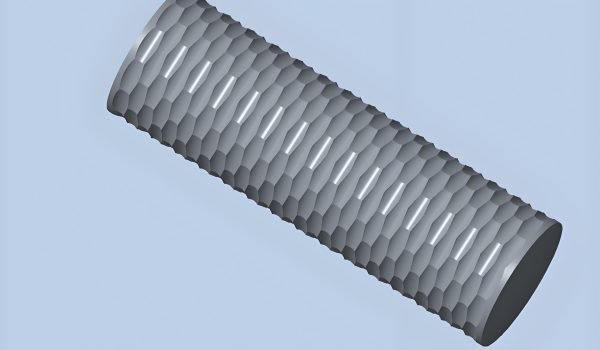
Did you know that nearly 80% of the tactile experience of a product is determined by its surface texture? This surprising fact highlights the importance of mold texturing in creating plastic parts that are not only visually appealing but also functional.
Mold texturing, also known as graining or engraving, is a critical aspect of injection molding that directly impacts the appearance and functionality of finished plastic parts. By applying various texturing methods, manufacturers can create a wide range of surface patterns, from simple stripes to complex designs that mimic natural materials like wood and leather.
This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamentals of the process involved in creating precisely textured molds, including different texturing methods and industry standards that guide texture selection and implementation.
What is Mold Texturing?
Mold texturing refers to the process of creating specific surface textures on molds used for injection molding. This process transforms ordinary plastic parts into products with enhanced visual appeal, tactile qualities, and perceived value. The right texture can significantly influence consumer perception of a product’s quality, making plastic parts appear more premium or resemble more expensive materials.
Why Mold Texturing Matters for Plastic Parts

Mold texturing matters for plastic parts because it serves both aesthetic and functional purposes. Beyond making products look more appealing, textured surfaces improve grip, reduce glare, enhance scratch resistance, and hide manufacturing imperfections like weld lines or sink marks. In competitive markets, distinctive texturing can become part of a brand’s visual identity, helping products stand out. Moreover, texturing decisions made early in the design process can impact material selection, draft angle requirements, and overall product development.
By incorporating mold texturing into your product design, you can enhance the overall quality and appeal of your plastic parts, ultimately contributing to a more successful product in the market.
Key Functions and Benefits of Mold Texturing
When it comes to injection molding, mold texturing is a key factor that influences both the aesthetic appeal and the performance of the product. You can achieve a wide range of surface finishes by applying different textures to the mold, which can significantly enhance the usability and durability of the final product.
Aesthetic Enhancement and Design Flexibility
Mold texturing offers substantial aesthetic enhancement and design flexibility. By creating various surface textures, you can improve the visual appeal of your product, making it more attractive to consumers. The ability to customize the surface finish allows for greater design flexibility, enabling you to meet specific design requirements and brand identities.
Concealing Manufacturing Imperfections
Textured surfaces can effectively conceal minor manufacturing imperfections, such as scratches or sink marks, thereby improving the overall appearance of the product. This is particularly beneficial for products where a flawless finish is not strictly necessary but a high-quality appearance is still desired. By masking these imperfections, you can maintain a high level of product quality without incurring additional costs associated with achieving a perfectly smooth finish.
Functional Benefits: Grip, Durability, and Performance
The functional benefits of mold texturing include improved grip, enhanced durability, and better performance. Textured surfaces provide a better grip, reducing the likelihood of the product slipping from the user’s hands, which is especially important for products used in wet conditions or applications requiring precise control. Moreover, textured finishes can increase the apparent hardness and scratch resistance of plastic parts, as minor abrasions become less visible. Properly designed textures can also improve product performance by adjusting surface friction according to the requirements of the application.
You can enjoy several benefits from mold texturing, including:
- Enhanced grip and ergonomics, making products safer and more comfortable to handle.
- Increased apparent hardness and scratch resistance, reducing the visibility of minor wear and tear.
- Improved product performance through tailored surface friction.
- Reduced glare and reflections, which is crucial for electronic devices and automotive interiors.
- Better paint adhesion and bonding with other components, solving multiple manufacturing challenges.
The Mold Texturing Manufacturing Process
To achieve the desired surface finish, the mold texturing process involves several critical stages. The process is complex and requires precision to produce the required texture on the mold surface.
Surface Preparation and Cleaning
The first step in the mold texturing process is surface preparation and cleaning. This stage is crucial as it ensures the mold surface is free from contaminants and ready for texturing. The surface is thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, oil, or other substances that could interfere with the texturing process.
Masking and Protection Techniques
Masking and protection techniques are applied to areas of the mold that are not intended to be textured. This is done to prevent the texturing process from affecting unwanted areas. The masking material is carefully applied to protect the mold surface, ensuring that only the desired areas are exposed to the texturing process.
Chemical Etching Process
The chemical etching process is a critical stage in mold texturing. It involves applying a chemical etchant to the mold surface to create the desired texture. The etching process requires careful control to achieve the precise texture and pattern.
Post-Etching Treatments
After the primary etching is complete, the mold undergoes post-etching treatments. These treatments include sandblasting or sandwashing to remove the black oxide layer formed during etching, revealing a clean, silvery surface. For textures that appear too sharp, a “round off” process may be applied to slightly soften the texture peaks. Additionally, specialized cleaning processes are used to remove chemical residues, and rust prevention treatments are applied to protect the newly textured surface.
