ significantly based on their functional characteristics. Jigs excel in operations that require precise tool positioning, particularly in drilling applications. Fixtures, however, are primarily used in processes like milling and grinding, where workpiece stability is paramount. The design complexity of jigs is generally higher due to the incorporation of tool guiding components, whereas fixtures are often simpler, focusing on robust clamping mechanisms. These differences influence when each type of workholding device is most appropriate in the manufacturing process sequence.
Design Principles of Fixtures and Jigs
Effective design of fixtures and jigs requires careful consideration of several factors, including ergonomics and safety. You must ensure that these workholding devices are not only precise but also safe and efficient to use.
The 3-2-1 Principle
The 3-2-1 principle is a fundamental concept in designing fixtures and jigs. It involves providing three points of contact on one plane, two on a second plane, and one on a third plane to fully locate a workpiece. This principle helps to ensure that the workpiece is properly constrained and supported, reducing the risk of movement during machining.
Clamping Considerations
Clamping is a critical aspect of fixture and jig design. You should consider the ease of handling and accessibility when designing clamping mechanisms. The goal is to ensure that the workpiece is securely held in place without obstructing the machining process or compromising operator safety.
“The design of fixtures and jigs is a critical aspect of manufacturing, requiring a balance between technical performance and human factors.”
A well-designed clamping system can significantly improve the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.