You can enhance the quality of the mold texturing process by understanding these post-etching treatments. The treatments ensure that the final textured surface meets the required standards and is free from defects. Quality control inspections verify texture depth, pattern accuracy, and surface consistency, often using specialized measurement tools and comparison to approved texture standards or sample plates.
Types of Surface Textures for Injection Molds
When it comes to injection molding, surface texturing is an essential consideration for producing parts that meet both aesthetic and functional requirements. The type of surface texture used can significantly impact the final product’s appearance, usability, and overall performance.
Chemical Texturing Methods
Chemical texturing methods involve using chemicals to etch the surface of the mold, creating the desired texture. This process is widely used due to its ability to produce complex patterns and textures on intricate mold designs.
The chemical etching process for injection molds involves several steps, including surface preparation, masking, and etching. The result is a textured surface that can enhance the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the molded part.
Laser Texturing Technology
Laser texturing technology represents the cutting edge of mold texturing, utilizing precisely controlled laser beams to modify the mold surface according to digital pattern data. This method offers exceptional precision and consistency, capable of creating up to 30-50 distinct layers, compared to the 3-5 layers possible with chemical texturing.
The combination of 3D computer modeling and 5-axis motion control enables laser texturing to accurately apply patterns to complex curved surfaces, undercuts, and areas that are difficult to reach with chemical methods. Additionally, laser texturing is environmentally friendly, eliminating the need for harsh chemicals and reducing waste disposal concerns.
- Laser texturing uses precisely controlled laser beams to ablate or modify the mold surface.
- It offers exceptional precision and consistency, creating up to 30-50 distinct layers.
- The technology combines 3D computer modeling and 5-axis motion control for complex surfaces.
- Laser texturing is environmentally friendly, reducing the need for harsh chemicals.
Surface Finish Standards and Grade Categories
The surface finish of a molded part is a critical aspect that is governed by specific standards and grade categories. These standards ensure that the final product meets the required specifications and quality.
SPI Surface Finish Standards
The Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI) has established surface finish standards to provide a common language for designers, molders, and manufacturers. These standards categorize surface finishes based on the level of texture and finish. Understanding SPI surface finish standards is essential for specifying the correct surface finish for your molded parts. The standards help to ensure that the parts are manufactured to the required quality and aesthetic standards.
Texture Depth and Draft Angle Requirements
Texture depth and draft angle are critical factors in mold texturing. The texture depth directly impacts the visual appearance of the part, while the draft angle affects the ease of part release from the mold. A good rule-of-thumb is to add a minimum of one degree of draft angle per 0.001″ of texture depth to prevent drag marks. The texture depth can range from as shallow as 2µm to as deep as 3mm, depending on the application requirements. For parts with limited draft angle, texture depth can be strategically reduced or blended to maintain part functionality.
When specifying texture depth, it’s essential to consider the material being molded, as some plastics replicate textures more precisely than others. This may require adjustments to the specified texture depth to achieve the desired finish. By understanding the relationship between texture depth and draft angle, you can ensure that your molded parts meet the required specifications and are manufactured efficiently.
Common Issues and Solutions in Mold Texturing
Achieving the desired texture on injection-molded parts can be fraught with difficulties, from material-related challenges to texture defects. Understanding these common issues and their solutions is crucial for ensuring high-quality outcomes in mold texturing.
Material-Related Challenges
Material-related issues can significantly impact the mold texturing process. For instance, surface defects such as pitting or uneven texture may become apparent after texturing, often indicating material porosity or inclusions. To address these challenges, it’s essential to inspect the material quality before proceeding with texturing. Additionally, adjusting the injection molding parameters, such as pressure, speed, and temperature, can help mitigate some material-related issues.
Troubleshooting Texture Defects
Texture defects can arise from various sources, including improper surface preparation, masking issues, and etching problems. Inconsistent texture depth or appearance often results from residual machining marks or oil contamination, which can be addressed by thorough surface cleaning and preparation. Boundary issues between textured and non-textured areas typically indicate masking problems, such as poor adhesion of protective tapes. Solutions include improving masking techniques and ensuring the etched surface is polished to prevent mold sticking or adhesion.
By understanding the causes of these common issues and applying the appropriate solutions, you can improve the quality of your mold texturing process and achieve the desired surface finish for your injection-molded parts.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Mold Texturing
To make informed decisions about mold texturing, it’s essential to understand the various elements that influence the process. The cost of applying surface texture to an injection mold is largely dependent upon the mold’s complexity, with intricate designs requiring more time and potentially increasing the cost.
Several factors contribute to the overall cost, including the type of metals used for the mold, the size of the mold, and the sophistication of the desired texture pattern. When evaluating texturing options, consider both the aesthetic benefits and functional advantages, such as improved grip and enhanced durability, which can significantly impact the final product’s performance and perceived value.
Successful mold texturing requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including part design requirements, material selection, and manufacturing process limitations. The selection of the texturing method should balance quality requirements against budget constraints. Early collaboration between product designers, mold makers, and texturing specialists is crucial to ensure that texture specifications are compatible with part geometry and material properties.
By understanding these factors and working with experienced texturing specialists, you can ensure successful implementation and consistent results, ultimately yielding returns through improved part quality and enhanced market appeal.